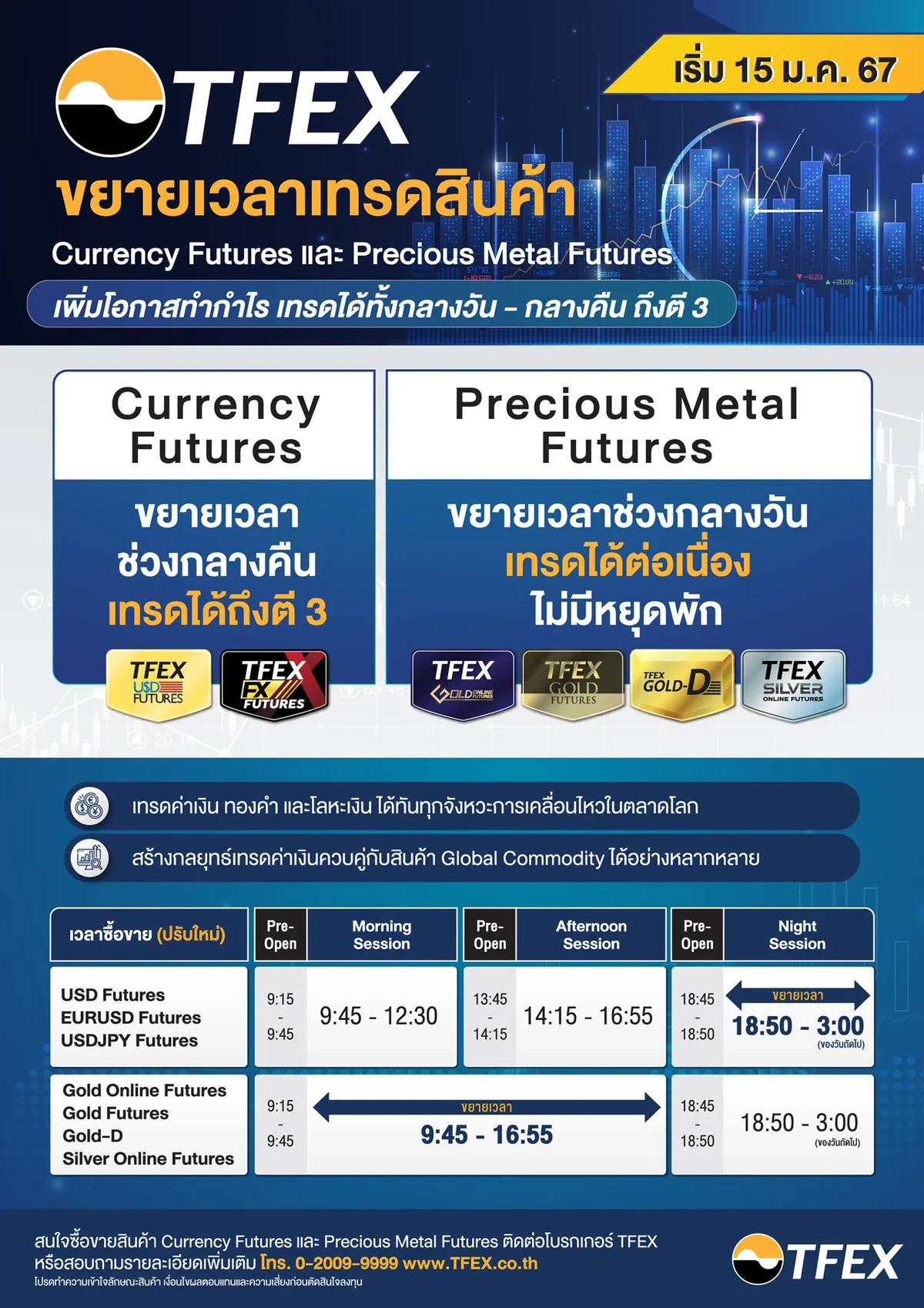
======================================================================
Perpetual futures trading has become one of the most attractive markets for traders and analysts alike, offering unique opportunities to profit from the price fluctuations of underlying assets. With its 24⁄7 trading availability and no expiry date, perpetual futures contracts have reshaped how traders approach speculative investments. This comprehensive guide will explore the ins and outs of perpetual futures trading, specifically from an analytical perspective, and offer a detailed analysis on how to navigate this complex yet rewarding market.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Perpetual Futures Trading
Perpetual futures are derivative contracts that allow traders to speculate on the future price of an asset without an expiry date. Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual futures do not require a settlement at a predetermined time, which provides traders with the flexibility to hold their positions indefinitely. This makes them an ideal choice for those looking to capture price movements over time, without worrying about expiration dates.
Perpetual futures are popular in cryptocurrency markets, but they are increasingly being adopted in other asset classes like commodities, equities, and forex. The perpetual nature of these contracts allows for greater flexibility in terms of trade duration and strategy.
How Perpetual Futures Work
Perpetual futures contracts are quite similar to traditional futures contracts in that they allow traders to speculate on the price movements of an underlying asset. However, the key difference lies in the absence of an expiration date. Instead, they have a funding mechanism in place that helps keep the contract price in line with the underlying asset’s spot price.
- Funding Rate: A funding rate is paid periodically, typically every 8 hours, between traders holding long and short positions. This rate ensures that the perpetual futures price stays close to the spot price of the underlying asset.
