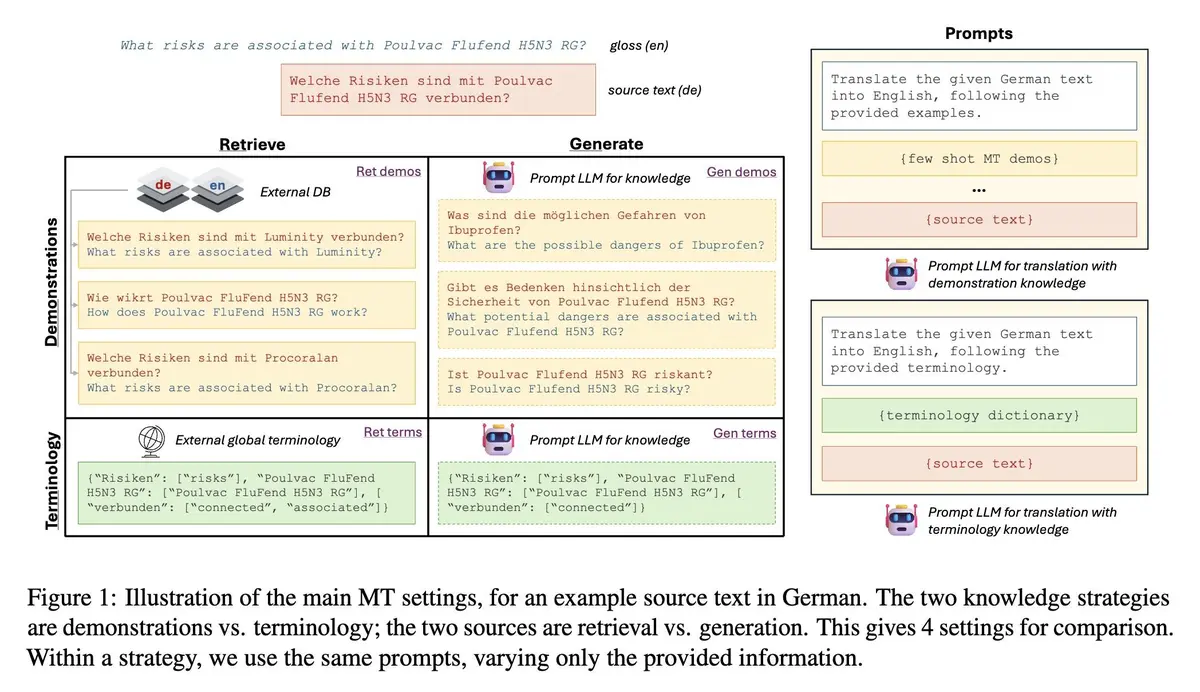
markdown
Copy code
Commodities Trading Leverage Insights and Trends
Leverage in commodities trading is one of the most powerful tools available to traders and investors. By magnifying both gains and losses, leverage can transform modest capital into large market exposure. This comprehensive guide explores commodities trading leverage insights and trends, offering strategies, comparisons, and practical tutorials for traders of all experience levels.
Understanding Commodities Leverage Trading
What Is Leverage in Commodities?
Leverage allows traders to control a large position in commodities with only a fraction of the required capital. This is achieved through borrowing or margin trading. For example, with 10:1 leverage, a \(1,000 deposit can control a \)10,000 position in gold, oil, or agricultural commodities.
Why Use Leverage in Commodities Trading?
The main reason is to maximize returns on smaller amounts of capital. Commodities such as crude oil, wheat, and copper often experience volatile price movements, and leverage provides a way to capture profit from even small percentage changes. However, leverage also magnifies losses, making risk management critical.
Visualizing how leverage multiplies gains and losses in commodities markets.
Key Trends in Commodities Leverage Trading
Increased Retail Participation
More retail traders are entering commodities markets thanks to user-friendly platforms and online tutorials. Platforms now offer commodities leverage trading for beginners, often paired with demo accounts to reduce early risks.
Algorithmic and Automated Trading
The adoption of trading bots and automation tools is reshaping leverage trading. Automated strategies can respond to market changes instantly, reducing human error.
Stricter Regulations
As leverage trading grows, regulators are imposing stricter rules on maximum leverage and margin requirements to protect retail investors.
Integration of Real-Time Analytics
The use of real-time commodities leverage trading analytics provides traders with instant feedback, helping them adjust strategies on the fly.
How Does Leverage Work in Commodities?
