
=============================================================================
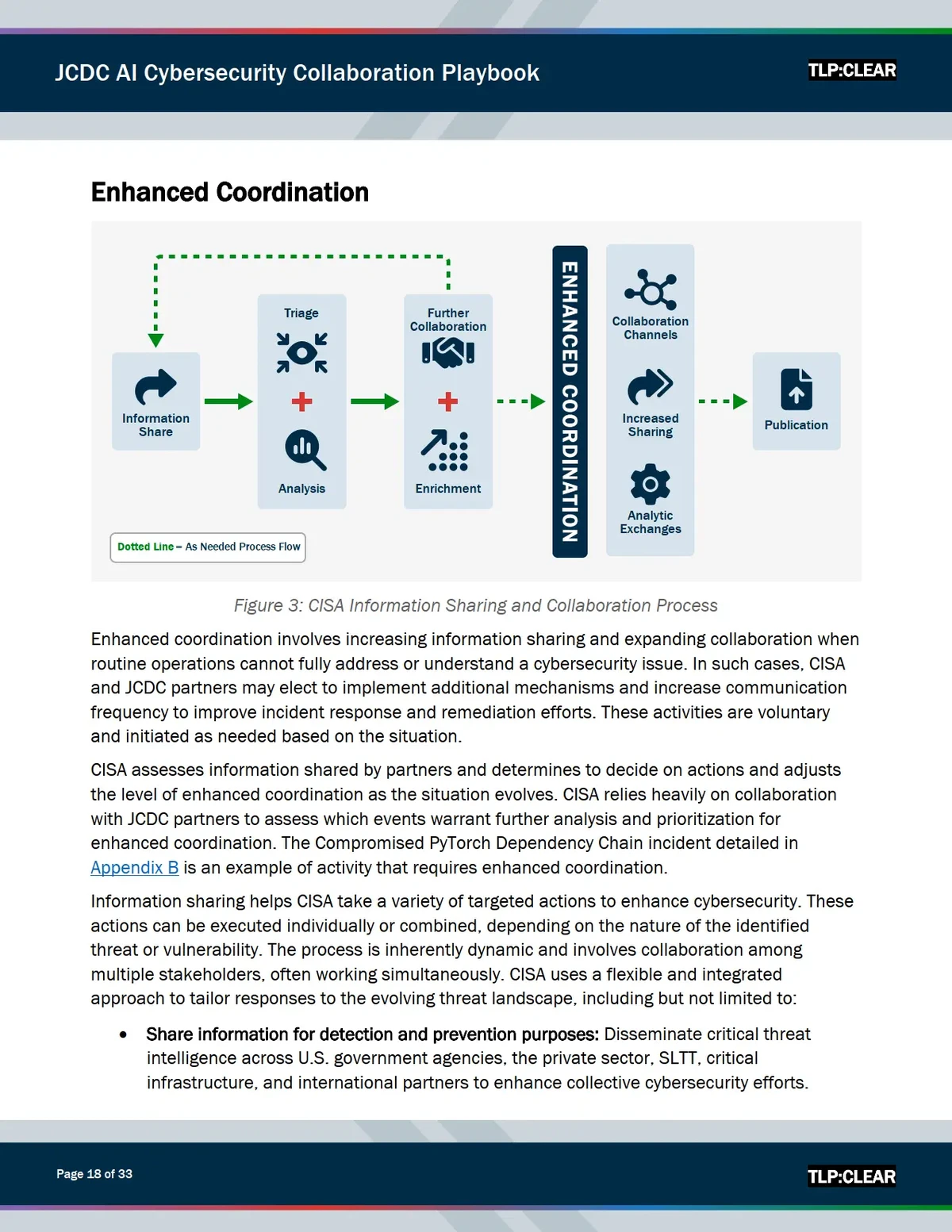
Introduction
For crypto traders, the spread—the difference between the bid and ask price—is one of the most important factors influencing profitability. While many beginners overlook it, spreads often make the difference between a winning trade and a losing one, especially in high-frequency, day trading, or leveraged trading environments.
This Crypto traders spread comparison guide is designed to help traders understand spreads in detail, compare strategies for managing them, and learn how to choose platforms or methods that minimize unnecessary costs. By combining personal trading experiences with the latest industry insights, this article will show you how to maximize profit potential while effectively mitigating risks.
What is Spread in Crypto Trading?
Definition of Spread
In crypto markets, the spread is the gap between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask). This difference is crucial because every trader pays the spread indirectly when entering or exiting a position.
- Tight Spread = small gap, usually on highly liquid pairs like BTC/USDT.
- Wide Spread = large gap, common on illiquid tokens or low-volume exchanges.
Why Spreads Matter
Spreads represent an implicit cost of trading. Even if you don’t see a commission fee, spreads can drain profitability. As such, knowing why is spread important in trading is fundamental for both retail and institutional investors.
Factors Influencing Spreads
1. Liquidity of the Asset
Major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum usually have tighter spreads due to higher trading volume. In contrast, smaller altcoins often show larger spreads.
