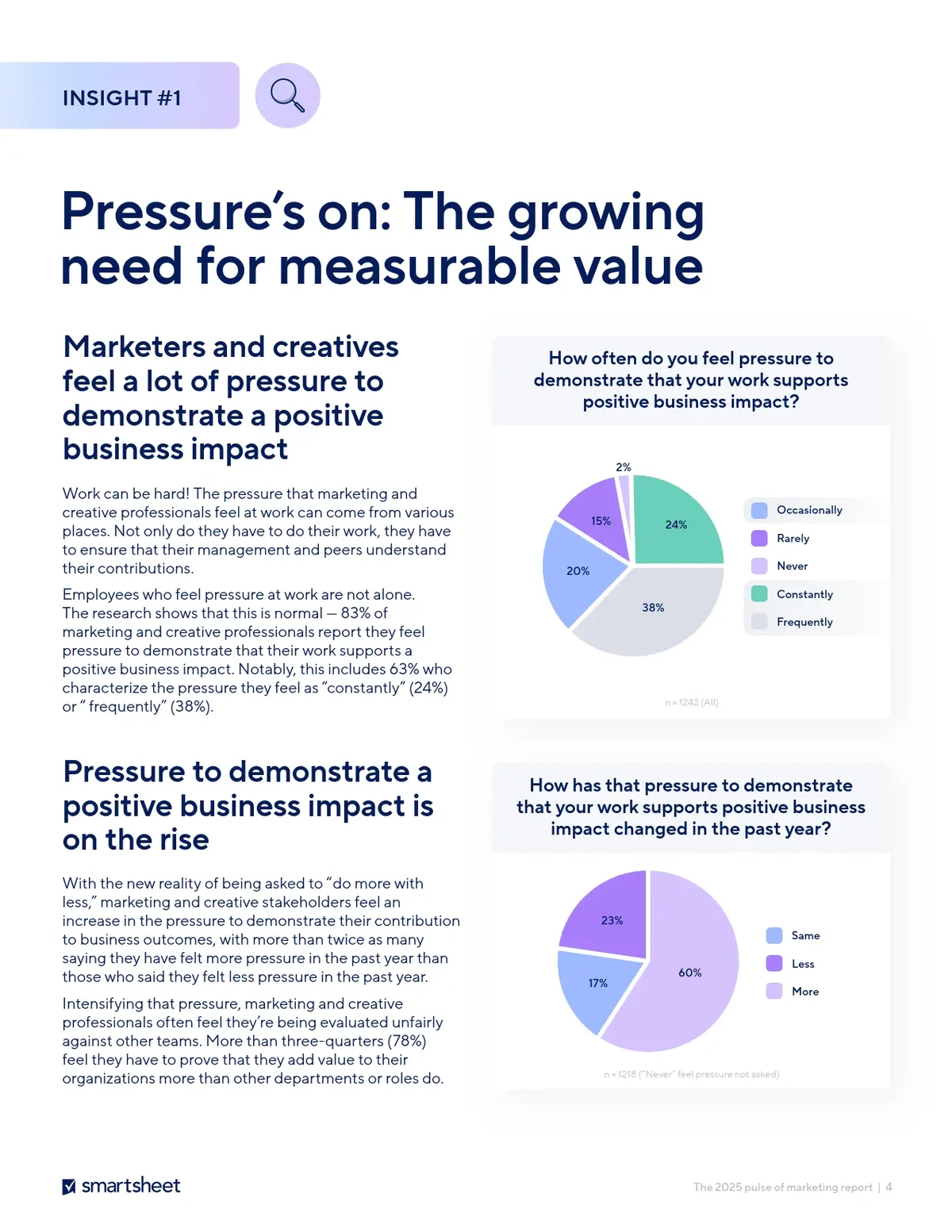
===============================================
Perpetual futures contracts have become a staple in the world of trading, especially for those engaging in cryptocurrency, forex, and commodity markets. Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual contracts do not have an expiration date, allowing traders to maintain positions indefinitely. This unique feature brings both opportunities and challenges, particularly when it comes to managing risk and maximizing profits. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the best strategies for trading perpetual futures contracts, offering practical insights for beginners and experienced traders alike.
Understanding Perpetual Futures Contracts
1.1 What Are Perpetual Futures Contracts?
A perpetual futures contract is a derivative instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price of an underlying asset without an expiration date. These contracts are similar to traditional futures contracts but differ in that they do not have a fixed maturity date. Instead, they are designed to track the price of the underlying asset over time and can be held indefinitely as long as margin requirements are met.
The main feature of perpetual futures is the funding rate, which is a mechanism that helps keep the perpetual futures price in line with the spot price of the underlying asset. This rate is paid between long and short positions at regular intervals, typically every 8 hours, and it can either favor long or short positions depending on the market conditions.
1.2 Why Are Perpetual Futures Popular?
Perpetual futures are particularly popular in cryptocurrency trading, where high volatility and market unpredictability are the norms. The lack of expiration dates allows traders to hold positions for as long as they desire, making them highly flexible for long-term strategies. Moreover, the availability of high leverage in perpetual futures contracts allows traders to take larger positions with less capital, amplifying both potential profits and risks.
Best Strategies for Trading Perpetual Futures Contracts
2.1 Trend Following Strategy
One of the most popular and effective strategies for trading perpetual futures is trend following. This strategy involves identifying and riding the momentum of an existing market trend, whether bullish or bearish.
2.1.1 How It Works
- Identify Market Trends: Traders use technical analysis tools like moving averages, the Relative Strength Index (RSI), or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to identify whether the market is in an uptrend or downtrend.
