

==========================================
Perpetual futures have revolutionized the derivatives market by offering traders 24⁄7 exposure without expiration dates. They are widely used in crypto trading, where arbitrage opportunities emerge due to inefficiencies, funding mechanisms, and fragmented liquidity across exchanges. In this guide, we will explore how to use perpetual futures for arbitrage, compare different methods, highlight risks, and provide practical strategies supported by professional insights and industry trends.
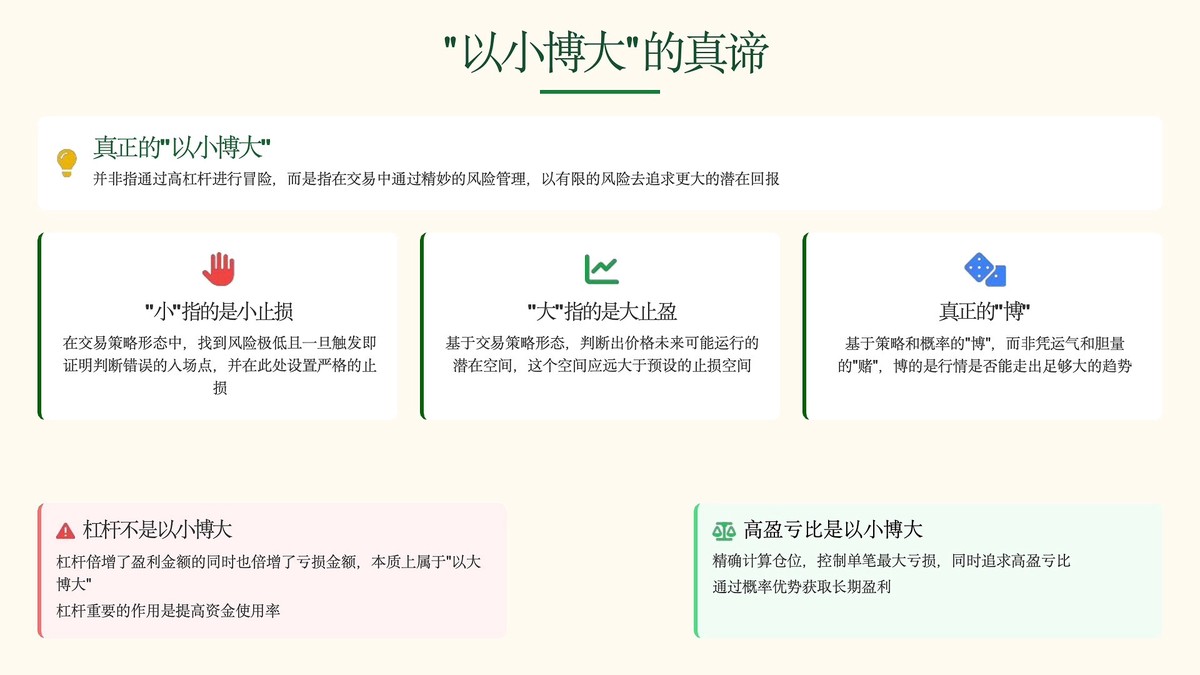
Understanding Perpetual Futures Arbitrage
What Are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual futures, often called perps, are derivatives contracts that track the price of an underlying asset without an expiry date. Unlike traditional futures, their prices are kept close to the spot market through funding payments between long and short traders.
This unique mechanism creates opportunities for arbitrageurs who exploit mispricings between spot and perpetual markets or across different exchanges.
Why Arbitrage Works in Perpetual Futures
Arbitrage in perpetual futures arises from three main factors:
- Funding Rate Mechanism – When the funding rate is positive, longs pay shorts; when negative, shorts pay longs.
- Price Divergences – Differences between spot and perp prices allow for cash-and-carry trades.
- Market Fragmentation – The crypto market is highly fragmented, with varying liquidity, leading to cross-exchange spreads.
If you’re wondering why perpetual futures are popular in trading markets, the answer lies in their efficiency, flexibility, and the consistent arbitrage opportunities they provide.
Common Arbitrage Strategies Using Perpetual Futures
1. Cash-and-Carry Arbitrage
This is the most widely used perpetual futures arbitrage strategy.
How It Works:
- Buy the asset on the spot market.
- Simultaneously short the perpetual contract when it trades at a premium.
- Collect funding payments and lock in the spread.
- Buy the asset on the spot market.
Advantages:
- Risk-neutral if executed correctly.
- Works best when funding rates are persistently high.
- Risk-neutral if executed correctly.
Disadvantages:
- Requires capital on both spot and futures exchanges.
- Exposure to exchange and counterparty risks.
- Requires capital on both spot and futures exchanges.
Example: If Bitcoin spot trades at \(50,000 and perpetual futures are priced at \)51,000 with a high funding rate, an arbitrageur can long spot and short perp to profit from the premium.