2. Market Volatility
During high volatility events (e.g., Bitcoin halving, regulatory news), spreads widen significantly as market makers adjust risk premiums.
3. Exchange Platform Policies
Different platforms apply unique spread management systems, leading to variations in spreads. Understanding why spreads vary on different platforms is essential for traders comparing exchanges.
4. Trading Pair
Fiat-to-crypto pairs often have different spreads compared to crypto-to-crypto pairs, mainly due to fiat on-ramp complexities.
Comparing Spread Management Strategies
Strategy 1: Choosing High-Liquidity Exchanges
The simplest approach to minimize spreads is selecting platforms with deep liquidity. Exchanges like Binance, OKX, and Bybit usually provide competitive spreads on popular pairs.
Advantages:
- Tight spreads reduce trading costs.
- Higher chance of order execution at favorable prices.
- Useful for short-term and high-frequency traders.
Disadvantages:
- Liquidity may be concentrated on major pairs.
- Smaller tokens can still have high spreads despite the exchange’s size.
Strategy 2: Using Limit Orders Instead of Market Orders
Market orders fill immediately at the best available price, which may include unfavorable spreads. Limit orders, however, allow traders to define entry and exit points, avoiding unnecessary spread costs.
Advantages:
- Eliminates slippage and spread costs when orders are matched.
- Provides control over trade execution.
- Particularly effective for patient traders.
Disadvantages:
- Execution is not guaranteed if the market never reaches the limit price.
- May lead to missed opportunities in fast-moving markets.
Comparative Analysis of Strategies
When evaluating which approach works best, it often depends on trading style:
- Day traders benefit more from high-liquidity exchanges with tight spreads, since frequent trades amplify the effect of spreads.
- Swing traders may prefer limit orders, since they can afford to wait for optimal entry points without rushing into the spread.
The most efficient practice is combining both—selecting a liquid exchange while primarily executing limit orders to minimize spread costs.
Spread Costs in Perpetual Futures
Spreads are not limited to spot trading; they play a critical role in futures markets as well. Traders must understand how does spread affect perpetual futures since wider spreads can increase margin requirements and impact liquidation thresholds.
Additionally, funding rates interact with spreads in futures, further influencing profitability. Knowing where to compare spread fees is essential when evaluating platforms for perpetual contracts.
Image Example
An example of a crypto order book showing bid-ask spreads.
Personal Experience in Spread Management
From my own trading journey, I’ve noticed that spreads eat significantly into profits during high-frequency trades. Early in my career, I used to place market orders on illiquid pairs, and although I was “winning” by price movement, the hidden cost of spreads wiped out most of my gains.
Switching to limit orders and sticking to high-liquidity exchanges was the turning point. I also started monitoring real-time spread dynamics, a practice common in professional traders’ spread strategies, to ensure my trades aligned with cost-efficient conditions.
Advanced Spread Comparison Techniques
1. Arbitrage Opportunities
Spreads vary across exchanges. Arbitrage traders exploit these differences by buying low on one platform and selling high on another.
2. Spread Analysis Tools
Spreadsheet tools for spread management or API-based monitors help traders identify when spreads widen, signaling market stress or arbitrage opportunities.
3. Institutional-Grade Strategies
For institutional investors, spread analysis for institutional investors involves integrating spreads into portfolio models to account for execution costs.
FAQs: Crypto Traders Spread Comparison Guide
1. How do I calculate the spread in crypto trading?
Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price. For example, if BTC/USDT has a bid of \(26,000 and an ask of \)26,010, the spread is $10. Understanding how to calculate spread in perpetual futures helps traders assess hidden costs before executing positions.
2. Why do spreads widen during high volatility?
Market makers demand higher compensation for the risk of sudden price moves. As liquidity dries up during volatile events, spreads widen to balance supply and demand.
3. How can retail traders lower spread costs effectively?
Retail traders can reduce spread costs by:
- Trading on high-liquidity exchanges.
- Avoiding market orders during volatile periods.
- Using limit orders whenever possible.
This is a practical example of how to lower spread costs without needing advanced strategies.
Conclusion: The Best Approach for Spread Management
Spreads are an unavoidable cost in crypto trading, but with the right strategies, traders can minimize their impact. The Crypto traders spread comparison guide shows that:
- High-liquidity exchanges are essential for day traders.
- Limit orders provide flexibility and cost savings for swing traders.
- Monitoring spreads is as critical as analyzing fees, slippage, and volatility.
The best practice is combining exchange selection with smart order placement while keeping track of spread variations across different platforms.
Final Thoughts
Mastering spreads is not just for professionals—every crypto trader can benefit from spread awareness. The next time you enter a trade, ask yourself: Is the spread eating into my profits?
If this guide helped you, share it with your trading community or drop a comment below about your own experiences with spreads. The more we share, the more efficient we all become in navigating the crypto markets.
Would you like me to also create a comparison table of spreads across major exchanges (Binance, Coinbase, Bybit, OKX, Kraken) so readers can instantly see differences?