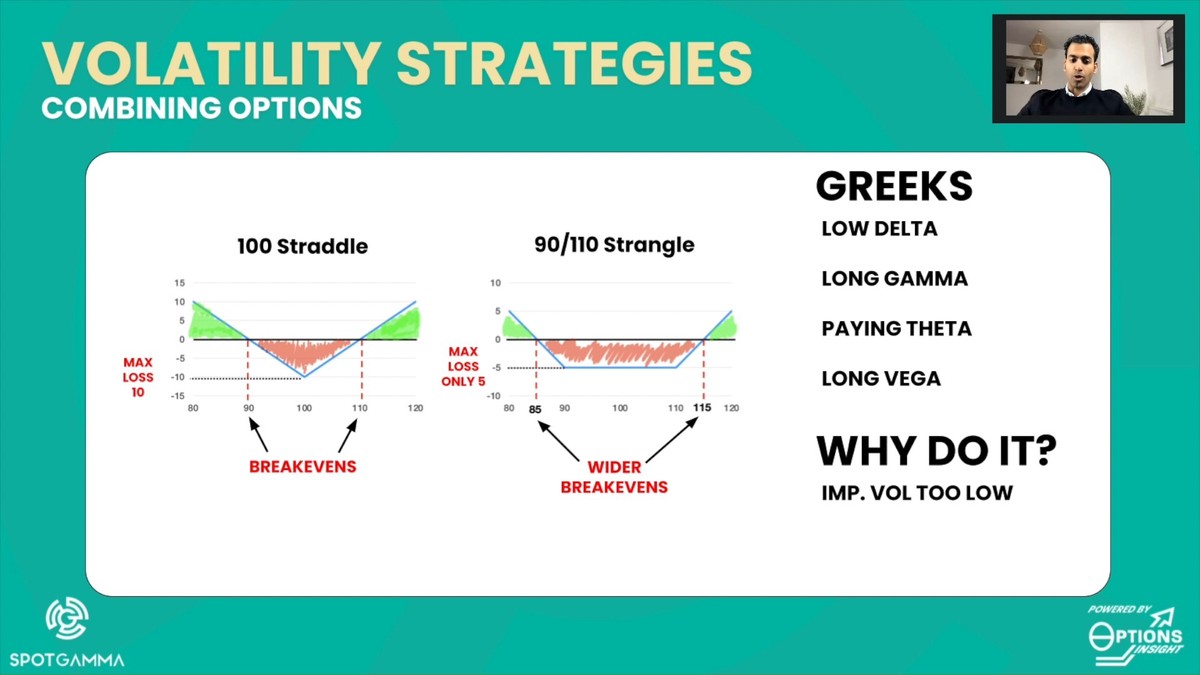
===============================================================
Understanding how trading fees differ across platforms is essential for both novice and professional traders. Trading fees can significantly impact profitability, especially for high-frequency, perpetual futures, or crypto traders. This guide explores the nuances of trading fees, compares different fee structures, and provides actionable strategies to optimize trading costs.
Understanding Trading Fees
What Are Trading Fees?
Trading fees are charges levied by exchanges or brokers for executing trades. These can vary widely depending on the platform, asset type, and trading volume. Common fee types include:
- Maker Fees: Charged when adding liquidity to the order book.
- Taker Fees: Charged when removing liquidity by executing against existing orders.
- Withdrawal Fees: Applied when transferring funds out of the platform.
- Funding Fees: Relevant for perpetual futures contracts and leveraged trades.
Why Trading Fees Matter
Even small fee differences can erode profits over time. For instance, a 0.1% fee per trade might seem negligible but can accumulate significantly for day traders or high-frequency traders executing hundreds of trades daily.
Internal Link Integration: Knowing how trading fees impact profits in futures helps traders understand why choosing the right platform is crucial.
Comparison of maker vs. taker fees across popular trading platforms.
Comparing Trading Fee Structures
1. Percentage-Based Fees
Most exchanges charge a percentage of the trade value. For example:
- Binance: 0.1% maker and taker fees by default.
- Kraken: 0.16% maker and 0.26% taker fees for standard accounts.
Pros: Transparent and easy to calculate.
Cons: Can be costly for high-volume trades.
