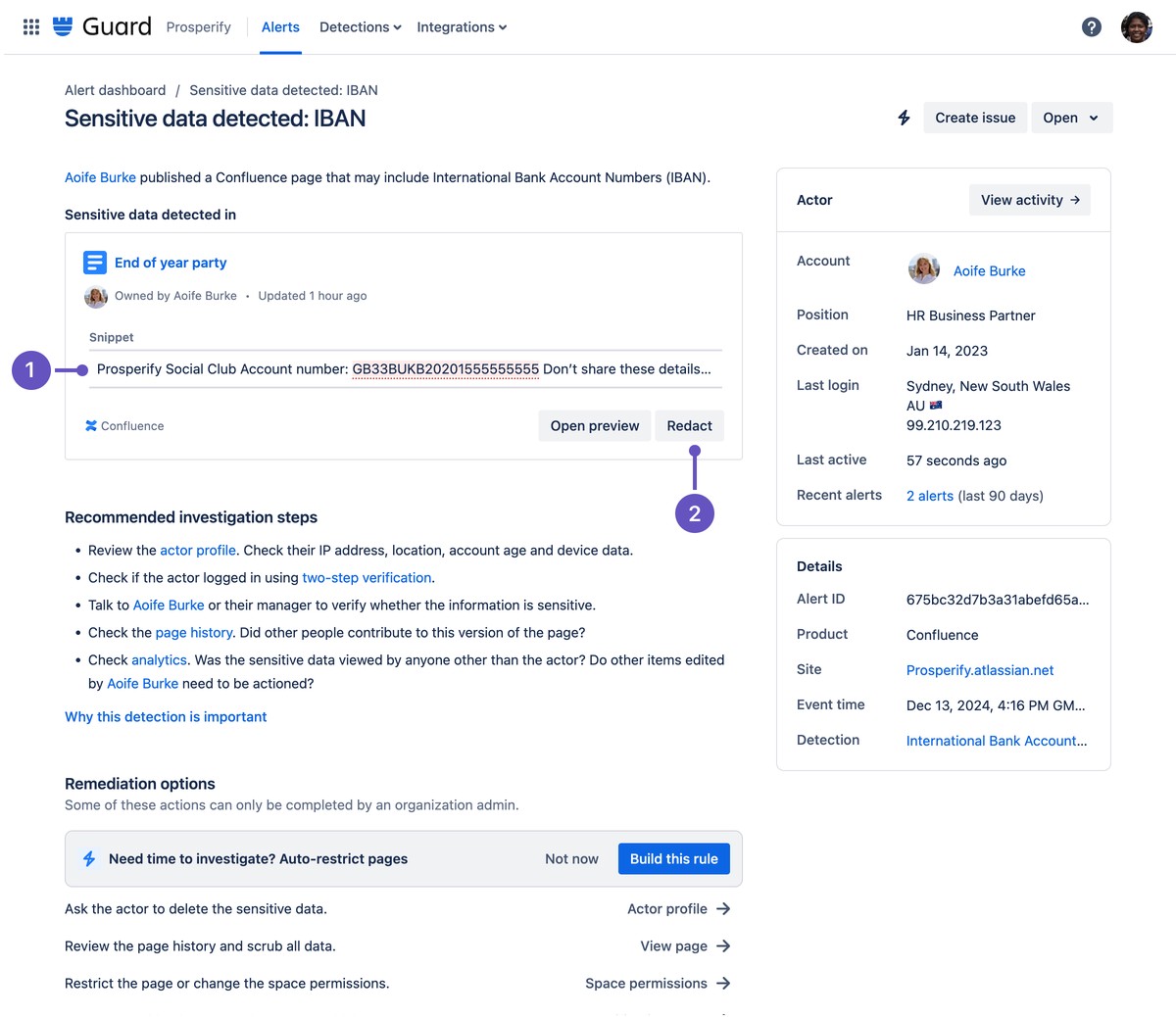

====================================================
Margin trading in perpetual markets can be highly rewarding but also extremely risky if not managed properly. Understanding how margin works and implementing effective strategies for margin management is crucial to avoid liquidation and ensure consistent profitability. This article provides expert tips and strategies to help you navigate the complexities of margin trading in perpetual markets. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, these insights will help you optimize your margin usage, mitigate risks, and enhance your trading success.
Understanding Margin in Perpetual Markets
Margin trading allows traders to control larger positions than their available capital by borrowing funds from a broker or exchange. In perpetual markets, where futures contracts have no expiration date, margin management becomes even more important due to the volatility and the risk of liquidation. Let’s break down the essential components of margin trading in these markets.
What is Margin?
Margin is essentially the collateral that a trader must deposit in order to open a leveraged position. The amount of margin determines the size of the position you can control. In perpetual markets, margin is used to secure a trader’s position, ensuring that they can meet any potential losses without exceeding the value of their account.
- Initial Margin: The minimum amount required to open a position.
- Maintenance Margin: The minimum amount you need to keep your position open. If your balance falls below this level, your position is at risk of liquidation.
- Leverage: The ratio of your position size to your margin. For example, with 10x leverage, you can control a position worth 10 times your initial margin.
Why Margin Trading in Perpetual Markets?
Margin trading allows you to amplify potential profits, but it also increases risk exposure. Perpetual contracts, unlike traditional futures, have no expiration date, meaning traders can hold positions indefinitely. However, this also means that market movements can result in extended periods of volatility, making risk management crucial.
