
=====================================================
Perpetual futures have become one of the most popular trading instruments in cryptocurrency and derivatives markets. They offer traders the ability to speculate on asset prices with leverage, magnifying both potential gains and risks. A critical concept in this process is knowing how to calculate leverage ratio in perpetual futures, which ensures proper risk management and sustainable trading strategies.
This guide explains step by step how leverage ratios are calculated, explores multiple approaches, compares their advantages and disadvantages, and provides expert insights into optimizing leverage in perpetual futures trading.
Understanding the Basics of Leverage in Perpetual Futures
What is Leverage in Perpetual Futures?
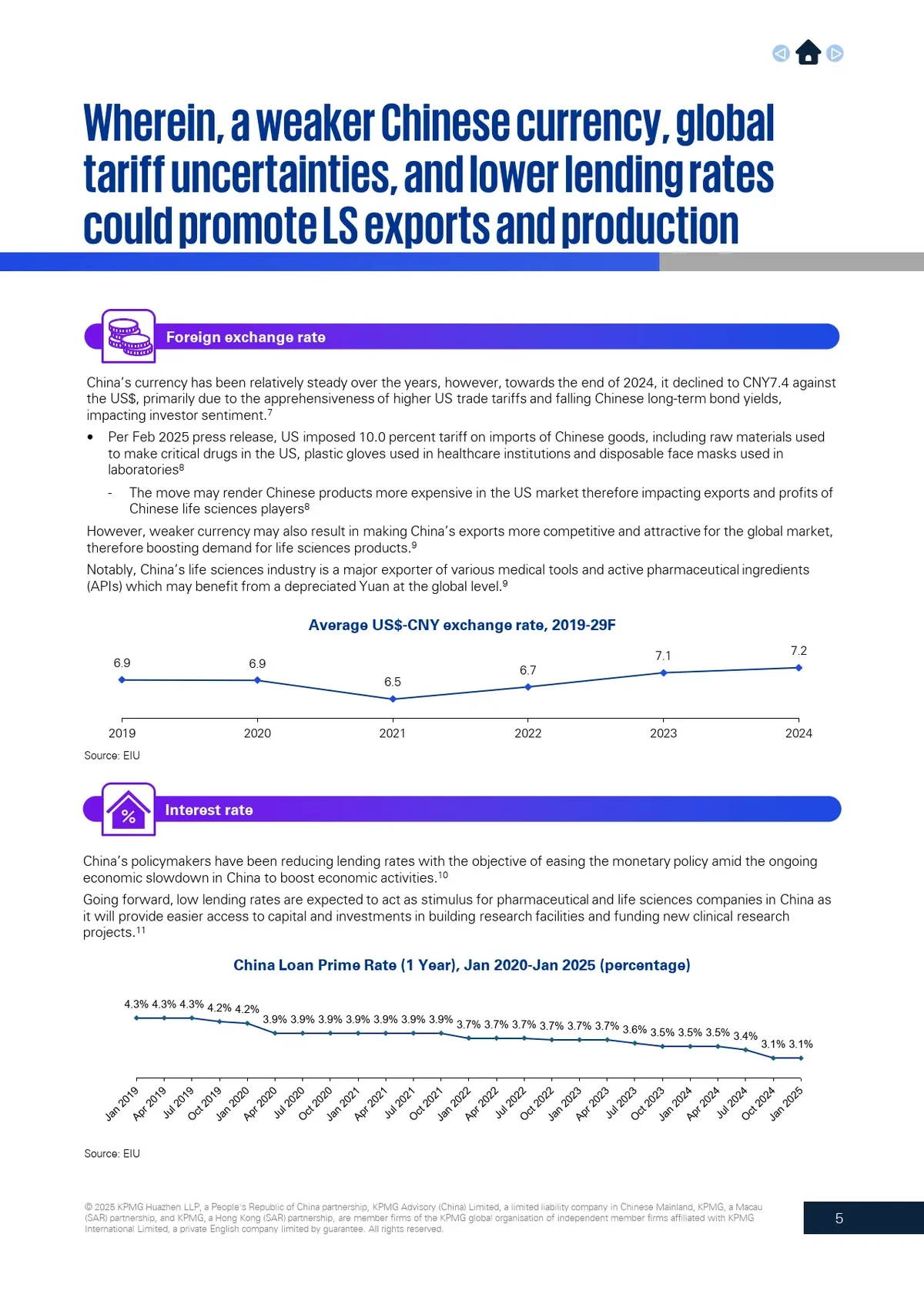
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position size with a smaller margin deposit. For example, with 10x leverage, a \(1,000 margin can open a \)10,000 position. This amplifies exposure, but it also increases liquidation risks.
Why is Calculating Leverage Ratio Important?
- Helps traders understand their true exposure to the market.
- Assists in setting appropriate stop-loss and risk management strategies.