The Mechanics
When trading leveraged commodities:
- Initial Margin: The amount a trader deposits (e.g., $5,000).
- Notional Value: The total value of the contract (e.g., $50,000).
- Leverage Ratio: Notional Value ÷ Margin (in this case, 10:1).
Example
If crude oil rises 3% on a $50,000 contract:
- Profit = $1,500.
- Margin Return = 30% on a $5,000 deposit.
If crude oil falls 3%:
- Loss = $1,500.
- Margin Return = –30%.
Understanding how leverage affects commodities markets is essential before committing capital.
Strategies for Commodities Leverage Trading
1. Trend-Following Strategies
These strategies involve buying when prices are trending upward and selling when they trend downward. They work best in volatile commodities such as oil and metals.
Pros:
- Easier to follow using moving averages and technical indicators.
- Aligns with market momentum.
Cons:
- Whipsaw movements in sideways markets can erode profits.
2. Mean Reversion Strategies
This method assumes that prices eventually return to a historical average. Traders look for overbought or oversold conditions.
Pros:
- Effective in range-bound commodities like certain agricultural markets.
- Provides multiple entry points for short-term trades.
Cons:
- Risky during strong one-directional moves.
- Requires quick reaction and strong discipline.
3. Hedging with Commodities Options
Traders often use leveraged commodity options to hedge other portfolio risks. For example, an investor exposed to airline stocks may hedge with oil futures options.
Pros:
- Offers portfolio protection.
- Can limit downside exposure.
Cons:
- Reduces potential upside.
- Requires knowledge of derivatives pricing.
Trend-following works best in directional markets, while mean reversion excels in ranges.
Comparing Strategies: Which Works Best?
- Trend-Following: Best for beginners due to simplicity and reliance on clear signals.
- Mean Reversion: More advanced, requiring experience and strong discipline.
- Hedging: Useful for professionals or institutions managing diversified portfolios.
Recommendation: Self-learners and retail traders should start with trend-following before exploring mean reversion or hedging strategies.
Risk Management in Commodities Leverage Trading
Trading with leverage requires strict discipline. Here are essential tactics:
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Protect capital by limiting downside exposure.
- Avoid Over-Leveraging: Start with 2x–3x leverage instead of maximum ratios.
- Diversify: Spread risk across commodities (e.g., gold, oil, wheat).
- Track Performance: Keep a trading journal and review trades regularly.
Learning how to reduce risk in leveraged commodities trading is crucial to long-term survival.
Best Practices for Commodities Leverage Trading
- Stay Updated: Follow the latest news on commodities leverage trading for market-moving events.
- Choose the Right Platform: Look for brokers offering transparent fees, fast execution, and strong educational resources.
- Combine Technical and Fundamental Analysis: Technical charts help with timing, while fundamentals (supply/demand, geopolitics) shape long-term trends.
- Start Small: Practice on demo accounts before committing large sums.
Core risk management steps in leveraged commodities trading.
Personal Experience: Lessons from Practice
When I first traded leveraged commodities, I underestimated volatility in crude oil. A 5% overnight swing wiped out half of my margin. After this setback, I shifted to using smaller leverage ratios and trend-following strategies. The result was more consistent performance and less emotional stress. From experience, leverage should be treated as a tool, not a shortcut to profits.
FAQ: Commodities Trading Leverage Insights and Trends
1. What is a safe leverage ratio for beginners?
Beginners should stick to 2x–3x leverage to limit exposure. High leverage (10x or more) can quickly wipe out capital in volatile commodities.
2. How do I choose the best commodities trading platform?
Look for brokers offering strong regulation, real-time analytics, and risk management tools. The best commodities trading platforms also provide educational tutorials.
3. Is leverage trading suitable for long-term investors?
It depends. Leverage is better suited for short- to medium-term strategies. Long-term investors may use leverage cautiously for hedging rather than speculation.
4. Can leverage trading be automated?
Yes, many traders now use commodities leverage trading automation tools. However, self-learners should first master manual strategies before automating.
5. Why is risk management so important in leveraged commodities trading?
Because leverage magnifies both profits and losses, without stop-losses and strict discipline, traders can face margin calls and account liquidation.
Conclusion
The world of commodities trading leverage insights and trends is dynamic and full of opportunities. From trend-following to hedging, traders have multiple strategies to choose from. However, risk management remains the cornerstone of success. By starting small, leveraging technology, and continuously learning, traders can navigate this complex but rewarding market.
Key insights and trends shaping leveraged commodities trad
”`