- Enter Positions in the Direction of the Trend: Once a trend is confirmed, traders open long positions in a bull market or short positions in a bear market.
- Exit Based on Trend Reversal Indicators: Traders exit when they see signs of trend reversal, such as when the price breaks through key support or resistance levels.
2.1.2 Advantages
- Simple and Effective: Trend-following strategies are easy to understand and can be highly profitable in trending markets.
- Reduced Risk: Since the strategy involves riding existing momentum, it reduces the risk of counter-trend moves.
2.1.3 Disadvantages
- Requires Patience: Traders may have to wait for the market to set a clear trend, which could take time.
- Can Lead to Losses in Sideways Markets: Trend-following strategies work best in trending markets and can lead to losses during market consolidation or sideways movement.
2.2 Range Trading Strategy
Range trading is another effective strategy for perpetual futures contracts, particularly in volatile or sideways markets. This strategy involves buying at support levels and selling at resistance levels, profiting from price fluctuations within a defined range.
2.2.1 How It Works
- Identify Support and Resistance Levels: Traders use tools like Bollinger Bands or horizontal trendlines to identify key levels where the price has bounced in the past.
- Open Long Positions at Support: When the price reaches the support level, traders open long positions, anticipating a price reversal.
- Open Short Positions at Resistance: Similarly, when the price reaches the resistance level, traders open short positions.
2.2.2 Advantages
- Works Well in Sideways Markets: Range trading is ideal for markets that are not trending and are instead moving within a narrow range.
- Higher Probability of Successful Trades: By trading within a defined range, traders can increase the probability of successful trades, especially if they use proper risk management.
2.2.3 Disadvantages
- Limited Profit Potential: The profit potential in range trading is limited by the boundaries of the range, which may not provide as much opportunity as trend-following strategies.
- Risk of Breakouts: If the price breaks out of the established range, traders can suffer significant losses.
2.3 Scalping Strategy
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that involves making a large number of small trades to capitalize on minor price movements. This strategy is particularly effective in highly liquid markets like cryptocurrency, where price fluctuations occur frequently.
2.3.1 How It Works
- Enter Trades Based on Small Price Movements: Traders use tight stop-loss and take-profit orders to capture small profits from rapid price fluctuations.
- Leverage High Liquidity: Scalpers take advantage of the liquidity in the market to enter and exit positions quickly, often holding positions for just a few seconds or minutes.
2.3.2 Advantages
- Quick Profits: Scalping allows traders to accumulate small but consistent profits over time.
- Low Exposure to Market Risk: Because trades are held for very short periods, scalpers are less exposed to long-term market risk.
2.3.3 Disadvantages
- Requires Significant Time and Effort: Scalping requires constant attention to the market and can be exhausting for traders.
- High Transaction Costs: Frequent trading leads to higher transaction costs, which can eat into profits.
Risk Management for Perpetual Futures Contracts
3.1 How to Minimize Risk
Risk management is crucial when trading perpetual futures contracts due to the high leverage available. Traders must carefully consider position size, stop-loss orders, and margin management to minimize their exposure to catastrophic losses.
3.1.1 Use Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
- Stop-Loss: A stop-loss order automatically exits a position if the price moves against the trader’s position beyond a certain threshold.
- Take-Profit: A take-profit order locks in profits when the price reaches a predetermined level.
3.1.2 Position Sizing
Proper position sizing helps ensure that a single loss doesn’t wipe out a trader’s entire capital. Traders should avoid using excessive leverage, which increases the risk of liquidation.
3.2 Common Mistakes in Perpetual Futures Trading
3.2.1 Over-Leveraging
While high leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Traders should avoid using maximum leverage and instead choose leverage levels that align with their risk tolerance.
3.2.2 Ignoring Market Conditions
Many traders fail to account for broader market conditions, leading them to take positions in unfavorable environments. Always conduct thorough market analysis before entering any trades.
3.2.3 Failing to Adjust Stop-Loss Orders
Traders should constantly monitor their positions and adjust stop-loss levels as the market moves. Leaving stop-loss orders unchanged can expose traders to unnecessary risk if market conditions change.
FAQs: Common Questions About Perpetual Futures Trading
4.1 How do perpetual futures contracts work?
Perpetual futures contracts are similar to traditional futures contracts but without an expiration date. They are designed to track the price of an underlying asset, and traders can hold positions indefinitely as long as margin requirements are met. Funding rates help keep the contract’s price in line with the spot price of the underlying asset.
4.2 What are the benefits of trading perpetual futures contracts?
Perpetual futures contracts offer several benefits, including the ability to hold positions indefinitely, the availability of high leverage, and the flexibility to trade both long and short positions. They are particularly popular in cryptocurrency markets due to the high volatility and 24⁄7 market availability.
4.3 How can I manage risk when trading perpetual futures?
Risk management strategies for perpetual futures include using stop-loss and take-profit orders, properly sizing positions, and avoiding excessive leverage. Traders should also be mindful of market conditions and adjust their leverage and risk tolerance accordingly.
Conclusion
Perpetual futures contracts are a powerful tool for traders looking to speculate on price movements in a variety of markets. Whether you’re using trend-following strategies, range trading, or scalping, the key to success lies in effective risk management and strategy implementation. By understanding the unique characteristics of perpetual futures contracts and applying the best strategies, traders can capitalize on opportunities while minimizing potential losses. Always remember that while leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify risks, so careful planning and risk management are crucial for long-term success.