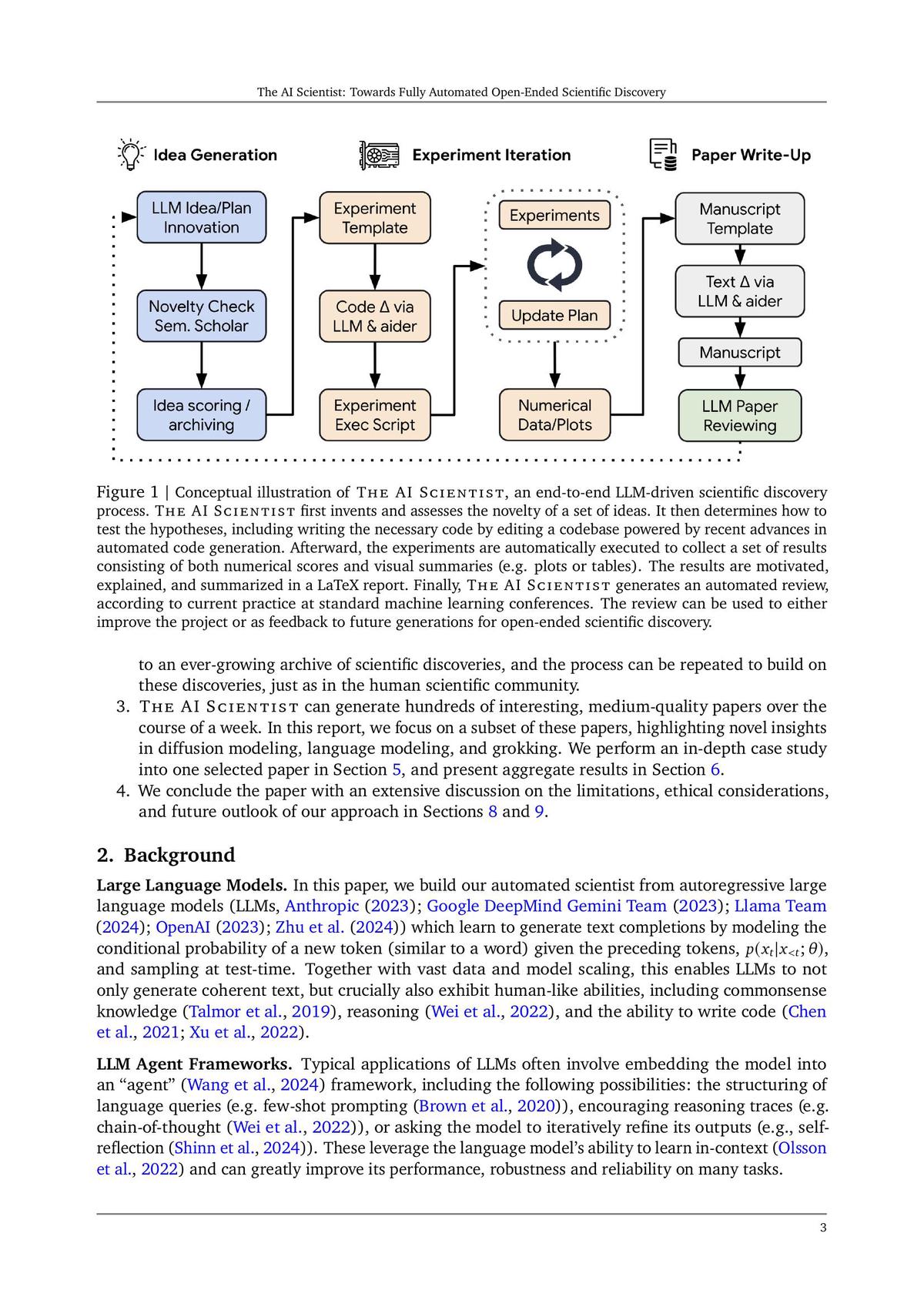
====================================================================
Arbitrage pricing is an essential strategy for commodity traders, particularly when dealing with perpetual futures. In an increasingly volatile and complex market, being able to leverage arbitrage opportunities can significantly enhance a trader’s profitability while managing risk. This article will delve into the principles of arbitrage pricing, explain its importance in perpetual futures, and provide valuable insights into how commodity traders can implement these strategies effectively.
Understanding Arbitrage Pricing in Perpetual Futures
Arbitrage pricing involves exploiting price discrepancies between different markets or instruments to lock in a risk-free profit. In the context of perpetual futures, this typically means capitalizing on differences in the spot price of a commodity and its perpetual futures price. These discrepancies arise due to factors such as market inefficiencies, supply and demand imbalances, and liquidity differences.
What Are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual futures are derivative contracts that do not have an expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. They are primarily used in markets like cryptocurrencies, commodities, and other financial assets. Unlike traditional futures, perpetual futures allow for continuous trading, making them ideal for arbitrage strategies.
Key Principles of Arbitrage Pricing for Commodity Traders
Arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures revolves around the ability to spot price inefficiencies and capitalize on them before they close. Here are some essential principles to keep in mind:
1. Price Inefficiencies
- Spot vs. Futures Price: One of the most common arbitrage opportunities arises when the spot price of a commodity diverges from its perpetual futures price. This discrepancy can be due to a variety of factors, including market sentiment, liquidity, and time decay in futures contracts.
