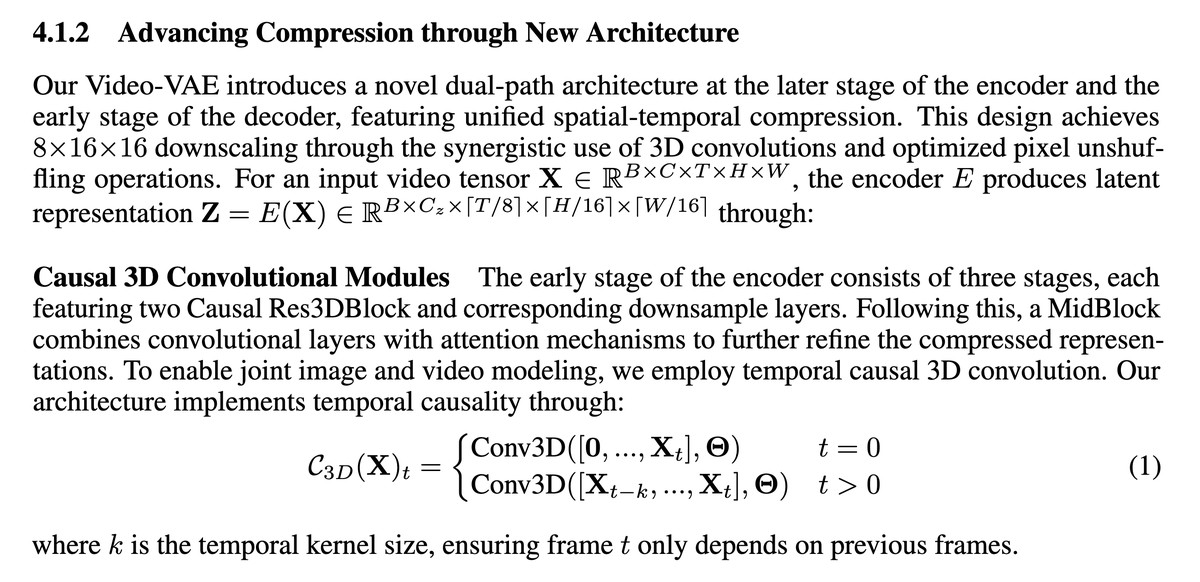

Fee Tier Audit Checklist for Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures trading has become increasingly popular due to its flexibility and potential for high returns. However, traders need to be vigilant about the fees associated with their trades. One of the most critical factors that can influence trading costs is the fee tier system provided by exchanges. This article offers an in-depth analysis of how to audit fee tiers for perpetual futures, including best practices, strategies, and a checklist for traders to optimize their fees.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Fee Tiers in Perpetual Futures
- How Fee Tiers Affect Perpetual Futures Profitability
- Key Considerations When Choosing a Fee Tier
- Fee Tier Audit Checklist for Perpetual Futures
- How to Calculate Fee Tier in Perpetual Futures
- Strategies for Optimizing Fee Tiers in Perpetual Futures
- FAQ
- Understanding Fee Tiers in Perpetual Futures
———————————————–
A fee tier system is a pricing model that exchanges use to determine the fees charged to traders based on their trading volume, account type, or other specific criteria. In perpetual futures trading, these fees are typically categorized into two types:
- Maker Fees: Fees paid by traders who add liquidity to the market (i.e., placing limit orders).
- Taker Fees: Fees paid by traders who remove liquidity from the market (i.e., executing market orders).
Exchanges often offer different fee tiers based on the trader’s activity level. Higher trading volumes can lead to lower fees, creating an incentive for frequent traders. Understanding how these fee tiers are structured is essential for reducing trading costs and maximizing profitability.
- How Fee Tiers Affect Perpetual Futures Profitability
——————————————————-
The fee tier system significantly impacts a trader’s profitability in perpetual futures. Small differences in fees may seem insignificant at first glance, but over time, they can add up. Here’s how:
- High Trading Volumes: Traders who place numerous trades within a given period can often access lower fee tiers. These reduced fees can result in substantial savings for high-frequency traders, such as day traders or algorithmic traders.
- Fee Impact on Strategy: For traders using strategies that involve frequent position adjustments, high fees can eat into profits. Lowering fees by selecting the right tier or platform can increase the effectiveness of a strategy.
- Fee Tier Optimization: Understanding how fee tiers impact profitability allows traders to select the best exchange and optimize their trading strategies. Traders must ensure that the fee structure aligns with their trading volume and strategy to maximize returns.
