========================================================
Jensen’s Alpha is one of the most widely used risk-adjusted performance metrics in finance, particularly for evaluating portfolio managers and their ability to generate excess returns over a benchmark index. While Jensen’s Alpha is primarily applied to traditional asset classes like stocks and mutual funds, its application in the derivatives market, specifically perpetual futures, has gained increasing attention. This article delves into a comparative study of Jensen’s Alpha in perpetual futures, examining how it functions in this context, the differences from traditional markets, and the significance for traders and investors.
What is Jensen’s Alpha?
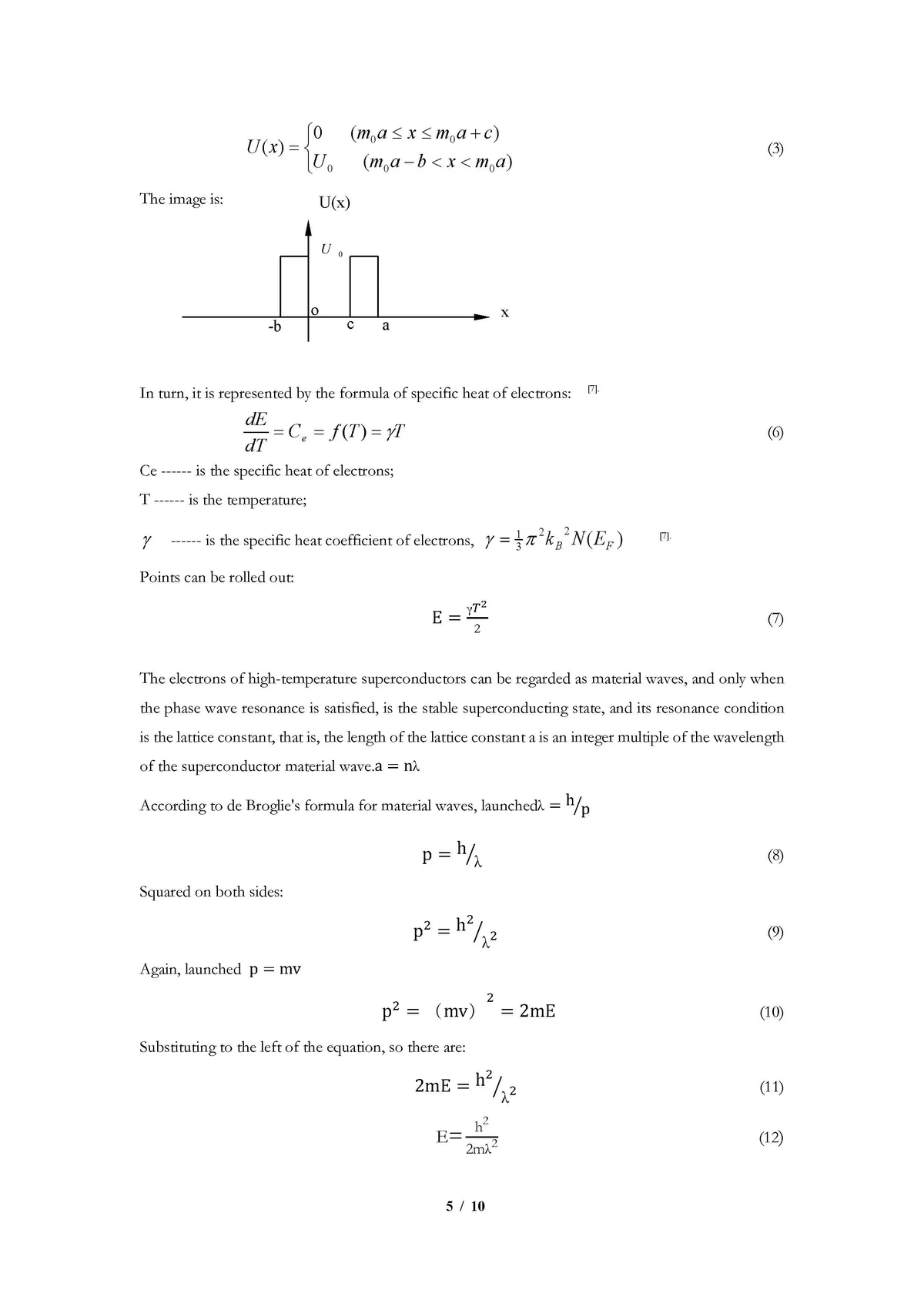
Before diving into its application in perpetual futures, it’s crucial to understand what Jensen’s Alpha measures. Jensen’s Alpha is a risk-adjusted return metric that calculates the excess return of a portfolio above or below the expected return based on the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). The formula for Jensen’s Alpha is:
α=Rp−[Rf+β(Rm−Rf)]\alpha = R_p - [R_f + \beta (R_m - R_f)]α=Rp−[Rf+β(Rm−Rf)]
Where:
- RpR_pRp = Portfolio return
- RfR_fRf = Risk-free rate
- β\betaβ = Portfolio’s beta (a measure of its sensitivity to market returns)
- RmR_mRm = Market return
A positive Jensen’s Alpha indicates that the portfolio manager is providing value beyond what would be expected given the market’s movements, while a negative alpha suggests underperformance.
Applying Jensen’s Alpha in Perpetual Futures
1. Understanding Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures are a unique derivative product primarily used in cryptocurrency markets and some commodities. Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual futures do not have an expiration date, which means they can be held indefinitely, as long as the trader has sufficient margin. This feature makes perpetual futures an ideal tool for hedging, speculation, and arbitrage strategies.
However, the lack of an expiration date and the influence of factors like funding rates make perpetual futures distinct from traditional futures contracts. The pricing and volatility factors for perpetual futures are also significantly influenced by market demand and supply dynamics, leading to different risk considerations compared to traditional financial markets.
