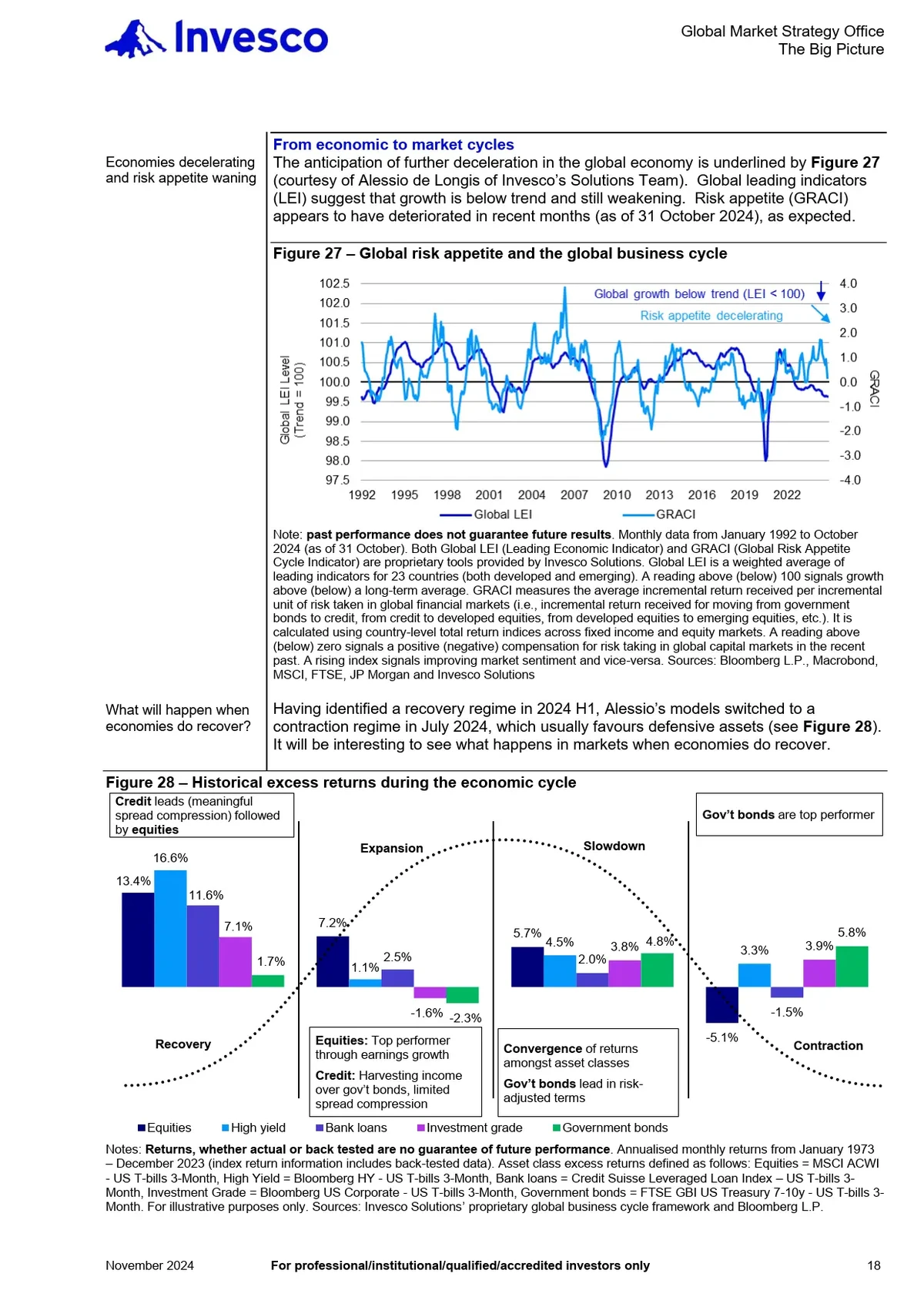
============================================
Perpetual futures trading is one of the most popular methods for speculating on price movements of assets, especially in the cryptocurrency and traditional financial markets. However, understanding how margin works in these markets is critical for success. Margin is a powerful tool that allows traders to amplify their positions, but it also carries significant risks. In this guide, we will explore how margin affects perpetual futures trading, the different types of margin used, strategies for managing margin efficiently, and the key risks involved.
What is Margin in Perpetual Futures Trading?
In the context of perpetual futures trading, margin refers to the collateral that a trader must deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. Margin allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. However, the use of margin also magnifies both potential profits and losses, making it crucial for traders to understand the margin system fully.
Types of Margin in Perpetual Futures
There are several types of margin used in perpetual futures markets, each serving a specific purpose:
- Initial Margin: This is the minimum amount of collateral required to open a position. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the total position size and is set by the exchange or platform offering the futures contract.
- Maintenance Margin: This is the minimum level of equity that must be maintained in the trading account to keep the position open. If your equity falls below this level, you may receive a margin call, and your position could be liquidated.
- Variation Margin: This margin reflects the daily changes in the market value of the position. If your position is making a profit, the variation margin increases, while if the position is losing, the margin decreases.