2. Tiered Fee Structures
Some platforms use volume-based tier systems:
- Higher monthly trading volumes reduce fees.
- Encourages traders to consolidate trades on a single platform.
Example:
- Binance VIP levels: Fee reductions for 30-day trading volumes exceeding certain BTC thresholds.
3. Fixed Fees
Less common but available on certain brokers, particularly for stock or options trading. Traders pay a fixed cost per trade regardless of size.
Pros: Predictable trading costs.
Cons: May be expensive for small trades.
4. Hidden or Additional Fees
Be aware of:
- Deposit or withdrawal charges.
- Spread costs in illiquid assets.
- Margin or overnight financing fees.
Internal Link Integration: Understanding where to check hidden trading fees ensures traders avoid unexpected costs.
Visual representation of different fee structures and their implications for traders.
Strategies to Minimize Trading Fees
Strategy 1: Optimize Order Types
- Use maker orders whenever possible to earn rebates and reduce costs.
- Avoid frequent market orders unless speed is critical.
Strategy 2: Leverage Volume-Based Discounts
- Consolidate trades on a single platform to qualify for tiered fee reductions.
- Track 30-day trading volume to unlock lower maker/taker fees.
Strategy 3: Choose Low-Fee Platforms
- Platforms like Binance, Bybit, and Kraken often offer competitive fees, particularly for crypto futures.
- Always cross-check withdrawal and funding fees.
Strategy 4: Monitor Fee Promotions
- Many exchanges offer temporary fee discounts or rebates for new users or high-volume traders.
- Take advantage of these campaigns for cost-effective trading.
Illustration showing how to reduce overall trading fees using tiered discounts and maker orders.
Fee Implications for Different Trader Types
High-Frequency Traders
- Frequent trades magnify the impact of taker fees.
- Automation and fee-optimized strategies are essential to maintain profitability.
Day Traders
- Fees must be carefully calculated to ensure intraday gains exceed trading costs.
- Use tools or spreadsheets to track fee impact on each trade.
Institutional Investors
- Often negotiate custom fee agreements for large volumes.
- May have access to reduced maker/taker fees or rebates.
Case Study: Trading Fees Impact
A retail trader executing 50 trades per week with a 0.1% fee per trade over a month:
- Total trading volume: $500,000
- Total fees paid: $500
Switching to a platform with 0.05% fees saves \(250/month. Over a year, this amounts to \)3,000 in savings, illustrating the tangible impact of platform fee differences.
Advanced Considerations
1. Fee Rebates and Incentives
Some platforms provide rebates for liquidity providers or volume milestones. Maximizing these can turn fees into net gains for frequent traders.
2. Cross-Asset Fee Comparison
Compare fees not only for spot trading but also for derivatives, margin trading, and perpetual futures. Differences can be substantial.
3. Automation and Fee Tracking Tools
- Utilize API integrations to automatically calculate fees per trade.
- Alerts for tier upgrades or fee promotions can further reduce costs.
FAQ: Trading Fees Across Platforms
1. Do all platforms calculate fees the same way?
No. Some charge a percentage of the total trade value, while others have fixed fees. Perpetual futures often include funding rates or overnight costs, which are not applied to spot trades.
2. Can fees erode profits in high-frequency trading?
Yes. Frequent trades amplify fee costs. Optimizing order types, using low-fee exchanges, and leveraging rebates are essential strategies to maintain profitability.
3. How do I find the lowest trading fees?
Compare platforms using online fee comparison tools, review hidden fees, and consider tiered structures for volume-based discounts. Where to find the lowest trading fees guides traders in selecting cost-effective exchanges.
Conclusion
Trading fees vary significantly across platforms and directly impact profitability. By understanding fee structures, leveraging tiered discounts, using maker orders, and monitoring hidden costs, traders can optimize their strategies. Both beginners and professional traders benefit from proactive fee management, ensuring that trading profits are maximized while costs are minimized.
Engage & Share: Share your experiences with trading fees on social media or trading forums to help other traders navigate platform differences effectively.
Workflow illustrating fee comparison, tier optimization, and strategy adjustments to minimize trading costs.
This guide provides actionable insights on how trading fees differ across platforms, helping traders make informed decisions and enhance profitability.