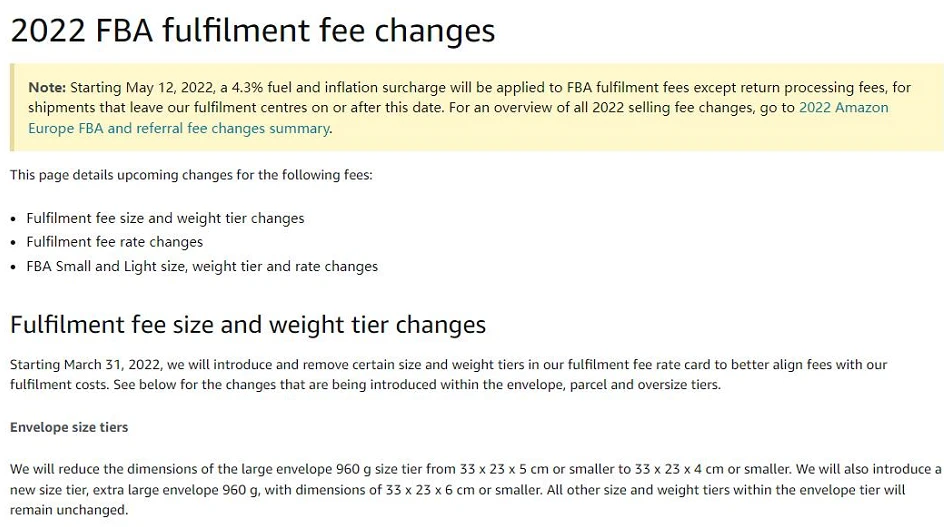

=========================================================
In the dynamic world of trading, fee structures play a critical role in determining profitability. Whether you are trading in perpetual futures, forex, or commodities, understanding fee tier policies is essential. Over the past few years, many brokers and trading platforms have made updates to their fee tier policies, offering traders various levels of fees based on their trading activity or volume. These changes have a profound impact on the overall cost of trading and require a closer look.
In this article, we will review the latest fee tier policy updates, explore how they affect traders, and provide actionable insights on how to optimize your trading strategy in light of these changes.
What Are Fee Tier Policies?
Understanding Fee Tiers
A fee tier system refers to a pricing structure used by brokers or trading platforms where traders are charged varying fees depending on their level of activity or the volume of trades they execute. The more a trader trades, the lower the fees they may pay. This tiered structure incentivizes high-frequency traders by offering discounts as they increase their trading volumes.
For example, a platform may offer three levels of fees:
- Tier 1 (Basic): Traders who execute fewer trades pay higher fees.
- Tier 2 (Intermediate): Traders who trade more frequently or in higher volumes pay moderate fees.
- Tier 3 (Advanced): High-volume traders or institutional traders enjoy the lowest fees.
Each platform or broker may structure their fee tiers differently, and it’s important for traders to understand how these tiers are calculated and how updates can affect their bottom line.
Why Fee Tier Updates Matter
Fee tier policies directly influence profitability. Even small changes in fees can make a big difference, especially for frequent traders or institutional investors. As brokers constantly update their fee policies, it’s crucial for traders to stay updated on these changes. Fee tier policy updates can affect:
- Trading Costs: Lower fees mean higher profitability, particularly for those executing large volumes of trades.
- Competitiveness: Brokers offering lower fees may attract more clients, especially those in high-frequency trading (HFT) or those trading with large capital.
- Customization: Some platforms now offer custom fee plans, allowing traders to negotiate fee structures based on their specific needs.
Latest Fee Tier Policy Updates: A Review
Over the last few months, several trading platforms have revised their fee structures. These updates vary depending on the platform, but they generally aim to benefit both retail and institutional traders by providing more flexibility and better value. Let’s explore some key fee tier policy updates.
1. Fee Reductions for High-Volume Traders
A significant trend in recent updates has been fee reductions for high-frequency traders (HFTs). Many exchanges have introduced lower fees for traders who meet a minimum trading volume or liquidity provision threshold. This encourages institutional investors and professional traders to increase their activity.
Example: Binance Futures
- Tier 1: 0.10% maker and taker fees for low-volume traders.