- Margin Call: If the account equity falls below the maintenance margin, the trader will receive a margin call from the exchange. This means additional funds must be deposited to maintain the position, or the position may be liquidated to cover the loss.
How Margin Affects Leverage in Perpetual Futures
Margin directly influences leverage, which is the ability to control a larger position with a smaller capital investment. Leverage amplifies both the potential for profit and the risk of loss.
Leverage and Margin Relationship
- Leverage is the ratio of the total value of the position to the margin required to open it. For example, if a trader uses \(1,000 in margin to control a \)10,000 position, the leverage is 10:1.
- Higher leverage means higher exposure to market fluctuations. While this increases the potential for higher returns, it also increases the likelihood of liquidation if the market moves against the position.
Example:
If you have \(1,000 in your account and you use 10x leverage, you can open a position worth \)10,000. If the asset moves by just 10% in your favor, you’ll double your initial investment. However, a 10% move against you could wipe out your entire margin, triggering a margin call or liquidation.
Impact of High Leverage on Risk
While high leverage offers the potential for high returns, it also increases the risk of losing your initial capital quickly if the market moves against you. As a result, managing margin effectively is critical for long-term success in perpetual futures trading.
Strategies for Managing Margin in Perpetual Futures Trading
Effectively managing margin is one of the most important aspects of successful perpetual futures trading. Here are some strategies to help you manage your margin efficiently and mitigate risks.
1. Start with Low Leverage
If you’re new to perpetual futures or leveraging positions, start with low leverage to understand the risks better. Using lower leverage reduces the chances of a margin call and helps you learn how to manage your trades.
Advantages of Low Leverage:
- Lower risk of liquidation: You are less likely to be forced out of a position if the market moves against you.
- Better risk control: You can experiment with different strategies without risking a large portion of your capital.
Disadvantages:
- Lower profit potential: While your risk is lower, so is your potential for gains. You need to manage risk carefully to balance the two.
2. Use Stop-Loss Orders to Manage Margin Risk
Stop-loss orders are one of the most effective ways to manage margin risk. A stop-loss order automatically closes your position if the price moves against you by a certain amount, helping you minimize losses.
Benefits of Stop-Loss Orders:
- Automated risk management: You don’t have to monitor your positions constantly, as stop-loss orders can automatically close positions when predefined levels are reached.
- Protection from large losses: Stop-loss orders prevent your losses from exceeding the margin amount you’re willing to risk.
3. Monitor Margin Levels Regularly
Keeping an eye on your margin levels is essential. Most trading platforms offer real-time margin tracking, which allows traders to assess whether they are at risk of falling below the maintenance margin.
Tools to Track Margin:
- Margin calculators: Some platforms offer built-in margin calculators that give you real-time feedback on your position’s margin status.
- Alerts: Set up margin level alerts to notify you when you’re nearing a margin call.
Key Risks of Margin in Perpetual Futures Trading
While margin can be a powerful tool for amplifying returns, it also comes with significant risks. Understanding these risks is critical to trading successfully with leverage.
1. Risk of Liquidation
One of the most significant risks when using margin is the potential for liquidation. If your margin falls below the required maintenance level, your position may be automatically liquidated to cover the losses. This can lead to the loss of your entire investment.
2. Amplified Losses
Leverage amplifies both profits and losses. If the market moves against your position, your losses can quickly exceed your initial margin, leading to a margin call or forced liquidation. In extreme cases, traders can lose more than their initial investment if not careful.
3. Market Volatility
The volatility of perpetual futures markets, especially in crypto assets, can lead to rapid price changes. This unpredictability increases the risks associated with margin trading. Traders must be prepared for sudden price swings and adjust their positions accordingly.
FAQ: Margin and Perpetual Futures Trading
1. How do I calculate margin for perpetual futures?
To calculate the margin required for a perpetual futures position, you can use the formula:
Margin=Position SizeLeverage\text{Margin} = \frac{\text{Position Size}}{\text{Leverage}}Margin=LeveragePosition Size
For example, if you want to control a \(10,000 position with 10x leverage, your margin requirement will be \)1,000.
2. Why is margin important in perpetual futures?
Margin is crucial in perpetual futures because it allows traders to control larger positions with smaller capital. Without margin, traders would need a significantly higher capital investment to take similar positions, reducing potential returns and limiting market participation.
3. How can I avoid margin calls in perpetual futures trading?
To avoid margin calls, maintain a margin buffer, use appropriate leverage, and set stop-loss orders. Regularly monitor your margin levels and market conditions to ensure you don’t overexpose your capital to unnecessary risk.
Conclusion
Margin plays a vital role in perpetual futures trading, enabling traders to leverage their positions for higher returns. However, it also introduces significant risks that need to be carefully managed. By understanding how margin works, adopting risk management strategies, and using the right tools, you can effectively navigate the complexities of leveraged trading.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, always remember that the key to success in perpetual futures trading is managing margin wisely. Always assess your risk tolerance, start with low leverage, and use margin responsibly to protect your capital.
Social Share Prompt
Was this article helpful in understanding how margin impacts perpetual futures trading? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and feel free to share this guide with others!