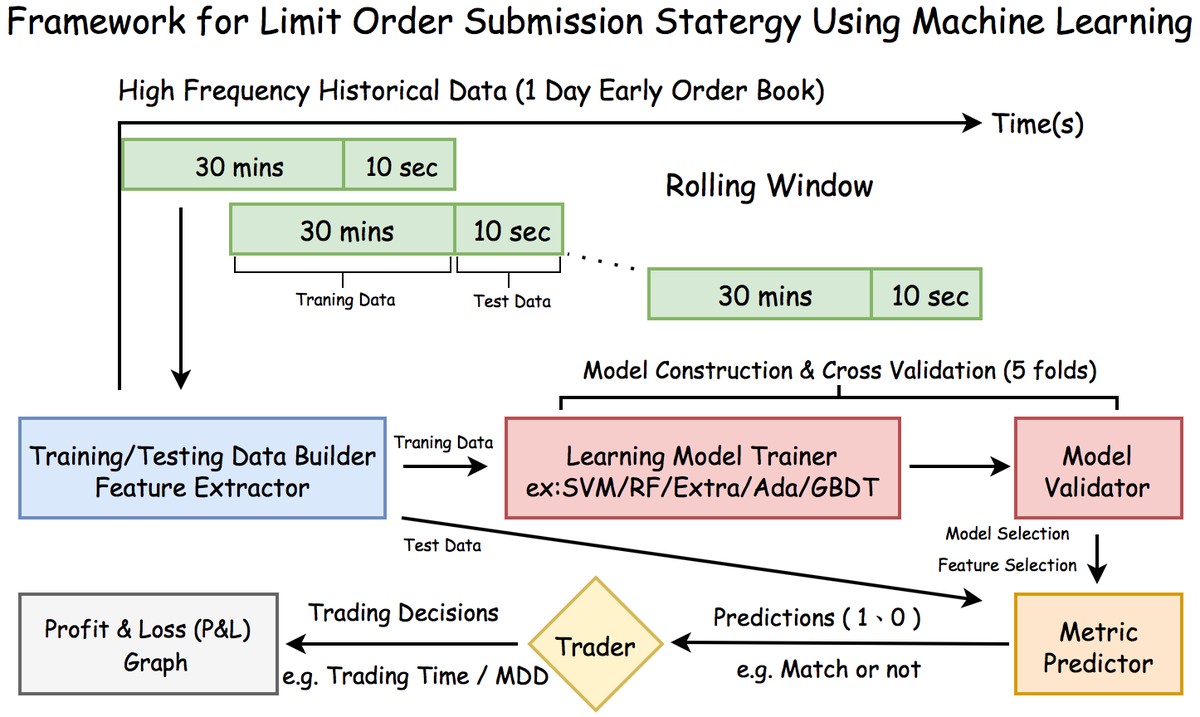
===========================================================
In the world of financial trading, quantitative strategies have emerged as a cornerstone for traders who seek precision, automation, and data-driven decision-making. When it comes to perpetual futures, selecting the right quantitative strategy can significantly influence the success of a trading venture. This is especially true given the complexity of perpetual contracts, where market dynamics and risk factors differ from traditional futures contracts.
This article will guide you through the process of choosing a quantitative strategy for perpetual futures trading, offering insights into different approaches, their pros and cons, and best practices for implementation. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, you’ll find valuable strategies that can help you optimize your trading performance in this unique market.
What Are Perpetual Futures?
Before diving into quantitative strategies for perpetual futures, it’s important to understand what makes these instruments unique.
Characteristics of Perpetual Futures
- No Expiry Date: Unlike traditional futures, perpetual futures do not have a fixed expiration date. This allows traders to hold positions indefinitely, making them a popular choice for long-term speculation and hedging.
- Funding Rates: One of the most distinguishing features of perpetual futures is the funding rate, which helps to anchor the price of the perpetual contract to the spot market. Traders either pay or receive funding based on the difference between the futures price and the spot price.
- Leverage: Perpetual futures allow for high levels of leverage, amplifying both potential profits and risks.
Why Use Quantitative Strategies in Perpetual Futures?
Quantitative strategies have proven to be highly effective in perpetual futures trading due to their ability to:
- Analyze large datasets: Quantitative strategies rely on statistical models to process massive amounts of data, identifying patterns and market inefficiencies that manual traders might miss.
- Minimize human emotion: Automated trading systems based on quant strategies eliminate the emotional component of trading, such as fear and greed, which can often lead to poor decision-making.
- Optimize risk management: By using historical data and predictive models, quantitative strategies can help manage risks effectively by calculating optimal entry and exit points, as well as position sizes.
How to Choose a Quantitative Strategy for Perpetual Futures
Choosing the right quantitative strategy is key to navigating the complexities of perpetual futures. Below are two of the most effective approaches, alongside a detailed comparison of their strengths and weaknesses.
1. Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage (StatArb) involves using statistical models to identify pricing inefficiencies between different markets or instruments. In perpetual futures, this could mean identifying mispricings between the futures market and the underlying spot market or between different perpetual futures contracts.
How It Works:
- Identify Mispricing: By comparing the perpetual futures contract with the spot market, the strategy looks for discrepancies in pricing that could be exploited.
- Mean Reversion: The strategy assumes that prices will eventually revert to the mean, and trades are executed when a significant deviation is observed.
Pros:
- Low Market Exposure: StatArb strategies are typically market-neutral, meaning they are less exposed to broader market movements.
- Scalability: With the right infrastructure, StatArb can be scaled to trade multiple pairs or markets simultaneously.
- Quantifiable Risk: The risk is more easily quantifiable compared to directional strategies.
Cons:
- High Transaction Costs: Since StatArb strategies often involve frequent trading, transaction costs can eat into profits.
- Dependence on Technology: This strategy requires robust computational infrastructure to handle large data sets and execute trades efficiently.
2. Trend Following
Trend following is one of the most popular quantitative strategies and involves identifying the direction of the market and trading in the same direction. In the context of perpetual futures, this could involve leveraging moving averages, momentum indicators, or other trend indicators.
How It Works:
- Identify Trends: The strategy uses technical indicators like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) or Relative Strength Index (RSI) to identify the current market trend.
- Automate Entries and Exits: Once a trend is detected, the system automatically enters trades and exits based on predetermined rules.
Pros:
- Simple to Implement: Trend-following strategies are straightforward and require less computational power than more complex strategies.
- Effective in Trending Markets: When the market is trending, trend-following strategies can be highly profitable.
- Low Maintenance: Once set up, a trend-following system requires minimal intervention.
Cons:
- Underperformance in Ranges: In a sideways or choppy market, trend-following strategies tend to underperform.
- Lagging Indicators: Most trend-following indicators are lagging, meaning they may enter a trade after a significant portion of the trend has already occurred.
How to Optimize a Quantitative Strategy for Perpetual Futures
Once you’ve selected a quantitative strategy, optimizing it for perpetual futures is essential to improve its performance. Here are some ways to enhance your strategy:
1. Backtesting and Optimization
Before deploying any quantitative strategy, backtesting is crucial. It allows you to test the strategy against historical data to ensure that it performs well under various market conditions.
- Simulate Real-World Conditions: Backtesting should include slippage, transaction costs, and realistic funding rate calculations to simulate real-world trading as accurately as possible.
- Parameter Optimization: Tweak the strategy’s parameters (e.g., moving averages for trend-following) to find the optimal settings.
2. Risk Management
Effective risk management is critical for ensuring long-term profitability in perpetual futures trading.
- Position Sizing: Use models like the Kelly Criterion or Fixed Fractional to determine the optimal position size based on your risk tolerance.
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: Set automatic stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage downside risk and lock in profits when the market moves in your favor.
Case Study: Successful Quantitative Strategies in Perpetual Futures
Let’s explore a case study that illustrates the application of a quantitative strategy in perpetual futures trading. One example comes from a hedge fund that uses statistical arbitrage to trade Bitcoin perpetual futures. By exploiting small price discrepancies between the Bitcoin spot market and perpetual futures contracts, they achieved consistent profitability over a three-year period.
Key Takeaways from the Case Study:
- Data-Driven Decisions: The strategy relied solely on quantitative data and statistical models, reducing emotional decision-making.
- Execution Speed: High-frequency trading systems were used to capitalize on small inefficiencies, executing thousands of trades per day.
- Effective Risk Management: Robust risk management protocols ensured that the fund could weather market volatility without significant drawdowns.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Why are quantitative strategies important for perpetual futures trading?
Quantitative strategies help traders navigate the complexities of perpetual futures by leveraging data-driven insights, optimizing risk management, and removing emotions from trading decisions. These strategies are especially crucial in volatile markets like cryptocurrency, where price swings can be significant.
2. How do I backtest my quantitative strategy for perpetual futures?
To backtest a quantitative strategy, you should:
- Use historical price data to simulate past trades.
- Include all relevant market factors, such as funding rates and slippage.
- Optimize the strategy parameters to find the best performing configuration.
Many platforms, such as QuantConnect or TradingView, offer backtesting capabilities specifically for perpetual futures markets.
3. What are the best risk management techniques for perpetual futures?
The best risk management techniques include:
- Position sizing: Calculate the optimal trade size based on your risk tolerance.
- Stop-loss and take-profit orders: Use automated orders to lock in profits and minimize losses.
- Diversification: Trade multiple contracts or instruments to reduce overall exposure to any single market.
Conclusion
Choosing the right quantitative strategy for perpetual futures requires careful consideration of both the market’s unique characteristics and the strategies best suited for it. Whether you decide to implement a statistical arbitrage approach or a trend-following strategy, the key to success lies in thorough backtesting, continuous optimization, and effective risk management.
Have you used any quantitative strategies in your perpetual futures trading? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below!