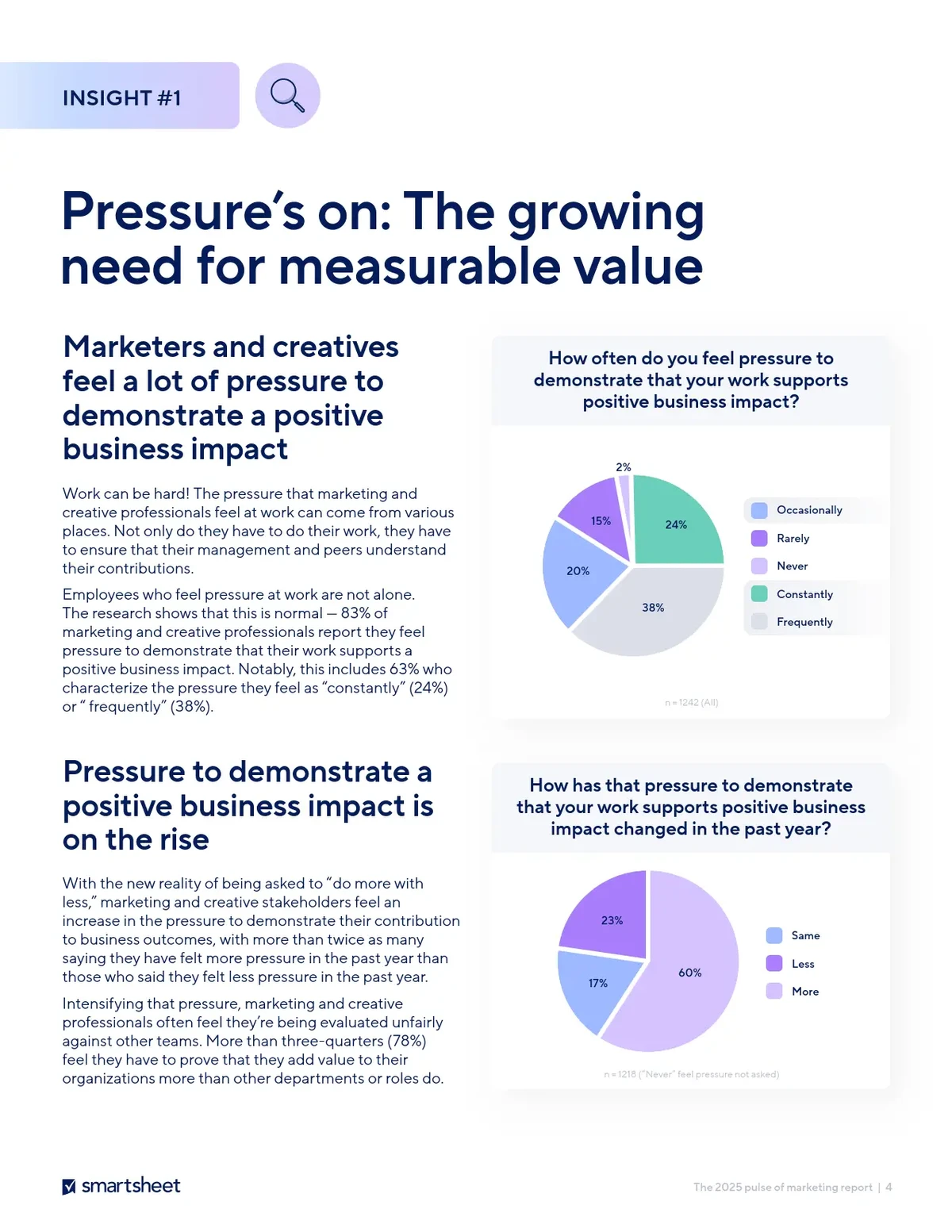

============================
Perpetual futures have become a popular instrument for traders and investors in both traditional and cryptocurrency markets. Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual futures do not have an expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore why trading perpetual futures can be a valuable addition to your trading strategy. We will also compare it with other trading instruments, discuss the key benefits, risks, and answer some frequently asked questions.
What are Perpetual Futures?
Before we dive into why you should trade perpetual futures, it’s essential to understand what they are. Perpetual futures are a type of derivative contract that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of an underlying asset without the need to own the asset itself. Unlike traditional futures, perpetual futures do not have a set expiration date, meaning positions can be held indefinitely as long as the trader maintains the necessary margin.
Key Features of Perpetual Futures
- No Expiration Date: Traders can hold their positions as long as they wish, making them different from traditional futures contracts that have set expiration dates.
- Funding Rate Mechanism: Perpetual futures use a funding rate system that ensures the price of the contract remains close to the spot price of the underlying asset. Traders either pay or receive funding fees periodically depending on market conditions.
- High Leverage: Many exchanges offer high leverage on perpetual futures, allowing traders to take larger positions with less capital.
Why Choose Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual futures offer several advantages for traders. Below, we explore some of the key reasons why perpetual futures can be an attractive option for both novice and experienced traders.
1. Flexibility in Positioning
Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual futures allow traders to hold positions for an indefinite period, as long as they maintain the required margin. This flexibility is ideal for traders looking for longer-term exposure to an asset without worrying about contract expiration.