2. Funding Rate Arbitrage
This method exploits the recurring payments between longs and shorts.
How It Works:
- Open positions to receive funding (e.g., short when funding is positive).
- Hedge directional exposure in the spot or another futures contract.
- Open positions to receive funding (e.g., short when funding is positive).
Advantages:
- Generates steady income from funding payments.
- Scalable across multiple exchanges.
- Generates steady income from funding payments.
Disadvantages:
- Requires frequent adjustments.
- Funding rates are volatile and may reverse.
- Requires frequent adjustments.
Funding arbitrage is attractive to professional trading firms that use perpetual futures, as it provides consistent low-risk returns when scaled.
3. Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
In fragmented crypto markets, perpetual futures often trade at different prices on separate exchanges.
How It Works:
- Buy on the cheaper exchange and sell on the expensive one.
- Lock in the spread until prices converge.
- Buy on the cheaper exchange and sell on the expensive one.
Advantages:
- Exploits inefficiencies in liquidity.
- Works well with high-frequency trading models.
- Exploits inefficiencies in liquidity.
Disadvantages:
- Requires fast execution and low latency.
- Involves high withdrawal and transaction costs.
- Requires fast execution and low latency.
Comparing Arbitrage Strategies
| Strategy | Best Market Condition | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash-and-Carry | High premium on perpetuals | Risk-neutral, structured returns | Capital intensive, exchange risk |
| Funding Rate Arbitrage | Consistently positive/negative funding | Steady income, repeatable | Funding rate reversals |
| Cross-Exchange Arbitrage | Fragmented markets with inefficiencies | High-frequency potential | Costly, operationally complex |
Based on personal trading experience, cash-and-carry arbitrage is the most reliable, especially when combined with robust risk management systems. However, funding arbitrage provides a steadier income stream, while cross-exchange arbitrage is suitable for traders with advanced infrastructure.
Risk Management in Perpetual Futures Arbitrage
Market Risks
Even though arbitrage is designed to be market-neutral, sudden price crashes, liquidity gaps, or funding spikes can cause losses.
Counterparty Risks
Funds held on exchanges are exposed to hacking, insolvency, or liquidation risks. It’s crucial to spread exposure across reliable platforms.
Execution Risks
Latency, slippage, and order mismatches can erode profits, especially in high-frequency environments.
Traders should study how to manage perpetual futures trading risks before deploying real capital.
Practical Steps to Start Arbitraging Perpetual Futures
- Choose a Reliable Exchange – Assess liquidity, fees, and stability. Understanding where to trade perpetual futures is a foundational step.
- Set Up Accounts Across Platforms – Necessary for cross-exchange arbitrage.
- Automate Execution – Use APIs and trading bots to reduce human error.
- Track Funding Rates – Monitor live funding rates to anticipate opportunities.
- Diversify Capital Allocation – Never concentrate exposure on one exchange.
Industry Trends Impacting Perpetual Futures Arbitrage
- High-Frequency Infrastructure – Professional firms now deploy ultra-low-latency systems to capture fleeting spreads.
- DeFi Perpetuals – On-chain perpetual protocols introduce new arbitrage opportunities but with smart contract risk.
- Regulatory Scrutiny – Increased oversight may impact access to leverage and arbitrage efficiency.
Example: Bitcoin Perpetual Arbitrage
Bitcoin perpetual arbitrage strategy illustration
This example shows how a cash-and-carry trade can lock in risk-neutral returns by exploiting funding payments and spot-perp price differences.
FAQ: Perpetual Futures Arbitrage
1. Is perpetual futures arbitrage risk-free?
No. While arbitrage reduces market exposure, it still carries risks such as exchange failure, funding volatility, and execution delays. The key is diversification and strict risk control.
2. How much capital do I need to start?
Small traders can begin with as little as $1,000 for basic arbitrage, but professional strategies often require six to seven figures to be meaningful after fees.
3. Which strategy is best for beginners?
Beginners should start with cash-and-carry arbitrage, as it is easier to understand and manage compared to cross-exchange setups. Over time, they can scale into more complex strategies.
Conclusion: The Best Arbitrage Path in Perpetual Futures
Arbitrage in perpetual futures offers traders a consistent and repeatable edge in crypto markets. Among all strategies, cash-and-carry remains the most reliable, while funding rate arbitrage provides additional income, and cross-exchange arbitrage suits more advanced players.
For long-term success, traders must combine risk management, automation, and exchange diversification. With proper execution, perpetual futures arbitrage can become a cornerstone of profitable quantitative trading.
Share Your Experience
Have you tried perpetual futures arbitrage? Which strategy has worked best for you? Share your insights in the comments and forward this article to fellow traders who are exploring arbitrage opportunities in crypto markets!
Would you like me to add a step-by-step infographic on setting up a cash-and-carry trade so the article becomes even more practical for beginners?