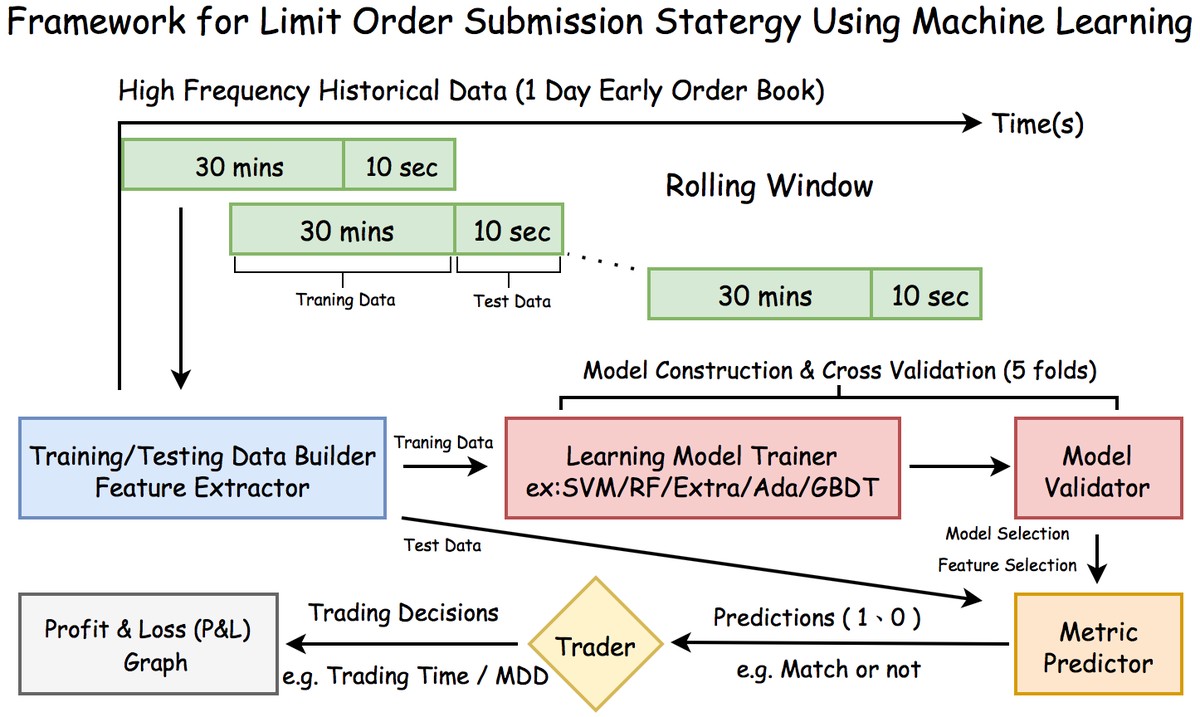
===================================================================================
Latency is the Achilles’ heel of high-frequency trading (HFT). In an environment where milliseconds matter, even the slightest delay can have a substantial impact on trading performance. High-frequency traders (HFTs) rely on speed, and latency—whether in data transmission, execution, or communication—can cost traders significant profits. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about latency in high-frequency trading, including how it impacts trades, how to measure it, and most importantly, strategies to reduce latency for optimal performance.
What Is Latency in High-Frequency Trading?
Latency, in the context of high-frequency trading, refers to the time delay between initiating a trade and its execution. A millisecond delay may seem insignificant, but in HFT, where algorithms operate at lightning speeds, these small delays can lead to missed opportunities, poor execution, and, ultimately, losses.
Key Factors Contributing to Latency:
- Network Latency: The time it takes for data to travel between the trading system and the exchange. Network latency is often caused by congestion or inefficient routing.
- Processing Latency: The time it takes for a system to process and respond to data. This includes algorithm execution, order matching, and trade confirmation.
- Market Latency: The time between a price change in the market and when that information is reflected in your system.
- Exchange Latency: Latency incurred at the exchange itself due to the speed of the exchange’s systems or the physical distance between a trader’s infrastructure and the exchange.
Why Is Latency Important in High-Frequency Trading?
Latency directly influences trading success in high-frequency environments. For HFTs, time is money—literally.
1. Competitive Advantage
In high-frequency trading, every trader’s goal is to act on information faster than others. Even a small latency gap can result in a missed arbitrage opportunity, a poorly executed trade, or a failure to close a position at the best price. Reducing latency gives traders an edge in capturing market inefficiencies before compe*****s.
2. Profit Margins
HFTs typically operate on very small profit margins per trade, but these margins accumulate over thousands or even millions of trades. A delay in executing orders can result in a lower profit per trade, which may significantly affect overall profitability in the long run.
