
=============================================
Introduction
Perpetual futures have become one of the most widely traded instruments in cryptocurrency and derivatives markets due to their flexibility, 24⁄7 liquidity, and leverage opportunities. However, with innovation comes complexity—and among the most significant yet often overlooked aspects is credit risk. This Perpetual futures credit risk analysis report provides a structured and in-depth framework to help traders, institutional investors, and brokers understand, measure, and mitigate risks associated with counterparties, market volatility, and systemic vulnerabilities.
Drawing on real-world experience, financial modeling, and industry best practices, this report examines multiple strategies for credit risk management, compares their strengths and weaknesses, and highlights a recommended approach that balances risk and profitability.
Understanding Credit Risk in Perpetual Futures
What is Credit Risk?
Credit risk refers to the potential loss resulting from a counterparty’s inability to fulfill contractual obligations. In perpetual futures, this includes risks of margin defaults, clearing failures, and systemic contagion due to excessive leverage.
Why Credit Risk Matters in Perpetual Futures Trading
Unlike traditional futures, perpetual contracts never expire. This means positions can remain open indefinitely, amplifying exposure to counterparty defaults and liquidation mechanisms. Market participants must therefore integrate credit risk frameworks to prevent cascading liquidations and forced unwinds.
Key Factors Influencing Credit Risk in Perpetual Futures
1. Leverage and Margin Requirements
High leverage magnifies both potential profits and losses. Exchanges that allow excessive leverage without strict margin monitoring create systemic vulnerabilities.
2. Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency and emerging asset markets are extremely volatile, meaning collateral values can collapse within minutes. This volatility is a primary driver of liquidation risk.
3. Counterparty Reliability
Exchanges, brokers, and clearinghouses serve as intermediaries. Their solvency and operational resilience are critical in managing systemic credit risk.
4. Liquidity Conditions
Thin liquidity during market stress increases slippage and makes liquidations less effective, leading to under-collateralized positions.
Methods for Perpetual Futures Credit Risk Analysis
Quantitative Credit Risk Models
These models use statistical and financial techniques to calculate probabilities of default (PD), exposure at default (EAD), and loss given default (LGD). Monte Carlo simulations, Value at Risk (VaR), and stress tests help institutions predict worst-case scenarios.
Pros:
- Data-driven and statistically robust.
- Effective for institutions with historical datasets.
- Enables scenario planning for extreme market events.
Cons:
- Requires large amounts of clean data.
- Complex to implement and prone to model risk.
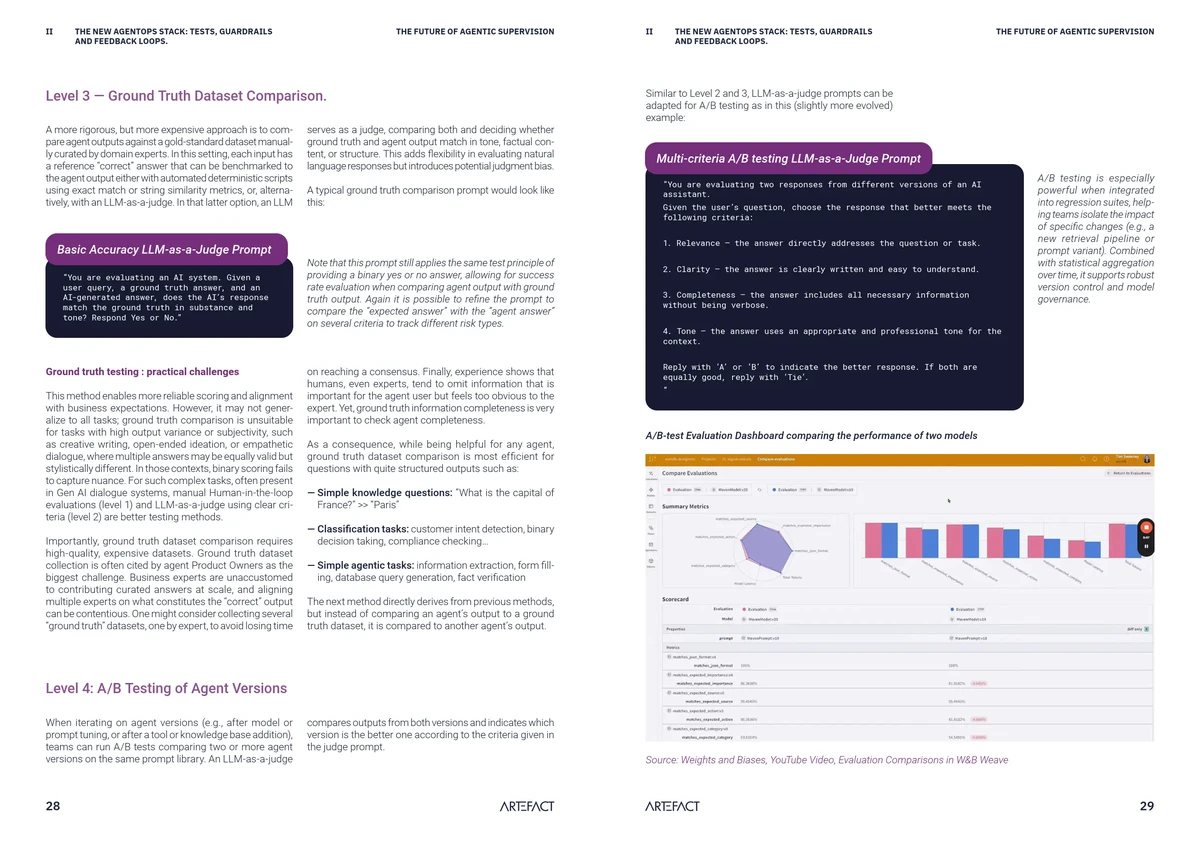
Qualitative Risk Assessment Frameworks
These rely on structured assessments, ratings, and expert judgment to evaluate exchange reliability, counterparty strength, and collateral adequacy.
