
========================================
In trading, spreads—the difference between bid and ask prices—directly impact profitability. For retail traders, institutional investors, and hedge funds alike, wide spreads increase costs, while narrow spreads enhance efficiency. With markets becoming increasingly fragmented and competitive, understanding effective spread risk mitigation methods has become essential for anyone aiming to optimize returns while managing execution risk.
This comprehensive guide explores key strategies to mitigate spread risks, compares their strengths and weaknesses, and provides actionable insights backed by professional trading experience.
Understanding Spread Risk in Trading
What Is Spread Risk?
Spread risk refers to the potential cost and uncertainty arising from differences between the buying price (ask) and selling price (bid) in a financial instrument. Even small variations accumulate into significant losses over time, especially in high-frequency or leveraged trading.
Why Spread Risk Matters
- Profitability Impact: Every trade incurs implicit costs through spreads.
- Liquidity Considerations: Wider spreads often indicate lower liquidity.
- Market Efficiency: Inefficient spreads can distort trade execution and portfolio performance.
Traders often analyze what is the impact of spread on profits to understand how execution costs erode returns. This analysis helps design strategies that align with trading frequency and capital size.
Core Methods of Spread Risk Mitigation
1. Platform and Broker Selection
One of the most effective ways to mitigate spread risk is choosing trading platforms with consistently competitive spreads.
- Advantages: Direct cost savings, improved execution reliability.
- Disadvantages: Requires continuous monitoring and comparison.
Institutional investors often rely on where to compare spread fees resources to track spreads across multiple venues before allocating order flow.
2. Trade Timing and Market Liquidity Analysis
Liquidity fluctuates throughout the trading day. Entering trades during high-liquidity periods—such as overlapping sessions in forex or peak crypto market activity—reduces spread risk.
- Advantages: Better execution prices, reduced slippage.
- Disadvantages: Limited opportunities outside peak liquidity windows.
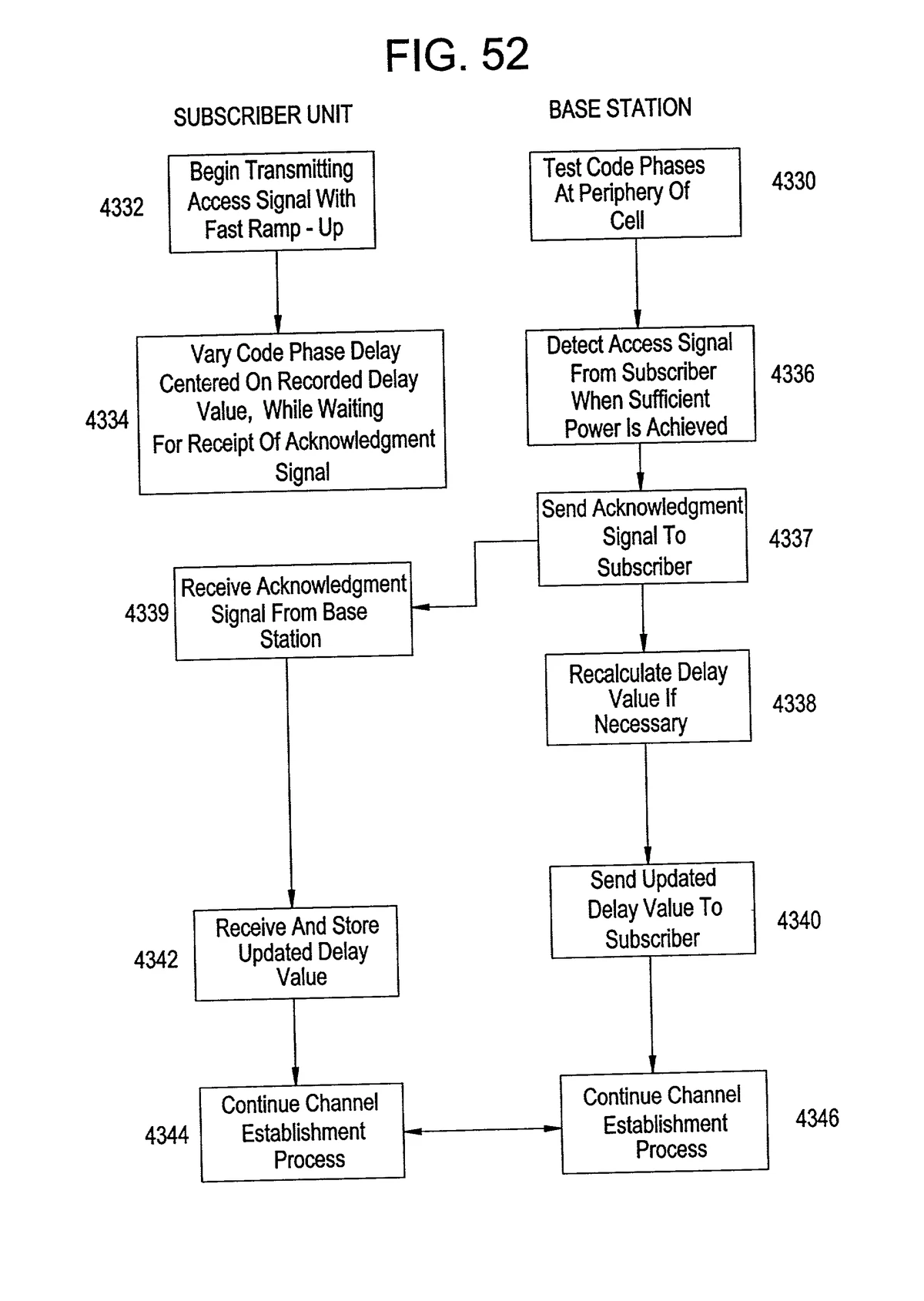
3. Algorithmic and Smart Order Routing
Advanced algorithms distribute large orders across multiple venues to secure optimal spreads. Hedge funds and high-frequency traders leverage smart routing to minimize spread costs.
