===============================================
Perpetual futures have become an essential instrument for both retail and institutional traders in the cryptocurrency, forex, and traditional financial markets. One of the key metrics often utilized in analyzing perpetual futures is beta, a measure of a contract’s volatility relative to a broader market or underlying asset. Beta analysis plays a crucial role in risk management, trade optimization, and the development of trading strategies. This article explores the importance of beta in perpetual futures analysis, how to use it effectively, and how you can find and interpret beta data.
What is Beta in Perpetual Futures?
In financial terms, beta is a measure of the volatility or systematic risk of a financial instrument in relation to the market as a whole. In the context of perpetual futures, beta measures how the price of the futures contract moves in relation to the underlying asset or the overall market.
Beta in Perpetual Futures: A Key to Risk Management
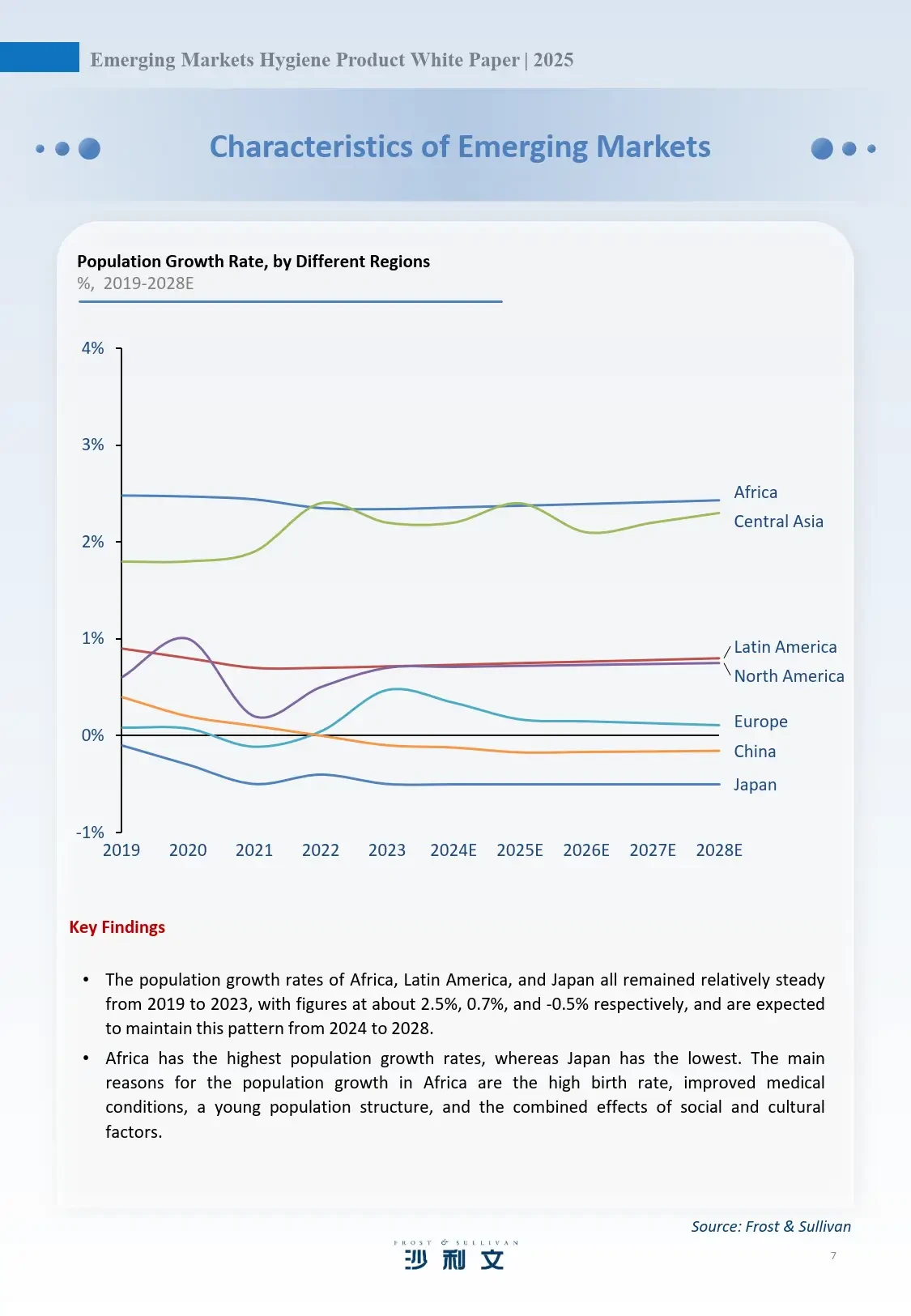
The volatility of perpetual futures contracts is critical to understanding their risk profile. By analyzing the beta, traders can determine how much a futures contract moves relative to market conditions. A high beta suggests that the futures contract is more volatile and could offer larger profits (or losses), while a lower beta indicates reduced volatility and potentially safer trading conditions.
How Beta Affects Perpetual Futures Trading
Understanding beta’s effect on perpetual futures trading can help traders optimize their strategies and manage risk more effectively. Beta can either be used to enhance returns or reduce exposure to market volatility, depending on the trader’s goals.
Using Beta for Strategy Optimization
Beta plays a significant role in constructing strategies for perpetual futures. Traders often look for high-beta assets when they want to capitalize on large price movements, while low-beta assets are more suitable for risk-averse traders who prefer stability.
1. Beta for Trend Followers
Traders who follow market trends may prefer high-beta assets because they tend to experience more significant price swings in the direction of the trend. Such assets can generate substantial profits in trending markets.