- Prevents over-leveraging, which is one of the leading causes of liquidation in perpetual futures.
Leverage magnifies both profits and risks, making calculation accuracy crucial.
Formula: How to Calculate Leverage Ratio in Perpetual Futures
The basic formula is:
Leverage Ratio = Position Size ÷ Margin Used
- Position Size: Total value of the open trade (contract size × entry price).
- Margin Used: The trader’s own capital allocated to open the position.
Example 1:
A trader opens a $20,000 BTC perpetual futures position with $2,000 margin.
Leverage Ratio = \(20,000 ÷ \)2,000 = 10x
Example 2:
If the same trader increases margin to \(4,000 while keeping position size \)20,000:
Leverage Ratio = \(20,000 ÷ \)4,000 = 5x
The higher the margin, the lower the leverage, reducing risk of liquidation.
Two Main Methods for Calculating Leverage Ratio
Method 1: Manual Calculation
Traders manually apply the formula using position size and margin.
Pros:
- Full control and transparency.
- Works across different exchanges and assets.
- Full control and transparency.
Cons:
- Time-consuming during volatile markets.
- Requires accurate data inputs.
- Time-consuming during volatile markets.
Method 2: Using Exchange Leverage Calculators
Many exchanges provide built-in tools to show leverage ratios automatically.
Pros:
- Fast and user-friendly.
- Often includes liquidation price calculation.
- Fast and user-friendly.
Cons:
- Reliance on exchange accuracy.
- May not account for hidden fees or funding rates.
- Reliance on exchange accuracy.
Recommendation: For beginners, leverage calculators are useful. For professionals, manual calculations provide deeper understanding and flexibility.
Example of leverage calculation shown on a trading interface.
Advanced Considerations in Leverage Ratio Calculation
1. Maintenance Margin
Besides initial margin, traders must maintain a minimum margin to keep positions open. If equity falls below this level, liquidation occurs.
2. Funding Rates in Perpetual Futures
Unlike traditional futures, perpetual contracts require funding rate payments, which can affect real leverage exposure.
3. Cross vs. Isolated Margin
- Cross Margin: Shares entire account balance to avoid liquidation.
- Isolated Margin: Limits margin to one position, providing more controlled risk.
How Does Leverage Affect Risk in Perpetual Futures?
High leverage ratios amplify risks significantly. For example, a 1% price movement against a 100x leveraged position wipes out the entire margin. This highlights the importance of proper calculation and conservative settings.
This aligns with the broader principle that explains why is leverage important in perpetual futures trading—it determines how long a trader can survive market volatility.
Personal Experience: Lessons from Misusing Leverage
Early in my trading career, I mistakenly applied 50x leverage without recalculating my margin after increasing position size. The trade was liquidated within minutes due to a minor price fluctuation.
Later, I learned to always recalculate leverage ratios before entering trades and switched to using step-by-step leverage setup in perpetual futures guides provided by exchanges. This improved my survival rate dramatically.
Strategies to Optimize Leverage Usage
Conservative Leverage (1x–5x)
- Best for beginners.
- Lower liquidation risk.
- Allows more breathing room for market volatility.
Moderate Leverage (5x–20x)
- Used by experienced traders.
- Balances risk and reward.
- Requires disciplined stop-loss management.
High Leverage (20x–100x)
- Mostly used by professional scalpers.
- High profit potential in short-term trades.
- Extremely risky and often unsustainable.
The higher the leverage, the steeper the risk curve becomes.
FAQs: How to Calculate Leverage Ratio in Perpetual Futures
1. What is the safest leverage ratio for beginners?
Beginners should stick to 1x–5x leverage. This provides exposure to trading strategies without excessive risk of liquidation. Over time, they can experiment with moderate leverage as they gain confidence.
2. Can I calculate leverage ratio differently for cross margin?
Yes. In cross margin mode, your entire account balance contributes to margin, so the effective leverage ratio may be lower than isolated margin. Traders should always check both methods to avoid unexpected liquidations.
3. Where can I find tools to calculate leverage ratio quickly?
Most exchanges have built-in calculators under the order placement panel. Alternatively, traders can use third-party tools or follow where to find leverage calculators for perpetual futures resources, which often include downloadable spreadsheets and online calculators.
Conclusion
Knowing how to calculate leverage ratio in perpetual futures is a fundamental skill that separates disciplined traders from reckless ones. Whether you calculate manually or rely on exchange tools, understanding the relationship between margin, position size, and leverage is critical for risk management.
For beginners, conservative leverage ratios paired with calculators are the best starting point. Experienced traders can optimize leverage depending on strategy, but must remain disciplined in monitoring risk exposure.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your trading community, and comment below about the leverage ratio you usually use in your perpetual futures trades. Let’s learn from each other’s strategies and experiences.
Would you like me to also create a step-by-step infographic showing manual leverage ratio calculation with real numbers for easy reference?