- Tier 2: 0.08% for traders who execute more than $1 million in monthly trading volume.
- Tier 3: 0.05% for those who trade over $10 million per month.
These fee updates benefit frequent traders, but those in lower tiers must adjust their strategies to meet the volume requirements for lower fees.
2. Dynamic Fee Structures Based on Liquidity
Some platforms now offer dynamic fee structures that adjust according to the liquidity of the market. These policies allow traders to enjoy lower fees when the market is liquid, thereby encouraging market participation and reducing spreads.
Example: Kraken
Kraken has introduced a system where the fee structure changes depending on the liquidity of the market. In highly liquid markets, fees drop significantly, benefiting those who trade large quantities of assets during peak times.
3. Introduction of Flat Fee Tiers for Beginners
Many brokers are introducing flat-fee systems for beginner traders. These updates aim to make trading more accessible and predictable for those just starting. Flat fees simplify the fee structure, making it easier to understand and budget for.
Example: eToro
eToro recently revamped its fee tier policy to include a flat-rate structure for traders with less than $10,000 in assets. This is particularly beneficial for beginners, as they do not have to worry about complex fee calculations based on their volume or frequency of trades.
How Fee Tiers Affect Perpetual Futures Traders
Impact on Profitability
For perpetual futures traders, understanding fee tiers is crucial to maintaining profitability. In perpetual futures markets, traders frequently enter and exit positions, which makes fee structures extremely important. High fees can erode profits, especially when executing many trades in a short period.
How to Calculate Fee Tiers in Perpetual Futures
Many brokers and exchanges calculate fee tiers in perpetual futures trading based on a trader’s monthly trading volume. The more frequently a trader enters and exits positions, the lower the fees they are charged.
Example:
- Tier 1 (Basic): 0.075% taker fee and 0.025% maker fee for monthly volumes under $1 million.
- Tier 2 (Intermediate): 0.05% taker fee and 0.015% maker fee for volumes over $5 million.
- Tier 3 (Advanced): 0.03% taker fee and 0.01% maker fee for volumes exceeding $10 million.
The key to reducing trading costs in perpetual futures is to carefully monitor your trading volume and try to meet the higher volume thresholds to unlock the lowest fees.
Strategies to Optimize Fee Tiers
1. Increase Trading Volume to Reach Lower Tiers
One of the most straightforward ways to optimize your fee tier is to increase your trading volume. If you are a frequent trader, aim to meet the higher volume thresholds to reduce your fees.
Benefits:
- Lower Fees: Higher volumes mean lower costs.
- Better Profit Margins: With reduced fees, your profit margins are expanded, making each trade more lucrative.
2. Use Fee Discounts and Promotions
Some platforms offer limited-time promotions or fee discounts for new traders or during special events. Taking advantage of these promotions can significantly reduce your trading costs.
Example: Bitfinex
Bitfinex recently introduced a promotion offering 50% off on all fees for new traders who meet specific volume targets. Such offers are an excellent way to maximize profits during periods of high market activity.
FAQ: Fee Tier Policy Updates
1. How do fee tiers impact my profitability as a trader?
Fee tiers are a crucial factor in your trading costs. The more you trade, the lower your fees could become, increasing your profitability. By optimizing your fee tier through increased volume or liquidity, you can significantly reduce your trading costs.
2. Are there any new fee tier updates for beginner traders?
Yes, many platforms are now offering flat fee structures for beginner traders, making it easier to understand and manage trading costs. These updates are designed to simplify the fee system and help new traders focus on building their skills without worrying about complex fee structures.
3. How do I calculate my fee tier in perpetual futures trading?
Fee tiers in perpetual futures trading are typically calculated based on your monthly trading volume. The more trades you execute, the lower your fees may be. It’s essential to track your trading activity and aim for higher volumes to unlock better fee rates.
Conclusion
Fee tier policy updates can have a significant impact on your trading strategy and profitability. By staying informed about the latest updates and optimizing your fee structure, you can reduce trading costs and improve your overall returns. Whether you are a high-frequency trader, an institutional investor, or a beginner, understanding fee tiers and adjusting your strategies accordingly is vital to long-term success.