
======================================================================
Introduction
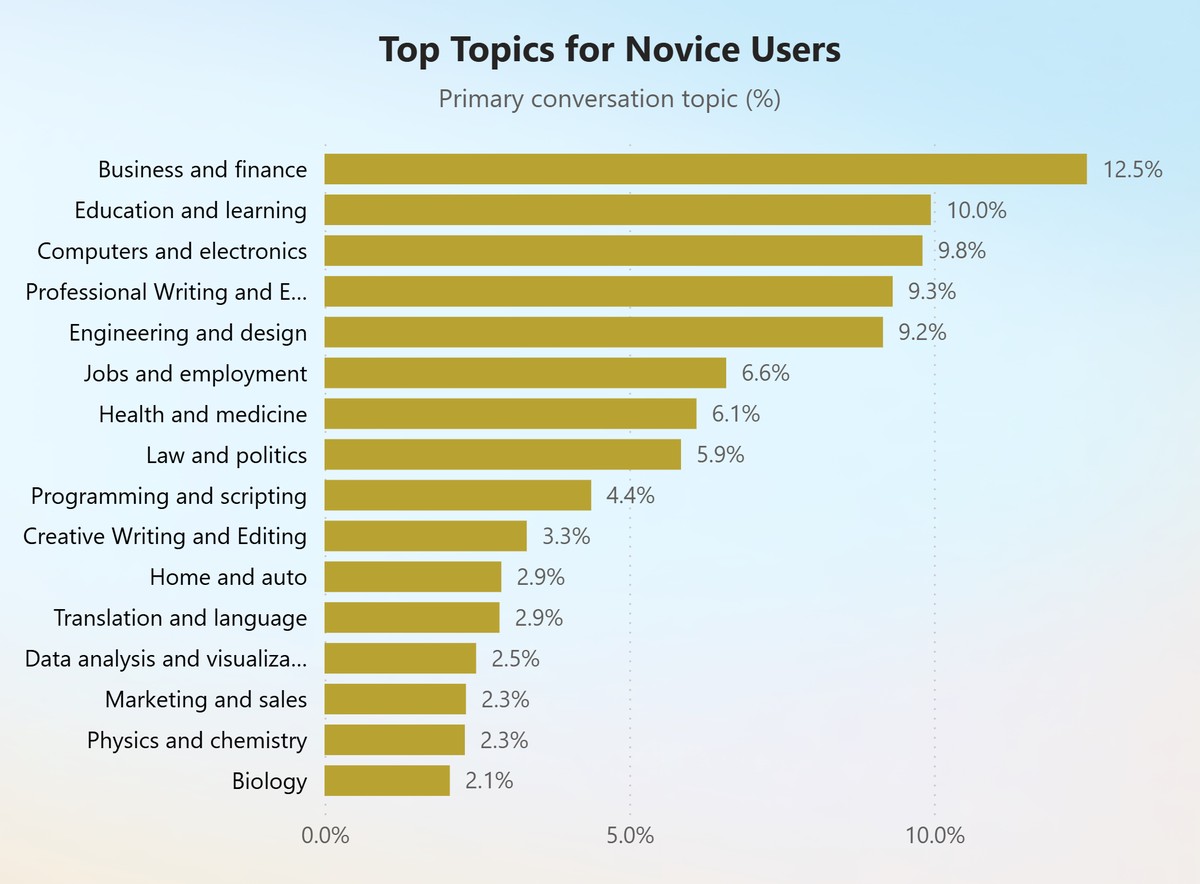
In the evolving derivatives landscape, institutional investors Sortino ratio benchmarks for perpetual futures are becoming a critical performance metric. As perpetual futures attract more sophisticated players—hedge funds, pension funds, and proprietary trading desks—the need for nuanced risk-adjusted return measures grows. Unlike the Sharpe ratio, which penalizes upside and downside volatility equally, the Sortino ratio isolates downside risk, providing a clearer picture of how strategies protect capital while pursuing alpha.
This in-depth guide explains why institutional investors use Sortino ratio benchmarks, compares at least two distinct methods of implementing them, and outlines how you can integrate these insights into your own trading or evaluation framework.
Institutional dashboard showing Sortino ratio benchmarks across multiple perpetual futures instruments
Understanding the Sortino Ratio in Perpetual Futures
Definition
The Sortino ratio measures risk-adjusted performance by focusing solely on downside deviation:
Sortino Ratio=Rp−Rfσd\text{Sortino Ratio} = \frac{R_p - R_f}{\sigma_d}Sortino Ratio=σdRp−Rf
- RpR_pRp: Portfolio or strategy return
- RfR_fRf: Risk-free rate
- σd\sigma_dσd: Downside deviation
For perpetual futures—highly leveraged, 24⁄7 instruments—the Sortino ratio gives institutional investors an edge in assessing asymmetric risk profiles.