- Funding Rate Arbitrage: In perpetual futures markets, the funding rate plays a crucial role. Traders can earn or pay a funding fee depending on whether the perpetual futures price is higher or lower than the spot price. This rate can create opportunities for arbitrage.
2. Transaction Costs
While arbitrage may seem like a straightforward strategy, transaction costs, such as spreads, fees, and slippage, can eat into profits. Therefore, minimizing these costs is critical when executing arbitrage strategies in perpetual futures markets.
3. Liquidity and Market Depth
High liquidity and market depth are essential for successfully executing arbitrage strategies. When liquidity is low, price discrepancies may be larger, but they are harder to exploit without affecting the market price.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Arbitrage Pricing | Exploit price differences between markets to lock risk-free profit. |
| Perpetual Futures | Derivatives without expiration, allow continuous trading for arbitrage. |
| Price Inefficiencies | Spot vs. futures price divergence and funding rate differences create opportunities. |
| Transaction Costs | Spreads, fees, and slippage reduce arbitrage profits. |
| Liquidity & Market Depth | High liquidity needed; low liquidity increases difficulty of execution. |
| Spot & Futures Arbitrage | Buy spot, sell futures (or vice versa) to profit from price divergence. |
| Pros – Spot/Futures | Low risk due to hedged positions, simple strategy. |
| Cons – Spot/Futures | Low margins, capital intensive. |
| Funding Rate Arbitrage | Exploit funding rate differences to earn fees or reduce costs. |
| Pros – Funding Rate | Low capital required, steady income if rates favorable. |
| Cons – Funding Rate | Subject to market volatility and changing funding rates. |
| Automation Tools | Use bots and algorithms for fast execution and monitoring. |
| Market News | Stay updated on rates, sentiment, and news for timely arbitrage. |
| Risk Management | Diversify, use stop-loss, monitor liquidity, manage position sizes. |
| FAQ – How It Works | Exploit spot and futures price differences; consider funding rates. |
| FAQ – Main Risks | Market volatility, funding rate changes, transaction costs, liquidity issues. |
| FAQ – Beginner Start | Learn markets, simulate trades, start small-scale live trading. |
| Conclusion | Master fundamentals, automation, and risk management for profitable arbitrage. |
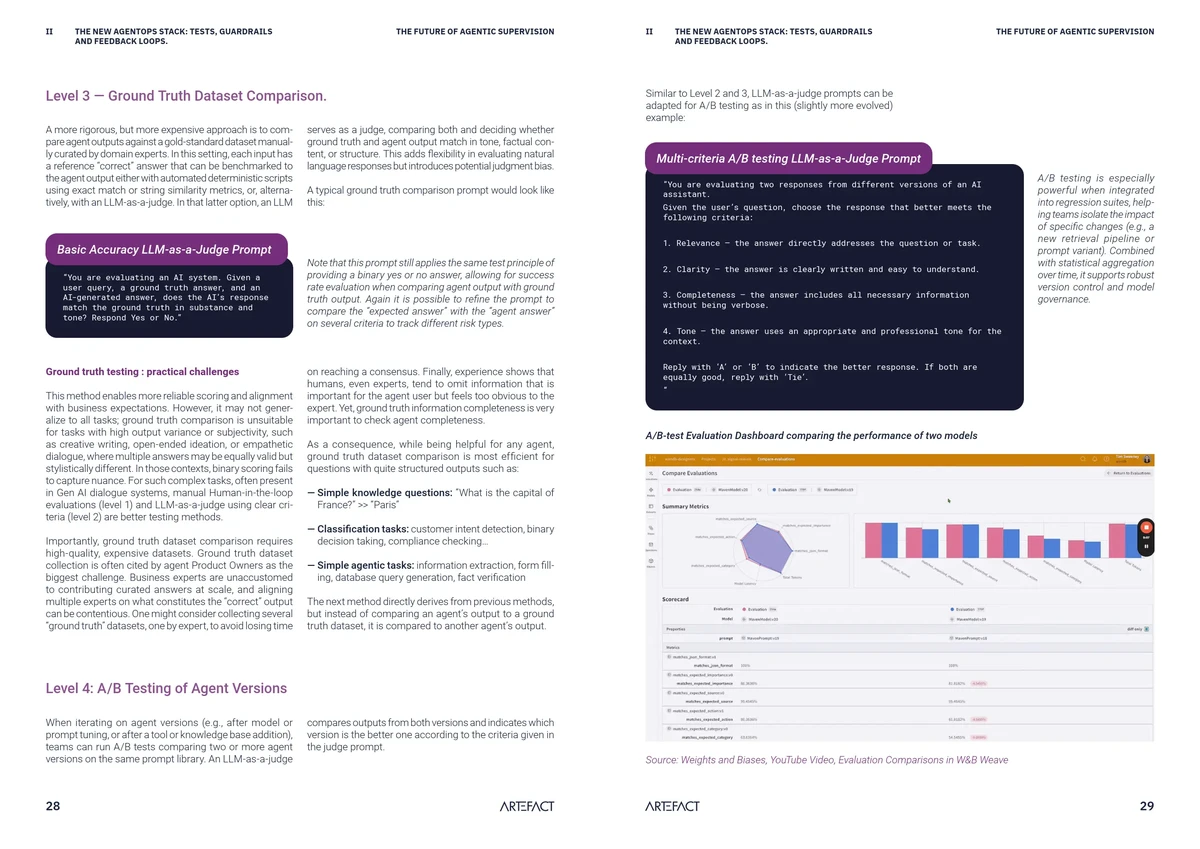
1. Spot and Futures Arbitrage
Spot and futures arbitrage is the most basic form of arbitrage, where traders buy the commodity in the spot market and simultaneously sell its equivalent perpetual futures contract, or vice versa, depending on the price discrepancy.
