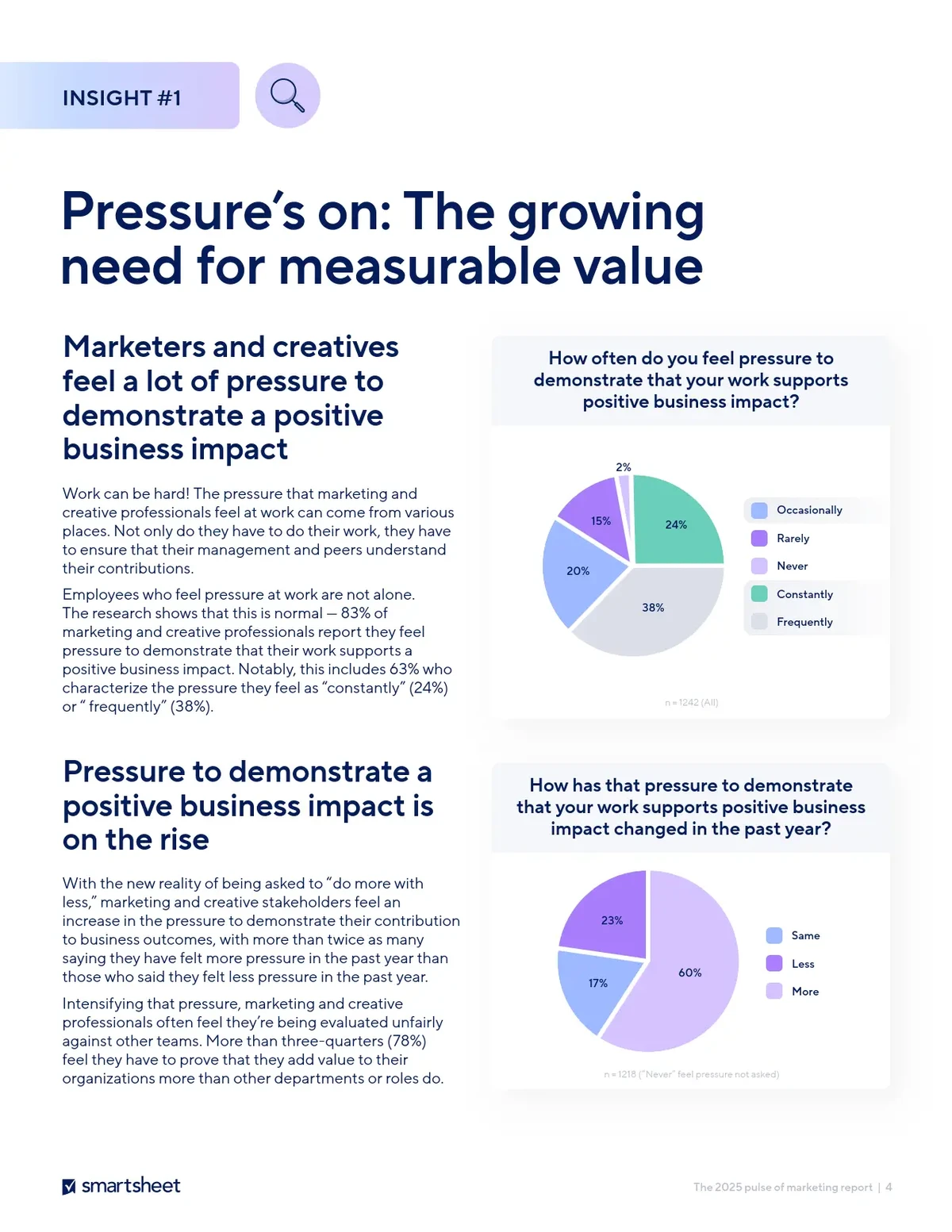
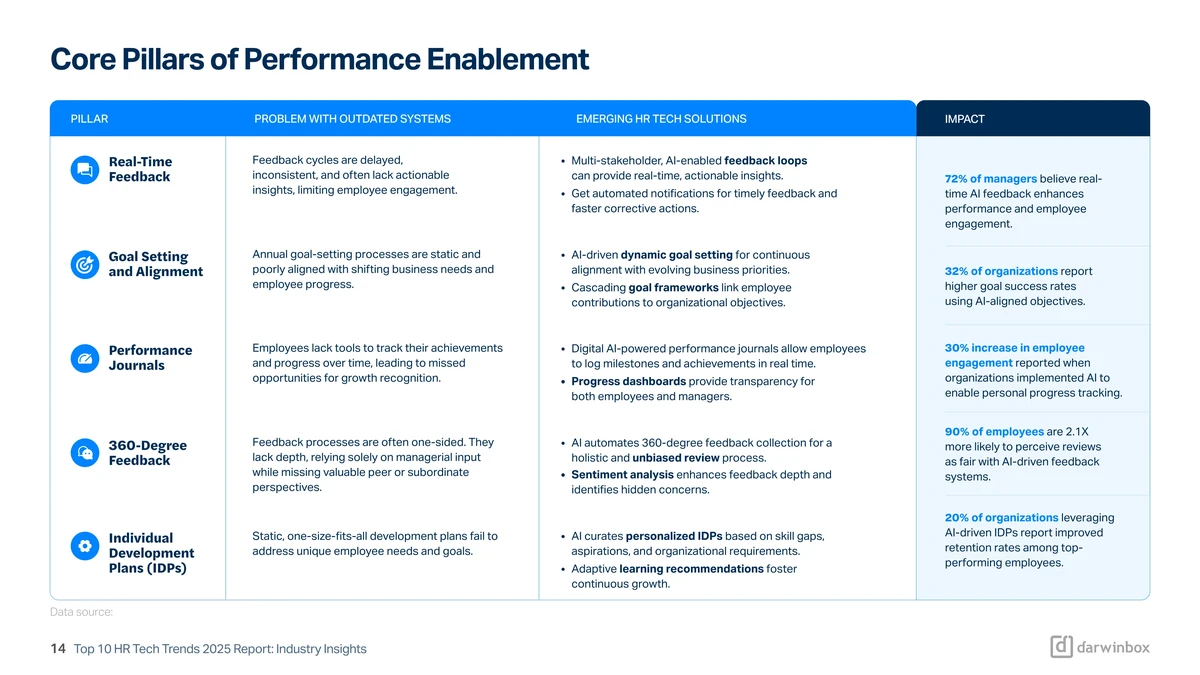
===================================================================
Introduction
Perpetual futures have revolutionized the trading landscape by providing traders with a derivative instrument that mimics spot market behavior but without an expiry date. Their unique funding mechanism—designed to keep prices aligned with the underlying asset—creates continuous opportunities for arbitrage. Knowing how to implement arbitrage pricing strategies in perpetual futures is essential for traders, investors, and institutions who want to exploit inefficiencies in price dynamics, manage risk, and build consistent profits.
This article explores key arbitrage methods, compares their pros and cons, and provides a detailed roadmap for executing arbitrage strategies in perpetual futures. It also explains the latest industry trends and risk management frameworks to ensure traders can apply these concepts effectively.
What is Arbitrage Pricing in Perpetual Futures?
Arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures refers to the practice of exploiting discrepancies between the price of the perpetual futures contract and its corresponding spot or futures markets. The goal is to capture profit from temporary mispricings without taking significant market direction risk.
For example, if Bitcoin perpetual futures trade higher than spot Bitcoin, traders can short perpetual contracts and simultaneously buy spot Bitcoin. Profits arise when the two converge due to funding rate adjustments.
Understanding how does arbitrage pricing work for perpetual futures? is crucial: it functions by balancing perpetual contracts with the underlying asset through funding fees and interest mechanisms.