Why Institutional Investors Prefer Sortino Over Sharpe
- Downside Protection Focus: Avoids penalizing volatility from upside returns.
- Better Alignment With Mandates: Pension funds or insurance portfolios emphasize capital preservation.
- Granular Risk Management: Enables slicing data by time frame, asset pair, or funding cycles.
This aligns closely with why use Sortino ratio in perpetual futures analysis, since volatility can be misleading in 24⁄7 crypto markets or thin overnight sessions.
Two Core Benchmarking Methods
Method 1: Historical Sortino Benchmarks
Institutional desks often compile rolling Sortino ratios using at least three years of historical data.
Steps:
- Compute daily returns of the perpetual futures strategy.
- Isolate negative returns to calculate downside deviation.
- Compare Sortino ratio to a peer group or index benchmark.
Advantages:
- Provides long-term perspective.
- Works well for stable strategies (e.g., basis trades).
Disadvantages:
- Slow to reflect regime changes.
- Requires extensive clean data, which can be costly.
Method 2: Forward-Looking Sortino Benchmarks
Another approach uses scenario modeling and Monte Carlo simulations to estimate future downside deviation.
Steps:
- Model return distributions based on current volatility and funding rates.
- Simulate potential downside moves.
- Calculate projected Sortino ratios under stress scenarios.
Advantages:
- Adapts to rapidly changing conditions.
- Captures tail risks and liquidity crunches.
Disadvantages:
- Heavily model-dependent.
- Requires sophisticated quantitative infrastructure.
Comparison chart of historical vs. forward-looking Sortino ratio benchmarks in perpetual futures
Comparing the Two Methods
| Aspect | Historical Benchmarks | Forward-Looking Benchmarks |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirement | High (3+ years) | Moderate (market scenarios) |
| Speed of Adaptation | Low | High |
| Complexity | Low/Medium | High |
| Best For | Long-term trend strategies | Active/quant trading |
Recommendation: Combine both. Use historical benchmarks for investor reporting and forward-looking benchmarks for risk management. This hybrid approach ensures stability without sacrificing adaptability.
Implementing Sortino Ratio Benchmarks in Practice
Step-by-Step
- Data Collection: Gather minute-level returns from your perpetual futures strategy.
- Downside Isolation: Only include returns below a minimum acceptable return (MAR).
- Benchmarking: Compare to index-level Sortino ratios or internal targets.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly recalibrate your MAR to reflect new market conditions.
This mirrors how to calculate Sortino ratio for perpetual futures in a systematic way, bridging the gap between theory and daily operations.
Tools for Institutional Investors
- Proprietary risk dashboards integrating Sortino metrics.
- Specialized analytics providers offering where to find Sortino ratio calculator for perpetual futures solutions with APIs.
- Cloud-based quantitative research platforms for automated updates.
Case Study: A Quant Hedge Fund
A quant hedge fund running high-frequency market-making strategies in BTC perpetual futures used a forward-looking Sortino model to adjust inventory risk. By simulating potential downside moves, they improved their Sortino ratio from 1.2 to 2.1 within six months—without sacrificing top-line returns.
Heatmap of Sortino ratios across different perpetual futures trading strategies
Advanced Tips for Improving Sortino Ratios
- Dynamic Leverage: Scale leverage inversely with downside deviation.
- Diversification Across Pairs: Reduce concentration in single perpetual pairs.
- Funding Rate Arbitrage: Optimize entry/exit times around funding cycles to smooth returns.
- Risk Budgeting: Allocate capital to strategies based on marginal contribution to downside deviation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a good Sortino ratio for perpetual futures?
For institutional-grade strategies, a Sortino ratio above 2.0 is often considered strong. However, this varies by volatility regime and asset class.
2. How does Sortino ratio affect perpetual futures performance?
A higher Sortino ratio generally signals more efficient use of risk capital—producing returns with less downside volatility. This can translate into lower drawdowns and better investor confidence.
3. Where can I get accurate Sortino ratio data for perpetual futures?
Many institutions build in-house dashboards. Retail or smaller asset managers can use third-party providers like risk analytics platforms, or integrate APIs from exchanges and data vendors. Always ensure data quality and backfill completeness to avoid skewed results.
Conclusion: Raising the Bar with Sortino Ratio Benchmarks
As perpetual futures markets mature, institutional investors Sortino ratio benchmarks for perpetual futures are no longer optional—they’re essential. Historical benchmarks provide credibility for reporting; forward-looking benchmarks provide agility for risk management. By combining both and leveraging specialized tools, institutions can achieve superior risk-adjusted returns.
If you found this guide insightful, share it with colleagues or comment below with your experiences benchmarking Sortino ratios in perpetual futures. By exchanging best practices, we can collectively elevate institutional standards in risk-adjusted performance.
Would you like me to build a downloadable Sortino Ratio Benchmarking Checklist PDF for institutional teams? It could serve as a ready-made framework for your risk committee.