How to Execute:
- Identify Price Divergence: Monitor the spot price and the perpetual futures price to identify significant price differences.
- Execute the Trade: Buy the commodity in the spot market and sell the equivalent perpetual futures contract if the futures price is higher than the spot price, or vice versa.
- Close the Positions: Once the price discrepancy narrows or closes, close both positions to lock in the arbitrage profit.
Pros:
- Low Risk: Since the positions are hedged, there is minimal market risk involved.
- Simple Strategy: The mechanics of the trade are relatively easy to understand and implement.
Cons:
- Low Profit Margins: The arbitrage opportunity may only yield a small profit, especially after transaction costs are accounted for.
- Capital Intensive: Spot and futures arbitrage often requires significant capital to generate meaningful returns.
2. Funding Rate Arbitrage
Perpetual futures markets use a funding rate to ensure that the futures price aligns with the underlying asset’s spot price. Traders can capitalize on this funding rate discrepancy by borrowing in the futures market to collect a positive funding fee or by shorting the futures market to pay a negative funding fee.
How to Execute:
- Monitor Funding Rates: Regularly check the funding rates of the perpetual futures market to identify profitable opportunities.
- Arbitrage Position: If the funding rate is positive, long the perpetual futures contract to earn the funding rate. If the funding rate is negative, short the contract to pay a lower funding rate.
- Repeat: Continuously monitor funding rates and adjust positions accordingly.
Pros:
- Low Capital Requirement: Funding rate arbitrage can be implemented with relatively low capital compared to spot and futures arbitrage.
- Steady Income: This method offers traders a consistent stream of income as long as funding rates remain favorable.
Cons:
- Market Risk: Funding rate arbitrage is subject to market volatility, and unexpected price movements can lead to losses.
- Changing Rates: Funding rates can fluctuate, making it difficult to predict how long a profitable arbitrage opportunity will last.
Best Practices for Commodity Traders in Perpetual Futures
1. Leverage Automation Tools
Arbitrage pricing strategies in perpetual futures can be highly time-sensitive, and the ability to react quickly is key. Automated trading tools and bots can help traders execute arbitrage strategies without the need for constant monitoring.
- Trading Bots: Use bots that are programmed to identify arbitrage opportunities and execute trades automatically when certain price conditions are met.
- Algorithmic Trading: Advanced algorithms can be customized to monitor multiple exchanges and identify arbitrage opportunities across different markets.
2. Stay Updated with Market News
Arbitrage opportunities can be fleeting, often disappearing as quickly as they arise. Staying updated with real-time market news, funding rate announcements, and changes in market sentiment can help traders anticipate potential arbitrage scenarios.
3. Risk Management
Although arbitrage is considered a low-risk strategy, effective risk management is still essential. Traders should:
- Diversify their positions across multiple contracts or markets.
- Use stop-loss orders and position sizing techniques to protect against unexpected market shifts.
- Continuously monitor liquidity levels to ensure they can enter and exit positions without significant slippage.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How does arbitrage pricing work for perpetual futures?
Arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures works by exploiting price differences between the spot market and perpetual futures contracts. Traders identify a divergence in prices, take positions in both markets (buying and selling), and then close them when the price discrepancy narrows. The funding rate in perpetual futures also plays a crucial role in determining arbitrage opportunities.
2. What are the main risks associated with arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures?
The primary risks include market volatility, funding rate fluctuations, transaction costs, and liquidity issues. While arbitrage is generally considered low risk, unexpected price movements and high transaction costs can reduce or eliminate profits.
3. How can beginners start using arbitrage pricing for perpetual futures?
Beginners can start by understanding the basics of spot and futures markets, along with funding rate dynamics. They should use simulation platforms to practice identifying price discrepancies and executing arbitrage trades without real financial risk. Once they are confident, they can transition to small-scale live trading.
Conclusion
Arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures is an advanced but highly effective strategy for commodity traders. By understanding the fundamentals of price inefficiencies, transaction costs, and market liquidity, traders can implement profitable arbitrage strategies. Whether you’re employing spot and futures arbitrage or funding rate arbitrage, automation tools, real-time data, and a robust risk management framework are essential for long-term success. By mastering these strategies, commodity traders can not only mitigate risk but also enhance their profitability in a competitive market environment.