
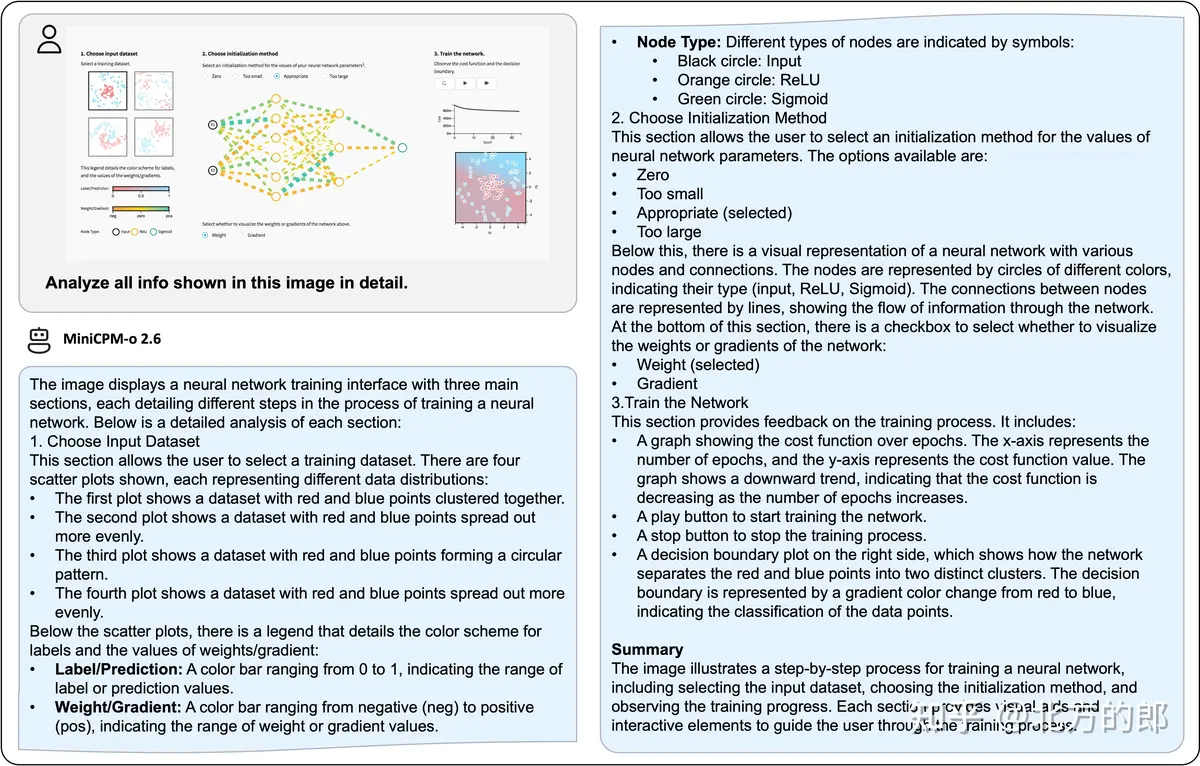
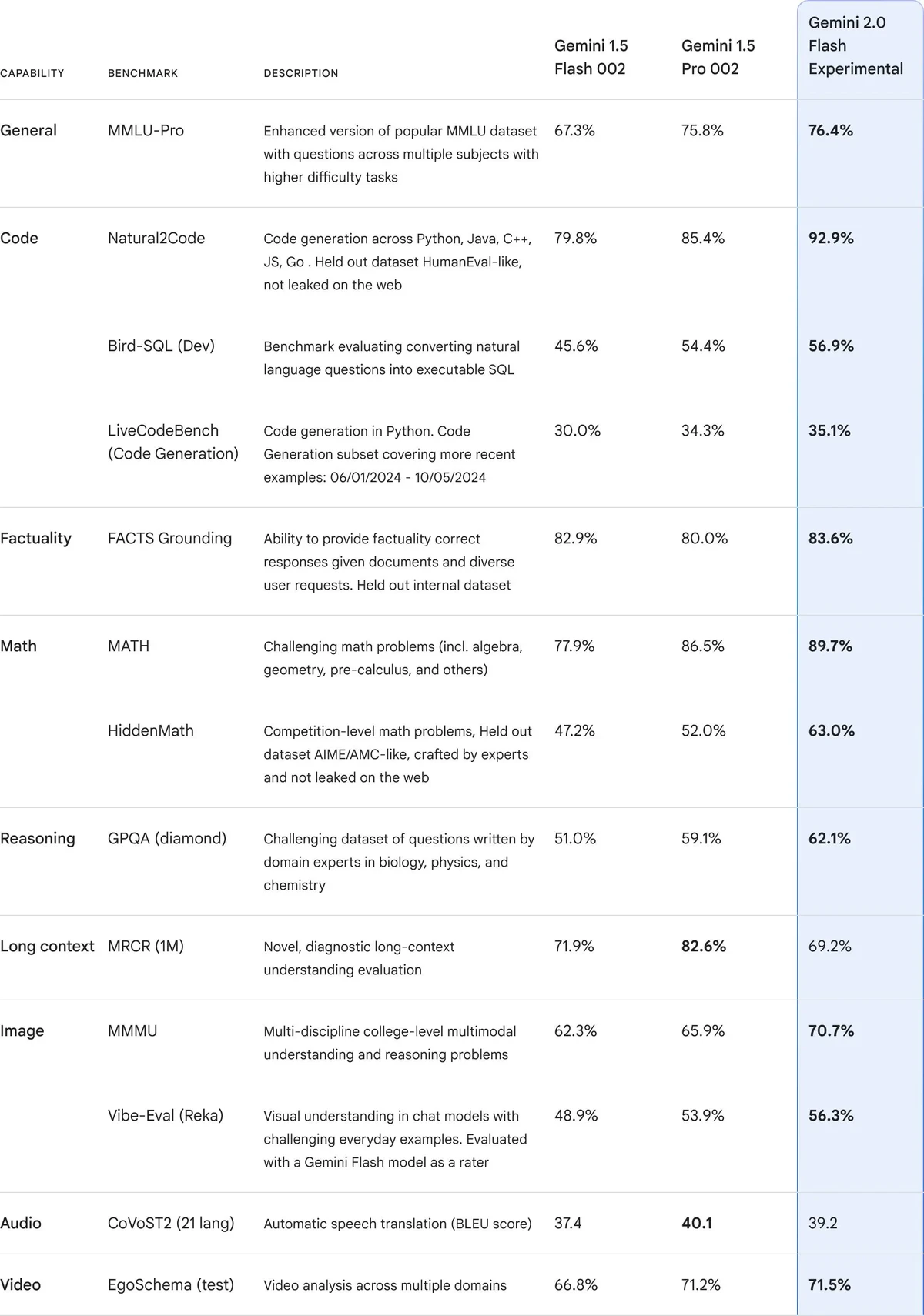
=============================================================
In the fast-moving world of derivatives and crypto trading, perpetual futures have become one of the most widely used instruments. While they offer opportunities for leverage, hedging, and arbitrage, they also expose traders to significant systematic risk—the kind of risk that cannot be diversified away. Designing effective solutions for minimizing systematic risk in perpetual futures is essential for both professional investors and retail traders seeking long-term survival in volatile markets.
This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of what systematic risk means in perpetual futures, practical solutions for reducing it, and real-world comparisons of different strategies. We’ll also explore the latest industry trends, include professional insights, and answer the most common questions traders face when managing systematic risk.
Understanding Systematic Risk in Perpetual Futures
What Is Systematic Risk?
Systematic risk refers to broad market risk that affects all assets, regardless of how well-diversified a portfolio is. In perpetual futures, this includes risks such as:
- Market-wide crashes (e.g., sudden BTC or ETH drops).
- Macro events like interest rate changes, inflation shocks, or regulatory decisions.
- Liquidity crunches where funding rates spike or positions cannot be unwound.
Unlike idiosyncratic risk (specific to one asset or project), systematic risk impacts the entire market structure.
Why It Matters in Perpetual Futures
Since perpetual futures allow traders to use leverage and hold positions indefinitely, systematic risk is magnified. Leverage amplifies both gains and losses, and in a sudden market-wide drawdown, liquidations can wipe out accounts faster than spot holdings. That’s why why systematic risk matters in perpetual futures trading is not only an academic question but a survival principle for every trader.
Types of systematic risk and their impact on perpetual futures positions
Core Solutions for Minimizing Systematic Risk
1. Hedging with Correlated Instruments
How It Works
Traders reduce systematic risk exposure by opening offsetting positions in correlated assets. For example:
- Long BTC perpetual futures, hedged with short BTC options.
- Long ETH perpetual futures, hedged with BTC-ETH correlation trades.