3. Algorithmic Trading Efficiency
Trading algorithms rely on low latency to function effectively. If there is a delay in transmitting or executing orders, the algorithm’s performance will degrade, which can cause an otherwise profitable strategy to underperform or even incur losses.
Types of Latency in Trading
Latency in high-frequency trading can occur at several points in the trading process, each contributing differently to performance. Here are the main types:
1. Network Latency
Network latency is the delay in transmitting data between systems and exchanges. It can be caused by factors like bandwidth limitations, routing issues, or poor network infrastructure.
Reducing Network Latency:
- Colocation: Hosting your trading system physically closer to the exchange’s infrastructure to reduce the distance data needs to travel.
- Private Network Connections: Using dedicated, high-speed lines rather than relying on public internet connections to ensure faster transmission.
2. Processing Latency
This type of latency happens when the trading algorithm processes incoming data. The more complex the algorithm, the longer it might take to execute.
Reducing Processing Latency:
- Optimized Algorithms: Use optimized coding practices and streamlined algorithms to minimize unnecessary computations.
- Faster Servers: Using high-performance hardware, such as FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) or ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit), to accelerate computation and order execution.
3. Exchange Latency
Exchange latency refers to the delay incurred at the exchange level. Exchanges with slower matching engines will result in slower execution speeds, adding unnecessary delays to the process.
Reducing Exchange Latency:
- Choose Low-Latency Exchanges: Selecting exchanges with faster matching engines or those that offer colocation services can reduce this latency.
- Direct Market Access (DMA): Direct access to exchanges without intermediaries can reduce the time it takes to send and receive data from the exchange.
Measuring Latency in High-Frequency Trading
Latency measurement is crucial for identifying bottlenecks in the trading system. Traders must monitor latency at every step to ensure optimal performance.
1. Ping Test
A basic method for measuring network latency. By sending small data packets to an exchange and measuring the response time, traders can assess network latency.
2. Round-Trip Time (RTT)
RTT measures the time taken for a data packet to travel from your system to the exchange and back. This is a more comprehensive measure that includes both network and processing latency.
3. Latency Benchmarks
Many traders and firms rely on latency benchmarks to compare the performance of different exchanges, data providers, and brokers. These benchmarks help traders identify where latency is coming from and how to optimize it.
Strategies for Reducing Latency
Reducing latency is not just about upgrading hardware. It requires a combination of strategies across hardware, software, and network infrastructure.
1. Hardware Optimizations
Investing in hardware upgrades such as dedicated high-speed servers, FPGAs, and GPUs can significantly reduce processing latency. Colocating these machines as close to the exchange’s systems as possible ensures that data travels the shortest possible distance.
2. Software Optimization
Trading algorithms should be optimized to minimize delays in processing. Code optimization, reduced complexity, and the use of efficient programming languages like C++ or assembly can significantly cut down processing times.
3. Colocation Services
One of the most effective strategies for reducing latency is colocation, which involves placing your servers in close physical proximity to the exchange’s infrastructure. Colocation services are available from most exchanges and can drastically reduce network latency by ensuring that the data doesn’t have to travel long distances.
4. Low-Latency Trading Infrastructure
Adopting low-latency trading infrastructure such as dedicated fiber-optic lines and custom-built hardware solutions ensures that trades are executed in microseconds, making it less likely that latency will impact trade performance.
5. Real-Time Latency Monitoring
Using advanced latency monitoring tools is crucial for detecting latency issues in real time. This enables traders to react quickly and adjust their strategies or fix issues before they impact performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Latency in High-Frequency Trading
1. How does latency impact algorithmic trading?
Latency affects algorithmic trading by delaying the execution of trade orders, causing discrepancies between the algorithm’s intended execution price and the actual execution price. This can reduce the overall effectiveness of the strategy, leading to less profitable trades.
2. What are the most common causes of latency in trading systems?
The primary causes of latency in trading systems include network congestion, suboptimal data routing, slow processing times in trading algorithms, and physical distance from the exchange. Each of these factors can add microseconds or milliseconds of delay, which can significantly impact trading outcomes.
3. Can latency be completely eliminated in high-frequency trading?
While it is impossible to completely eliminate latency, it can be minimized to a point where it has little to no impact on trading performance. Using advanced hardware, optimized software, and colocation can reduce latency to the point where it becomes negligible.
Conclusion: Mastering Latency for High-Frequency Trading Success
In high-frequency trading, every microsecond counts, and latency can make or break a trading strategy. By understanding how latency works, identifying its sources, and implementing strategies to reduce it, traders can significantly enhance their performance and profitability. Whether it’s optimizing hardware, improving software algorithms, or utilizing colocation services, minimizing latency is key to succeeding in the competitive world of high-frequency trading.
By taking proactive steps to measure and reduce latency, high-frequency traders can stay ahead of the competition, capture more opportunities, and make the most of every market movement.