- Leverage: Perpetual futures trading often involves leverage, allowing traders to amplify potential returns (or losses). However, leverage can significantly increase the risk, especially in volatile markets.
Key Advantages of Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures offer several advantages over traditional futures or spot trading:
- No Expiry: Traders can hold their positions for as long as they wish, provided they manage their funding payments.
- High Liquidity: The 24⁄7 nature of perpetual futures markets ensures high liquidity and opportunities for quick entry and exit.
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller capital investment, making it possible to gain higher returns (with higher risks).
- Hedge Against Market Movements: Traders can use perpetual futures contracts to hedge their portfolios against price fluctuations.
Perpetual Futures Trading Strategies for Analysts
As an analyst, understanding the underlying strategies behind perpetual futures trading is essential for making informed decisions. Below are two widely-used strategies that analysts employ to navigate the perpetual futures market:
Trend Following Strategy
A trend-following strategy involves identifying the market’s prevailing trend and making trades that align with it. Traders using this strategy will typically:
- Identify an uptrend or downtrend using tools like moving averages, momentum indicators, and price action.
- Enter trades when the trend is confirmed and exit when the trend shows signs of reversal.
- Use stop-loss orders to manage risk.
Pros:
- Can provide high profits during strong market trends.
- Simple to implement and requires fewer decisions once a trend is identified.
Cons:
- Can lead to losses if trends reverse unexpectedly.
- Traders might miss out on profits if the market consolidates or trends remain weak for long periods.
Mean Reversion Strategy
The mean reversion strategy is based on the idea that prices eventually revert to their mean or average over time. Traders using this strategy typically:
- Look for extreme price movements away from a defined mean or average price.
- Enter trades when the price deviates significantly from the mean, betting that the price will revert back.
- Exit trades when the price returns to the mean or shows signs of reversal.
Pros:
- Can be highly profitable in choppy or range-bound markets.
- Provides opportunities to capitalize on price corrections.
Cons:
- May result in significant losses if the price fails to revert and continues in the opposite direction.
- Requires careful identification of price levels and timing of entry and exit.
How to Analyze Market Conditions for Perpetual Futures
To succeed in perpetual futures trading, analysts must be able to analyze market conditions effectively. Below are some key factors to consider:
Market Sentiment Analysis
- Investor Sentiment: Analyzing the overall sentiment of market participants can provide valuable insights into the likely direction of asset prices. This can be done by looking at sentiment indicators, social media analysis, and news sentiment.
- Open Interest: Tracking open interest (the number of outstanding contracts) helps identify whether there is strong participation in the market. High open interest may indicate increased volatility or a buildup of positions.
Technical Analysis
- Chart Patterns: Identifying chart patterns like head and shoulders, triangles, or double tops can help predict future price movements.
- Indicators: Use indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Bollinger Bands to gauge overbought or oversold conditions.
On-Chain Analysis (For Cryptocurrencies)
For cryptocurrencies, on-chain analysis can be particularly useful. Analysts monitor blockchain data such as transaction volumes, wallet activity, and address balances to identify potential price trends.
Perpetual Futures Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential in perpetual futures trading, given the high volatility and leverage involved.
Position Sizing
One of the most important aspects of risk management is proper position sizing. Analysts recommend calculating the size of your position relative to your account balance and the amount of risk you’re willing to take. A general rule is not to risk more than 1-2% of your total capital on a single trade.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit
Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels can help limit potential losses and lock in profits at predefined levels. These levels should be based on technical analysis or volatility, and the positions should be adjusted as market conditions change.
Perpetual Futures Trading Platforms and Tools
To effectively trade perpetual futures, you need the right platform and tools. Some of the most popular platforms include:
- Binance Futures: Offers a wide range of perpetual futures contracts, including for cryptocurrencies and traditional assets.
- Bybit: Known for its advanced trading features, including leverage options and detailed risk management tools.
- FTX: Provides a variety of perpetual futures contracts and is favored for its liquidity and user-friendly interface.
For analysis, tools such as TradingView for charting and CoinGecko for cryptocurrency market data can complement your trading setup.
Challenges in Perpetual Futures Trading for Analysts
While perpetual futures trading offers numerous opportunities, it also presents challenges:
- High Volatility: The volatility of perpetual futures markets can lead to significant gains but also major losses.
- Funding Fees: The cost of holding positions due to funding fees can erode profits over time.
- Leverage Risk: Using leverage increases the potential for both profits and losses, requiring careful risk management.
FAQ
1. How do I start with perpetual futures trading?
To get started, open an account on a platform that offers perpetual futures trading, such as Binance or Bybit. Begin by learning about the asset you’re trading, understanding the risks involved, and practicing with smaller positions before scaling up.
2. What are the best strategies for perpetual futures trading?
Some of the best strategies include trend-following and mean reversion. Each strategy has its strengths depending on market conditions, so it’s important to understand the current market environment before deciding.
3. How can I mitigate risks in perpetual futures trading?
Effective risk management techniques include using proper position sizing, setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, and being cautious with leverage. Additionally, always stay informed about market trends and sentiment to anticipate price movements.
Perpetual futures trading offers traders and analysts the ability to speculate on the price of assets with leverage and flexibility. However, to navigate this market successfully, analysts must understand the underlying mechanics, develop effective strategies, and use the right tools for analysis and risk management. By staying informed and practicing sound trading principles, analysts can make the most of this exciting and dynamic trading opportunity.