Advantages:
- No need to roll over contracts, which can incur additional costs in traditional futures trading.
- Allows traders to implement long-term strategies or take advantage of market volatility without time constraints.
Disadvantages:
- Funding rates can add up, especially in volatile markets.
- Long-term holding may be subject to more fees than anticipated.
2. Leverage and High Potential Returns
Perpetual futures contracts allow traders to use leverage, meaning they can take larger positions with less capital. This can significantly amplify both profits and risks, which makes perpetual futures an appealing tool for experienced traders.
Advantages:
- Amplifies potential profits on smaller price movements.
- Allows traders to trade larger volumes without needing substantial capital.
Disadvantages:
- Increased risk: High leverage can lead to significant losses, especially in volatile markets.
- Requires careful margin management to avoid liquidation.
3. Liquidity and Market Access
Most exchanges that offer perpetual futures also provide high liquidity, meaning it is easier to enter and exit trades without slippage. This makes perpetual futures an attractive option for day traders and high-frequency traders who require fast execution and minimal market impact.
Advantages:
- High liquidity ensures tight spreads, which can improve the overall efficiency of trades.
- Provides access to a wide variety of assets, including cryptocurrencies, commodities, and indices.
Disadvantages:
- Liquidity can sometimes be lower during market downturns, making it harder to execute large trades.
How Perpetual Futures Compare to Other Trading Instruments
To understand the value of perpetual futures, it’s helpful to compare them to other popular trading instruments, such as traditional futures and spot trading.
Perpetual Futures vs. Traditional Futures
Traditional futures contracts have a set expiration date, meaning they are typically settled within a specific time frame, such as monthly or quarterly. Traders must close or roll over their positions before expiration, which may lead to additional costs or complications. Perpetual futures, on the other hand, do not have these time constraints, giving traders the ability to hold positions as long as they wish.
Key Differences:
- Expiration Date: Perpetual futures do not expire, whereas traditional futures require settlement on a specific date.
- Funding Rate: Perpetual futures have a funding rate mechanism to keep the price in line with the underlying asset, while traditional futures are more influenced by supply and demand.
Perpetual Futures vs. Spot Trading
Spot trading involves buying and selling assets like stocks or cryptocurrencies for immediate delivery. Unlike perpetual futures, spot trading does not involve leverage, and traders own the underlying asset once the transaction is completed. While spot trading is less risky due to the absence of leverage, it also offers limited opportunities for maximizing returns.
Key Differences:
- Leverage: Perpetual futures allow leverage, whereas spot trading does not.
- Ownership: In spot trading, traders own the asset; in perpetual futures, traders only speculate on price movements without owning the asset.
Risks of Trading Perpetual Futures
While perpetual futures offer significant advantages, they also come with inherent risks. Understanding these risks and employing proper risk management strategies is crucial for success.
1. Market Volatility
The price of perpetual futures is subject to the same market volatility as the underlying asset. This volatility can result in rapid price swings, which can be especially dangerous for leveraged traders.
Risk Management Tip:
- Use stop-loss orders and carefully monitor margin levels to protect against unexpected market movements.
2. Funding Rates
Traders who hold positions in perpetual futures for extended periods may face periodic funding payments. While these fees are generally small, they can add up over time, especially in highly volatile markets.
Risk Management Tip:
- Regularly assess the funding rate and consider closing or adjusting positions when funding fees are too high.
3. Leverage Risks
As with any leveraged trading, the potential for significant losses increases. If a trade moves against you, high leverage can quickly deplete your margin, leading to liquidation of your position.
Risk Management Tip:
- Keep leverage at a manageable level and use margin alerts to stay informed about your position’s risk exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the main advantages of trading perpetual futures?
The primary advantages of trading perpetual futures include flexibility in holding positions without expiration dates, the ability to use leverage for larger positions, and the access to a wide variety of markets with high liquidity. These features make perpetual futures a preferred choice for traders seeking long-term exposure and high potential returns.
2. How do I calculate perpetual futures fees?
Perpetual futures fees typically consist of trading fees, funding rates, and potentially withdrawal fees. The trading fees depend on the platform you use and the liquidity of the asset, while the funding rate is calculated periodically based on the difference between the perpetual futures price and the spot price of the underlying asset.
3. What are the best strategies for trading perpetual futures?
The best strategies for trading perpetual futures depend on the trader’s risk tolerance and market conditions. Some popular strategies include trend-following, scalping, and arbitrage. It’s important to have a solid risk management plan in place, such as setting stop-loss orders and using proper position sizing to avoid excessive risk exposure.
Conclusion
Trading perpetual futures offers a unique set of benefits, including flexibility, leverage, and access to high-liquidity markets. Whether you are a novice trader looking to understand the basics or an experienced trader seeking advanced strategies, perpetual futures provide opportunities to profit from market movements without the need to own the underlying asset. However, as with any leveraged product, they come with risks, including volatility, funding rates, and the potential for liquidation if margin requirements are not managed carefully. By understanding how perpetual futures work and using sound risk management practices, traders can effectively harness their potential for substantial returns.