2. Beta for Risk-Averse Traders
On the other hand, risk-averse traders may prefer low-beta futures contracts. These tend to move more slowly, providing less opportunity for large profits but offering more predictable price action.
Beta’s Role in Hedging
Another essential use of beta in perpetual futures is in hedging. Traders can use beta to hedge their positions in related markets by taking an opposite position in a futures contract that correlates with their main trade. For instance, if a trader has a long position in a cryptocurrency and a high-beta perpetual future is likely to move in the opposite direction, the trader could short that perpetual future to reduce exposure.

How to Calculate Beta in Perpetual Futures?
Calculating beta in perpetual futures is a fundamental process for any trader looking to understand the risk characteristics of their positions. Beta is calculated by comparing the returns of the futures contract to the returns of the benchmark market, typically using historical price data.
The Formula for Beta
The formula for calculating beta is:
Beta=Covariance (Asset, Market)Variance (Market)\text{Beta} = \frac{{\text{Covariance (Asset, Market)}}}{{\text{Variance (Market)}}}Beta=Variance (Market)Covariance (Asset, Market)
Where:
- Covariance (Asset, Market) measures how the asset’s returns move relative to the market.
- Variance (Market) measures how the market as a whole fluctuates.
For instance, if you are trading a Bitcoin perpetual future, you would calculate beta by comparing Bitcoin’s price movements to the broader crypto market or Bitcoin’s historical volatility.
Step-by-Step Guide to Beta Calculation
- Collect Historical Data: Gather historical data on both the asset (futures contract) and the benchmark market.
- Calculate Returns: Calculate daily or weekly returns for both the futures and the market.
- Covariance and Variance: Calculate the covariance between the asset’s returns and the market’s returns. Then, calculate the variance of the market’s returns.
- Apply the Formula: Use the beta formula to calculate the asset’s beta.
Using Beta Data for Strategic Decisions
Once you have the beta value, you can use it for various purposes, including:
- Position sizing: Adjust your position size according to the beta value. High-beta assets should have smaller position sizes to manage risk.
- Market selection: Select markets with the appropriate beta for your strategy. For example, aggressive traders may look for high-beta markets, while conservative traders may prefer low-beta markets.

Sources of Beta Data for Perpetual Futures
Finding accurate beta data for perpetual futures is essential for traders who want to optimize their strategies. There are several sources where you can get beta data:
1. Trading Platforms
Most advanced trading platforms that offer perpetual futures, such as Binance, Kraken, or FTX, often provide tools that allow traders to calculate or view the beta of a specific futures contract.
2. Financial Data Providers
Data providers such as Bloomberg, Yahoo Finance, and CoinGecko offer market data and may provide beta calculations for specific assets or perpetual futures contracts.
3. Custom Beta Calculation Tools
Some traders may opt for custom tools that calculate beta in real-time. These tools can be integrated with platforms like MetaTrader or TradingView, where traders can input their own data and calculate beta on the fly.
How to Interpret Beta in Perpetual Futures Analysis
Interpreting beta in perpetual futures analysis requires an understanding of market behavior and asset characteristics. Below are some interpretations of beta values:
1. High Beta (>1)
A beta greater than 1 indicates that the futures contract is more volatile than the market. These assets are likely to experience larger price movements, both upward and downward. High-beta assets can be beneficial for traders looking for aggressive price movements, but they also come with higher risk.
2. Low Beta ()
A beta less than 1 suggests that the futures contract is less volatile than the market. These assets experience smaller price fluctuations and are generally seen as less risky. Low-beta assets may not offer the large gains that high-beta assets provide, but they can offer more predictable price action.
3. Beta of 1
A beta of 1 means that the asset’s price moves in line with the market. It is neither more nor less volatile than the market. Traders can use assets with a beta of 1 if they want to mirror market movements without taking on additional risk.
Beta Strategies for Perpetual Futures Traders
1. Risk Management Strategy Using Beta
Traders can apply beta-based risk management by adjusting position sizes depending on the asset’s volatility. For instance, if you are trading a high-beta asset, you might reduce your position size to limit potential losses. On the other hand, with low-beta assets, you can take larger positions as the volatility is lower.
2. Portfolio Diversification Using Beta
By combining high-beta and low-beta assets in your portfolio, you can create a balanced risk profile. This strategy allows traders to take advantage of large movements in high-beta assets while mitigating risk through low-beta assets.
3. Hedging Strategies Using Beta
Beta can also be used to hedge positions. For example, if you have a long position in a high-beta asset, you could short a low-beta asset that moves inversely, reducing your exposure to overall market risk.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How can I get accurate beta data for perpetual futures?
You can get accurate beta data from trading platforms like MetaTrader or TradingView, financial data providers like Bloomberg or Yahoo Finance, or by using custom tools designed for real-time beta calculations.
2. Why is beta important in perpetual futures trading?
Beta helps traders understand the volatility and risk of perpetual futures contracts. By analyzing beta, traders can adjust their strategies to either capitalize on high volatility or reduce exposure to risk, depending on their risk tolerance and market conditions.
3. How do I use beta to hedge my position in perpetual futures?
To hedge with beta, you can take an opposite position in a correlated asset. For example, if you have a long position in a high-beta perpetual future, you might short a low-beta asset to reduce exposure to volatility and risk.
Conclusion
Incorporating beta analysis into your perpetual futures trading strategy is a powerful way to manage risk, optimize returns, and make informed decisions. By calculating and interpreting beta values, traders can adjust their positions, hedge effectively, and select the right markets for their trading goals. As you continue to build your expertise in perpetual futures, understanding and using beta will help you navigate volatile markets more confidently.
If you found this guide helpful, please share it with your network and leave your thoughts in the comments. Happy trading!