2. Jensen’s Alpha in the Context of Perpetual Futures
In perpetual futures, Jensen’s Alpha can be used to assess the risk-adjusted returns of trading strategies, whether for individual traders or institutional investors. However, the metrics for calculating Alpha in perpetual futures differ slightly due to the non-traditional characteristics of these products.
Key Differences:
- No Expiration Date: The lack of a fixed expiry date for perpetual futures means traders can hold positions indefinitely, allowing them to capture long-term trends and funding rate advantages. This differs from traditional futures where time decay is a significant factor.
- Funding Rates: One of the unique aspects of perpetual futures is the funding rate, a mechanism that ensures the price of perpetual futures stays in line with the spot market. Traders are either paid or charged funding depending on the position they hold, which must be factored into the calculation of Jensen’s Alpha.
- Market Liquidity: In contrast to traditional futures markets, perpetual futures markets can exhibit greater volatility due to lower liquidity, especially in less established markets like cryptocurrencies. This volatility must be accounted for when evaluating the excess returns using Jensen’s Alpha.
Comparative Study of Jensen’s Alpha in Traditional vs. Perpetual Futures Markets
1. Traditional Futures Markets
In traditional futures markets (such as those for commodities or equity indices), Jensen’s Alpha is typically used to assess a portfolio’s performance against a benchmark, such as an index or commodity futures index. Traders in these markets use Jensen’s Alpha to evaluate how well their strategies are performing compared to market trends.
Benefits of Using Jensen’s Alpha in Traditional Futures:
- Predictable Risk: Traditional futures markets tend to have more predictable and stable funding rates and volatility compared to perpetual futures.
- Clear Benchmarking: In markets like the S&P 500 or crude oil, it is easier to define a benchmark against which excess returns can be compared.
Limitations:
- Limited Flexibility: Traditional futures contracts come with fixed expiration dates, which might limit the flexibility of some strategies.
- Time Decay: The decay of value due to the approaching expiration date can skew the performance analysis of strategies that rely on long-term holdings.
2. Perpetual Futures Markets
Perpetual futures markets, especially in crypto trading, present an entirely different set of dynamics. The ability to hold positions indefinitely without the pressure of expiration offers a unique advantage, but also introduces complexities when it comes to risk assessment.
Advantages of Using Jensen’s Alpha in Perpetual Futures:
- No Expiration Date: This eliminates the time decay factor, allowing traders to hold positions longer and potentially capture more upside, which can lead to higher alpha.
- Funding Rate Insights: By factoring in the funding rate, traders can measure how much they are benefiting or being penalized based on their positions, which can improve the accuracy of Jensen’s Alpha in predicting returns.
- High Leverage: Perpetual futures often allow high leverage, which can amplify both potential returns and risks, making Jensen’s Alpha even more relevant as a risk-adjusted performance measure.
Limitations:
- High Volatility: The greater volatility in cryptocurrency markets or other less liquid markets can make it harder to accurately assess performance, as large price swings might lead to erratic alpha results.
- Complex Risk Factors: Funding rate fluctuations, extreme market moves, and lack of regulation in some perpetual futures markets can lead to distorted alpha readings, especially if not accounted for correctly.
Practical Application and Strategies for Evaluating Jensen’s Alpha in Perpetual Futures
1. Using Jensen’s Alpha for Hedging Strategies
Traders using perpetual futures for hedging might focus on generating positive alpha by managing funding rates and market volatility. By aligning their positions with the broader market movements and carefully calculating their excess returns, they can potentially use Jensen’s Alpha to evaluate the effectiveness of their hedge.
2. Optimizing Risk-Adjusted Returns
For traders and investors looking to optimize their risk-adjusted returns, combining Jensen’s Alpha with other performance metrics such as Sharpe Ratio or Sortino Ratio can provide deeper insights into portfolio performance, helping them navigate the complexities of perpetual futures.
3. Institutional Investors and Perpetual Futures
Institutional investors can leverage Jensen’s Alpha in a comparative analysis of different trading desks or portfolios, especially when assessing their involvement in perpetual futures markets. By evaluating excess returns and risk, institutions can fine-tune their trading strategies to outperform the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How is Jensen’s Alpha calculated in perpetual futures?
Jensen’s Alpha in perpetual futures is calculated using the same formula as traditional markets, with adjustments for funding rates and volatility. The main difference lies in how the benchmark is defined, as perpetual futures markets often do not have a clear “market index” like traditional futures. Traders may use spot prices or a specific index that represents the market’s trend.
2. Why is Jensen’s Alpha important for perpetual futures trading?
Jensen’s Alpha is crucial for perpetual futures trading as it helps measure whether a trader is generating returns above the risk-adjusted expected returns. This metric helps traders assess the effectiveness of their strategies and manage risk in highly volatile and liquid markets.
3. Can institutional investors benefit from using Jensen’s Alpha in perpetual futures?
Yes, institutional investors can benefit significantly from using Jensen’s Alpha in perpetual futures. By evaluating performance based on risk-adjusted returns, they can identify top-performing strategies, optimize risk exposure, and enhance portfolio performance across various trading desks.
Conclusion
Jensen’s Alpha provides valuable insights into the risk-adjusted returns of perpetual futures strategies. While its application in perpetual futures markets differs from traditional futures markets, especially considering factors like funding rates and volatility, it remains an essential tool for traders and investors looking to optimize their strategies. Whether you are an institutional investor or a retail trader, understanding and applying Jensen’s Alpha to your perpetual futures positions can give you a clearer picture of your portfolio’s performance and improve decision-making in these dynamic markets.