Expert Strategies for Managing Margin
Effective margin management in perpetual markets can be achieved through a combination of solid strategies, tools, and disciplined risk management. Here are expert strategies to optimize your margin use:
1. Start with Conservative Leverage
One of the most common mistakes beginners make in margin trading is overleveraging. While it might be tempting to use high leverage to increase potential profits, the risk of liquidation also increases. Experts recommend starting with lower leverage, such as 2x or 3x, until you gain more experience.
Pros of Conservative Leverage:
- Lower risk of liquidation.
- Allows you to ride out market fluctuations without forced closing of positions.
- Lower risk of liquidation.
Cons:
- Slower potential profits, but more sustainable in the long run.
- Slower potential profits, but more sustainable in the long run.
2. Implement Dynamic Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are essential tools in managing margin effectively. These orders allow traders to automatically close a position when a certain price level is reached, protecting them from excessive losses and locking in profits.
- Stop-Loss: A limit order to sell when the market moves against your position. This helps mitigate risk by closing the position at a predetermined loss level.
- Take-Profit: A limit order to sell when the market reaches a certain profit level.
Dynamic stop-loss and take-profit levels adjust according to market conditions. For example, you can use trailing stops that follow the price as it moves in your favor, locking in profits as the market trends in your direction.
3. Monitor Margin Ratio Regularly
Your margin ratio is the percentage of margin used relative to the total value of your position. Keeping track of your margin ratio is critical for avoiding margin calls or liquidation. If the ratio becomes too high, you may need to deposit additional funds to avoid liquidation.
- Maintaining a Low Margin Ratio: Aim to keep your margin ratio lower than 50% to avoid liquidation triggers and give your positions more breathing room.
- Regular Monitoring: Set up notifications or alerts to monitor your margin ratio. Many trading platforms allow you to track your margin usage in real-time, giving you the ability to act quickly if needed.
Advanced Techniques for Margin Management
As you gain more experience in perpetual markets, you can employ advanced margin management techniques to further reduce risks and enhance profitability.
1. Hedging to Offset Risk
Hedging involves opening positions that are opposite to your primary position to reduce the overall risk exposure. For example, if you have a long position in Bitcoin, you can open a short position in the same asset to hedge against potential price declines.
Benefits of Hedging:
- Reduces the likelihood of liquidation in volatile markets.
- Can protect profits if the market moves against your original position.
- Reduces the likelihood of liquidation in volatile markets.
2. Risk-Based Position Sizing
Risk-based position sizing allows you to determine the size of your positions based on your overall risk tolerance. This technique involves calculating the percentage of your capital that you are willing to risk on each trade and adjusting the size of your positions accordingly.
- Formula for Position Sizing:
Position Size=Account Equity×Risk PercentageStop-Loss Distance\text{Position Size} = \frac{\text{Account Equity} \times \text{Risk Percentage}}{\text{Stop-Loss Distance}}Position Size=Stop-Loss DistanceAccount Equity×Risk Percentage
Benefits:
- Reduces the risk of overexposure.
- Helps preserve capital and prevent large losses.
- Reduces the risk of overexposure.
3. Using Automated Margin Management Systems
Many professional traders and institutions use automated systems for margin management. These systems continuously monitor market conditions and automatically adjust your positions, stop-loss, and take-profit levels based on predefined parameters.
Advantages:
- Real-time monitoring of margin levels.
- Instant adjustment of positions to minimize risks.
- Increased efficiency, especially in high-frequency trading scenarios.
- Real-time monitoring of margin levels.
How Margin Affects Perpetual Futures Trading
Margin plays a significant role in determining both the potential profitability and the risk exposure in perpetual futures trading. A higher margin allows you to open larger positions, but this also increases the risk of liquidation in case the market moves against you. Effective margin management strategies are essential for maximizing returns while minimizing potential losses.
Pros of Using Margin in Perpetual Markets:
- Amplifies profits on successful trades.
- Enables trading larger positions with limited capital.
- Provides flexibility for longer-term trades due to the lack of expiration.
- Amplifies profits on successful trades.
Risks of Using Margin:
- High leverage increases the risk of liquidation if the market moves against you.
- Margin calls can require immediate action, leading to forced liquidation if not managed properly.
- Trading fees and interest on borrowed capital can erode profits.
- High leverage increases the risk of liquidation if the market moves against you.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the best leverage for margin trading in perpetual markets?
The best leverage depends on your risk tolerance and trading experience. Experts recommend starting with lower leverage (2x to 3x) to minimize risk. As you gain experience, you may gradually increase your leverage, but always be mindful of the risks involved.
2. How can I avoid liquidation when using margin?
To avoid liquidation, always monitor your margin ratio closely and ensure it stays well below your liquidation threshold. Set dynamic stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and consider using hedging strategies to reduce risk.
3. What is the role of stop-loss orders in margin trading?
Stop-loss orders are critical for risk management. By automatically closing your position when the market moves against you, stop-loss orders help you protect your capital and avoid excessive losses, especially when trading on margin.
Conclusion
Effective margin management in perpetual markets requires a combination of strategy, discipline, and tools. By starting with conservative leverage, using dynamic stop-loss and take-profit orders, regularly monitoring your margin ratio, and employing advanced techniques like hedging and risk-based position sizing, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with margin trading. Automated margin management systems can further enhance your trading efficiency, allowing you to navigate the volatility of perpetual markets with greater confidence.