Advantages
- Limits downside exposure during broad market crashes.
- Provides insurance against volatility spikes.
Disadvantages
- Requires additional margin and complex position management.
- May reduce potential profit if the hedge isn’t optimized.
2. Dynamic Position Sizing Based on Volatility
How It Works
Traders use volatility-adjusted risk models to reduce position size when implied or realized volatility rises. For instance, if BTC volatility spikes to 100%, position size is automatically cut by half.
Advantages
- Directly controls exposure to market turbulence.
- Adaptable to changing environments.
Disadvantages
- May limit profits during strong directional trends.
- Requires reliable volatility forecasting models.
3. Cross-Market Diversification
How It Works
Instead of only trading BTC perpetuals, traders allocate across BTC, ETH, altcoin baskets, and even non-crypto perpetuals (like FX or commodities on certain exchanges).
Advantages
- Reduces reliance on a single market driver.
- Spreads exposure across uncorrelated assets.
Disadvantages
- Systematic risk in crypto often spills over across assets.
- Limited availability of non-crypto perpetual futures.
4. Systematic Risk Control via Stop-Loss and Circuit Breakers
How It Works
Implement automatic liquidation thresholds or circuit breakers triggered by market-wide stress conditions (e.g., if BTC falls 15% in one day).
Advantages
- Ensures survival in catastrophic market events.
- Removes emotional bias during panic conditions.
Disadvantages
- Stops can trigger at temporary liquidity wicks.
- May lock in losses prematurely.
Comparing the Strategies
| Method | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hedging | Protects against volatility | Costs margin & fees | Advanced traders, funds |
| Dynamic Position Sizing | Adapts to volatility | Limits upside | Quantitative traders |
| Cross-Market Diversification | Reduces asset-specific risk | Crypto assets often correlated | Institutions, portfolio managers |
| Circuit Breakers | Ensures survival | May close positions too early | Retail traders, beginners |
Recommendation: The most effective approach combines dynamic position sizing with hedging, giving both adaptability and downside protection.
Comparison of different systematic risk management solutions in perpetual futures
Industry Trends and Advanced Approaches
- AI-driven risk forecasting: Machine learning models predict volatility clusters and market stress.
- Cross-exchange arbitrage: Reducing exposure to systematic risk by capturing funding rate discrepancies.
- On-chain derivatives risk hedging: Using decentralized options and synthetic assets.
- Stress testing: Funds now routinely test their portfolios against extreme systematic risk events (e.g., 50% BTC drawdown in 24 hours).
These approaches are gradually being adopted by hedge funds and institutional players, but retail traders can also apply scaled-down versions.
Internal Linking for Deeper Learning
A critical part of effective risk management is understanding how to assess systematic risk in perpetual futures before taking on leverage. Additionally, knowing how systematic risk affects perpetual futures investments helps traders structure portfolios that are both profitable and resilient.
FAQ: Common Questions on Minimizing Systematic Risk in Perpetual Futures
1. Can I completely eliminate systematic risk in perpetual futures?
No. Systematic risk is inherent to the market and cannot be fully removed. However, through hedging, position sizing, and diversification, traders can minimize exposure and reduce the probability of catastrophic losses.
2. How does leverage amplify systematic risk?
Leverage multiplies both gains and losses. A 10% market drop may result in a 100% loss if a trader is using 10x leverage without risk controls. That’s why systematic risk is far more dangerous in perpetual futures compared to spot markets.
3. What tools are best for monitoring systematic risk in crypto perpetual futures?
- Volatility indices (e.g., BTC VIX equivalents).
- Funding rate trackers across exchanges.
- Correlation matrices to identify systemic contagion.
- Stress test simulations in portfolio management software.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Minimizing systematic risk in perpetual futures is not about avoiding risk altogether, but about designing intelligent solutions that keep you in the game long enough to benefit from opportunities. The combination of hedging, adaptive position sizing, and circuit breakers forms a practical foundation for traders of all levels.
Now it’s your turn:
- What strategies do you currently use to handle systematic risk?
- Do you prefer hedging with options, or adjusting position sizes dynamically?
Share your thoughts in the comments and forward this article to fellow traders who need to strengthen their systematic risk management. Together, we can make perpetual futures trading safer and smarter.
Would you like me to also draft a step-by-step “Systematic Risk Management Checklist for Perpetual Futures Traders” as a printable companion to this article?