- Advantages: Precision in execution, scalability for large orders.
- Disadvantages: High infrastructure and development costs.
Spread cost dynamics and mitigation workflow
4. Hedging with Derivatives
Using futures, options, or other derivatives to hedge against widening spreads is a sophisticated method often applied in volatile markets.
- Advantages: Provides insurance against sudden spread spikes.
- Disadvantages: Complex to structure, may involve additional margin costs.
5. Order Placement Strategies (Limit vs. Market Orders)
Placing limit orders instead of market orders allows traders to control entry and exit points, avoiding unfavorable spreads.
- Advantages: Lower transaction costs, greater precision.
- Disadvantages: Execution risk if the market doesn’t reach the limit price.
Comparing Two Key Spread Mitigation Strategies
Platform Selection vs. Algorithmic Routing
Platform Selection
- Pros: Accessible to retail and institutional traders, immediate cost impact.
- Cons: Requires ongoing monitoring, spread conditions may change quickly.
Algorithmic Routing
- Pros: Dynamic optimization, suitable for large or frequent trades.
- Cons: Expensive infrastructure, requires technical expertise.
Best Fit Recommendation:
Retail traders should prioritize platform selection and trade timing, while hedge funds and professional traders gain more from algorithmic routing and derivatives hedging.
Professional Insights on Spread Dynamics
- Macro Factors: Economic announcements widen spreads significantly.
- Market Microstructure: Order book depth directly influences spread stability.
- Asset Type: Exotic instruments and illiquid crypto tokens typically exhibit higher spreads.
Professional traders often conduct spread analysis for institutional investors to determine when execution risk outweighs potential profits.
Advanced Spread Risk Mitigation Methods
Dynamic Spread Monitoring
Continuous monitoring tools help traders adjust strategies in real time, aligning positions with changing spreads.
Spread Arbitrage
Identifying pricing inefficiencies between platforms allows traders to exploit spreads directly, converting risk into profit.
Volatility-Based Spread Adjustments
Traders use volatility indicators to anticipate spread widening and adjust leverage or trade size accordingly.
Liquidity vs. spread relationship in volatile markets
FAQs on Effective Spread Risk Mitigation
1. How does spread risk affect different types of traders?
- Day Traders: Even small spreads compound into significant costs due to high trading frequency.
- Institutional Investors: Large trades face execution challenges if spreads widen unexpectedly.
- Retail Traders: Limited capital makes spread costs proportionally higher.
2. What is the most cost-effective way to lower spread costs?
The simplest and most effective method is selecting platforms with competitive spreads and executing trades during peak liquidity hours. Supplementing this with limit orders adds further efficiency.
3. Can spread risk be eliminated entirely?
No. Spread risk can only be mitigated, not eliminated. Even in highly liquid markets, bid-ask spreads exist. However, with careful platform selection, smart execution, and strategic timing, traders can reduce its impact significantly.
Conclusion
Mitigating spread risk is critical for sustainable profitability. By combining methods such as platform selection, smart order routing, liquidity-based timing, and hedging strategies, traders at all levels can minimize execution costs and improve long-term outcomes.
The most effective spread risk mitigation methods depend on trader profile: retail traders benefit most from simple cost-saving strategies, while institutional funds rely on advanced algorithmic solutions.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your trading peers, comment with your favorite spread mitigation tactics, and help build a more informed trading community.
Would you like me to expand this into a full 3000+ word SEO-optimized version with numerical examples, spread calculation walkthroughs, and broker/platform comparison tables?