- Key Considerations When Choosing a Fee Tier
———————————————-
When auditing and choosing the best fee tier, traders need to consider the following:
- Trading Volume: Higher trading volumes often lead to lower fees. If you are a high-volume trader, opting for a platform that rewards frequent trading with discounts is a good choice.
- Fee Structure Transparency: Some exchanges have complex fee structures. It’s essential to review the fee schedule carefully to understand how fees are calculated.
- Platform Incentives: Certain exchanges offer incentives or rebates that reduce effective trading fees for traders who meet specific conditions, such as holding platform tokens or staking.
- Liquidity and Slippage: While lower fees are attractive, traders must also consider the liquidity of the market. Low fees on a less liquid platform could result in higher slippage, negating the cost savings.
- Fee Tier Audit Checklist for Perpetual Futures
————————————————-
To ensure that you are optimizing your trading fees, follow this comprehensive fee tier audit checklist:
Step 1: Review the Fee Structure
- Understand the exchange’s maker and taker fees.
- Check the fee schedule to identify the different tiers based on trading volume or account type.
- Look for any hidden fees or extra charges that could apply under certain conditions.
Step 2: Evaluate Trading Volume Requirements
- Determine the minimum trading volume required to reach a lower fee tier.
- Consider if your current trading volume qualifies for a discount or if you need to adjust your strategy to meet higher volumes.
Step 3: Compare Platforms
- Compare the fee structures of different platforms to find which offers the best value based on your trading behavior.
- Consider the liquidity and market depth on each platform. Lower fees are not valuable if liquidity is poor.
Step 4: Analyze Fee Discounts and Rebates
- Check if the exchange offers any rebates or incentives for frequent traders.
- Explore the possibility of using exchange-specific tokens or staking to access lower fees.
Step 5: Monitor Fee Changes
- Keep track of any updates to the fee structure, especially if you are a frequent trader.
- Some exchanges periodically adjust their fee tiers based on market conditions or changes in their business model.
Step 6: Test Real-World Application
- Simulate trades on different fee tiers to see how fees impact your overall profitability.
- Use backtesting tools or paper trading to analyze fee impacts in a controlled environment before committing real funds.
- How to Calculate Fee Tier in Perpetual Futures
————————————————-
To calculate your fee tier, you need to understand how exchanges categorize traders based on their trading volume. Here’s a simple process for determining your fee tier:
- Track Your Trading Volume: Monitor the total value of your trades over a given period (usually 30 days). Different exchanges have varying thresholds for each tier.
- Check the Fee Schedule: Most exchanges publish their fee schedules, including volume-based discounts. Find your volume range and identify the applicable fee tier.
- Calculate Maker vs. Taker Fees: Depending on whether you are adding or removing liquidity, calculate both the maker and taker fees.
- Evaluate the Net Impact: Consider how the fees will impact your overall profitability, especially if you are an active trader.
- Strategies for Optimizing Fee Tiers in Perpetual Futures
———————————————————–
1. Volume-Based Strategies
If you are a frequent trader, target exchanges that offer lower fees for higher trading volumes. This could involve increasing the size or frequency of your trades to qualify for discounts.
- Advantages: Lower fees can reduce trading costs and increase profits over time.
- Disadvantages: Increasing trading volume may expose you to more market risk, and it requires disciplined risk management.
2. Token Staking or Rebates
Some exchanges allow traders to stake their platform-specific tokens to unlock reduced fees or even earn fee rebates.
- Advantages: This can be a cost-effective way to reduce fees without changing your trading volume.
- Disadvantages: This method requires holding a significant amount of the exchange’s native token, which introduces additional exposure to market fluctuations.
- FAQ
——
1. What is the best way to reduce fees in perpetual futures trading?
The best way to reduce fees is to increase your trading volume to qualify for lower fee tiers, use token staking for fee rebates, or choose platforms that offer low fees for frequent traders.
2. How do fee tiers affect profitability in perpetual futures?
Fee tiers directly impact profitability by either lowering or increasing the cost of each trade. For high-frequency traders, even small differences in fees can significantly affect returns.
3. Are there any hidden fees in perpetual futures trading?
Yes, exchanges often have hidden fees such as withdrawal fees, funding fees, or fees for certain types of orders. It is essential to review the full fee schedule to avoid surprises.
In conclusion, understanding and auditing your fee tiers in perpetual futures is crucial for maximizing profitability. By following the fee tier audit checklist, comparing platforms, and employing optimization strategies, you can minimize trading costs and improve overall performance. Whether you’re a beginner or a professional trader, ensuring you’re on the right fee tier can make a significant difference in your trading success.