Pros:
- Flexible, adaptable to limited data environments.
- Useful for novice perpetual futures investors.
- Accounts for behavioral and operational risks not captured by quantitative models.
Cons:
- Subjective and dependent on analyst expertise.
- Less precise for high-frequency trading or institutional portfolios.
Recommended Approach: Hybrid Credit Risk Analysis
A hybrid model combining quantitative analysis with qualitative insights offers the most comprehensive risk framework. Traders can rely on quantitative tools for real-time monitoring while using qualitative reviews to account for governance, exchange integrity, and macroeconomic factors.
Credit Risk Mitigation Strategies
1. Collateral Management and Margin Optimization
Maintaining adequate collateral and adaptive margin calls ensures that defaults are minimized. Exchanges increasingly employ dynamic margining systems based on volatility indexes.
2. Clearinghouse and Insurance Funds
Centralized clearing mechanisms reduce bilateral credit risk, while insurance funds act as a buffer to absorb losses from defaults.
3. Position and Leverage Limits
Traders and institutions should impose maximum exposure caps and avoid concentration in illiquid perpetual contracts.
4. Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
Regular stress testing using market shock scenarios helps investors gauge their resilience to sudden liquidity events.
Industry Trends in Perpetual Futures Risk Management
- AI-driven credit risk monitoring: Machine learning models are now being deployed to predict liquidation probabilities and early warning signals.
- Blockchain transparency: On-chain analytics enhance transparency of collateral flows and reduce hidden leverage.
- Regulatory oversight: Authorities are tightening reporting standards for derivatives exchanges, particularly around capital adequacy and credit exposure.
Credit risk cycle in perpetual futures showing default triggers, margin calls, and systemic effects
Case Study: Credit Risk Event in Crypto Perpetual Markets
In 2020, a major perpetual futures exchange experienced cascading liquidations when Bitcoin dropped over 40% in a single day. The lack of liquidity led to underfunded insurance pools, exposing traders to systemic credit risk. This highlighted the importance of combining best practices for managing credit risk in perpetual futures with robust clearing mechanisms.
Practical Guidance for Traders
How to Assess Credit Risk in Perpetual Futures
- Monitor exchange margin policies.
- Track insurance fund reserves.
- Evaluate liquidity depth before entering high-leverage positions.
Risk Management Tips for Traders
- Always use stop-loss orders.
- Diversify across exchanges.
- Regularly reassess exposure against volatility indexes.
FAQ
1. How can traders evaluate credit risk in perpetual futures?
Experienced traders should combine on-chain analytics, liquidity metrics, and exchange solvency checks. Tools such as order book depth charts, volatility indexes, and margin fund transparency reports provide critical insights. For institutional traders, stress testing models can quantify potential exposures under extreme scenarios.
2. What are the best practices for managing credit risk in perpetual futures?
Best practices include maintaining adequate collateral buffers, limiting leverage, diversifying across instruments and exchanges, and using hybrid credit risk models. Institutional investors often employ both VaR-based monitoring and governance reviews of counterparties.
3. Why is credit risk essential for perpetual futures investors?
Credit risk directly determines the likelihood of forced liquidations and losses during extreme volatility. Without credit risk management, even profitable trading strategies can collapse under systemic stress. Understanding credit risk is therefore essential not only for capital preservation but also for long-term strategy sustainability.
Conclusion
This Perpetual futures credit risk analysis report highlights that credit risk is an unavoidable but manageable component of derivatives trading. While quantitative models offer precision and predictive power, qualitative assessments capture the human and operational factors often missed by numbers. The hybrid model is the optimal solution, balancing accuracy with flexibility.
As perpetual futures markets mature, integrating effective credit risk mitigation in perpetual futures will become a decisive factor for both retail traders and institutional investors.
If you found this report insightful, share it with your network, leave a comment below, and join the discussion—because credit risk awareness is the key to safer, smarter perpetual futures trading.