Why Arbitrage Pricing Matters in Perpetual Futures
- Market Efficiency: Arbitrage ensures perpetual futures remain tied to their underlying assets.
- Profit Opportunities: Skilled traders can earn risk-adjusted returns without needing a directional bet.
- Risk Hedging: Institutions use arbitrage as a hedge against volatility.
- Portfolio Diversification: Provides traders with an alternative revenue stream independent of price trends.
This is why many professionals emphasize why is arbitrage pricing important for perpetual futures?—because it maintains both market balance and profitability potential.
Key Arbitrage Pricing Strategies in Perpetual Futures
1. Spot-Futures Arbitrage (Cash-and-Carry)
How It Works
- Buy the underlying asset in the spot market.
- Short the perpetual futures contract.
- Hold until price convergence.
Pros
- Relatively low risk compared to speculative trades.
- Profits are predictable if funding rates are positive and stable.
Cons
- Requires significant capital for spot asset purchases.
- Exposure to funding rate changes if miscalculated.
2. Funding Rate Arbitrage
How It Works
Perpetual futures use funding payments between long and short traders to align contract prices with spot. Traders exploit this by:
- Going long in spot markets.
- Taking an opposite perpetual futures position to capture positive funding payments.
Pros
- Can generate consistent income in high funding environments.
- Low directional risk if positions are properly balanced.
Cons
- Funding rates are volatile and may flip unexpectedly.
- Requires constant monitoring and adjustments.
3. Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
How It Works
Arbitrageurs look for price discrepancies in perpetual futures contracts across different exchanges.
- Buy perpetual futures on one exchange at a lower price.
- Simultaneously sell on another exchange at a higher price.
Pros
- Fast execution can yield high profits in volatile markets.
- No need for spot asset holdings.
Cons
- Requires fast technology and multiple exchange accounts.
- High transaction fees and transfer times may erode profits.
4. Triangular Arbitrage with Perpetual Futures
How It Works
Uses three correlated assets (e.g., BTC, ETH, USDT) across spot and perpetual futures to lock in arbitrage profits.
Pros
- Exploits inefficiencies in correlated assets.
- Suitable for high-frequency trading bots.
Cons
- Complex execution requires advanced algorithms.
- Small mispricings can vanish within seconds.
Comparing Arbitrage Pricing Strategies
| Strategy | Capital Requirement | Complexity | Risk Level | Profit Consistency | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot-Futures Arbitrage | High | Medium | Low | Medium | Institutional Traders |
| Funding Rate Arbitrage | Medium | Low | Medium | High (volatile) | Experienced Retail |
| Cross-Exchange Arbitrage | Medium | High | Medium | High (short-term) | Algo Traders |
| Triangular Arbitrage | High | Very High | Medium | High (if executed) | Hedge Funds |
Recommendation: Beginners should start with spot-futures arbitrage due to its lower risk and transparency. Advanced traders with technical resources can benefit more from cross-exchange or triangular arbitrage.
Practical Implementation Framework
Step 1: Data Analysis and Monitoring
Track real-time perpetual futures prices, funding rates, and spreads across multiple exchanges. Using arbitrage bots or APIs significantly improves efficiency.
Step 2: Capital Allocation
Divide capital across exchanges and wallets to avoid transfer delays. Diversify between funding rate and cross-exchange arbitrage.
Step 3: Execution and Risk Controls
- Set stop-loss triggers.
- Use partial hedges if volatility spikes.
- Automate execution to minimize slippage.
Step 4: Continuous Optimization
Re-evaluate models weekly based on funding rate changes, liquidity, and exchange fees.
Risk Management in Arbitrage Pricing
Even low-risk arbitrage carries challenges. Key risk areas include:
- Funding Rate Risk: Unexpected reversals in funding direction.
- Exchange Risk: Outages, liquidity crunches, or insolvency.
- Execution Risk: Delays causing missed arbitrage windows.
- Fee Erosion: High transaction and withdrawal costs reducing net profits.
This makes it vital to learn how to minimize risk in arbitrage pricing for perpetual futures by diversifying exchanges, using bots, and managing position sizes.
Industry Trends and Insights
- Rise of AI Arbitrage Models: Machine learning models forecast spreads and funding rates with high accuracy.
- Crypto Hedge Funds Adoption: Institutions increasingly rely on arbitrage to stabilize returns.
- Decentralized Perpetual Futures: Platforms like dYdX and GMX provide new opportunities for DeFi arbitrage.
- Regulatory Impact: Compliance and KYC requirements are shaping exchange arbitrage strategies.
Example Visualization
Illustration of arbitrage opportunities between spot and perpetual futures
FAQ: Arbitrage Pricing in Perpetual Futures
1. What factors influence arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures?
Several factors drive arbitrage opportunities, including funding rates, liquidity, exchange policies, transaction fees, and volatility in the underlying asset. These are the key factors that influence arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures and must be constantly monitored.
2. How long does it take to master arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures?
It depends on the trader’s experience and resources. Retail traders can understand the basics in a few weeks, but building profitable, automated systems may take months or years. Institutional traders rely on advanced quantitative teams to refine these strategies.
3. Why choose arbitrage pricing in perpetual futures over regular futures arbitrage?
Unlike traditional futures that expire, perpetual futures offer continuous opportunities due to their funding rate mechanism. This makes them more attractive for arbitrageurs seeking consistent income and flexibility without waiting for expiry cycles.
Conclusion
Learning how to implement arbitrage pricing strategies in perpetual futures can transform trading from risky speculation into structured, low-risk profitability.
- For beginners: Start with spot-futures arbitrage.
- For advanced traders: Explore funding rate and cross-exchange arbitrage.
- For institutions: Combine triangular arbitrage with machine learning for scale.
The perpetual futures market rewards precision, speed, and discipline. By implementing robust arbitrage strategies, traders can capture inefficiencies, optimize leverage, and build a sustainable trading edge.
👉 What arbitrage pricing strategy do you use in perpetual futures? Share your thoughts in the comments, and spread this guide with traders looking to sharpen their arbitrage skills!