
=====================================================================================
In the fast-paced world of futures trading, the ability to systematically test and optimize strategies before deploying capital is critical for profitability. Robust backtesting processes allow traders, whether retail or institutional, to evaluate performance, identify weaknesses, and fine-tune strategies under historical market conditions. This article provides a comprehensive guide to developing and implementing robust backtesting processes for futures, ensuring both accuracy and actionable insights.
Understanding Backtesting in Futures Trading
What is Backtesting?
Backtesting involves simulating a trading strategy against historical data to evaluate its effectiveness. For futures markets, backtesting provides insights into risk-adjusted returns, drawdown potential, and overall profitability.
Importance in Futures Trading
Backtesting is crucial because:
- It identifies potential weaknesses before real capital is deployed.
- It helps optimize entry and exit rules for futures positions.
- It allows evaluation of strategies under various market conditions, including volatility spikes and low liquidity periods.
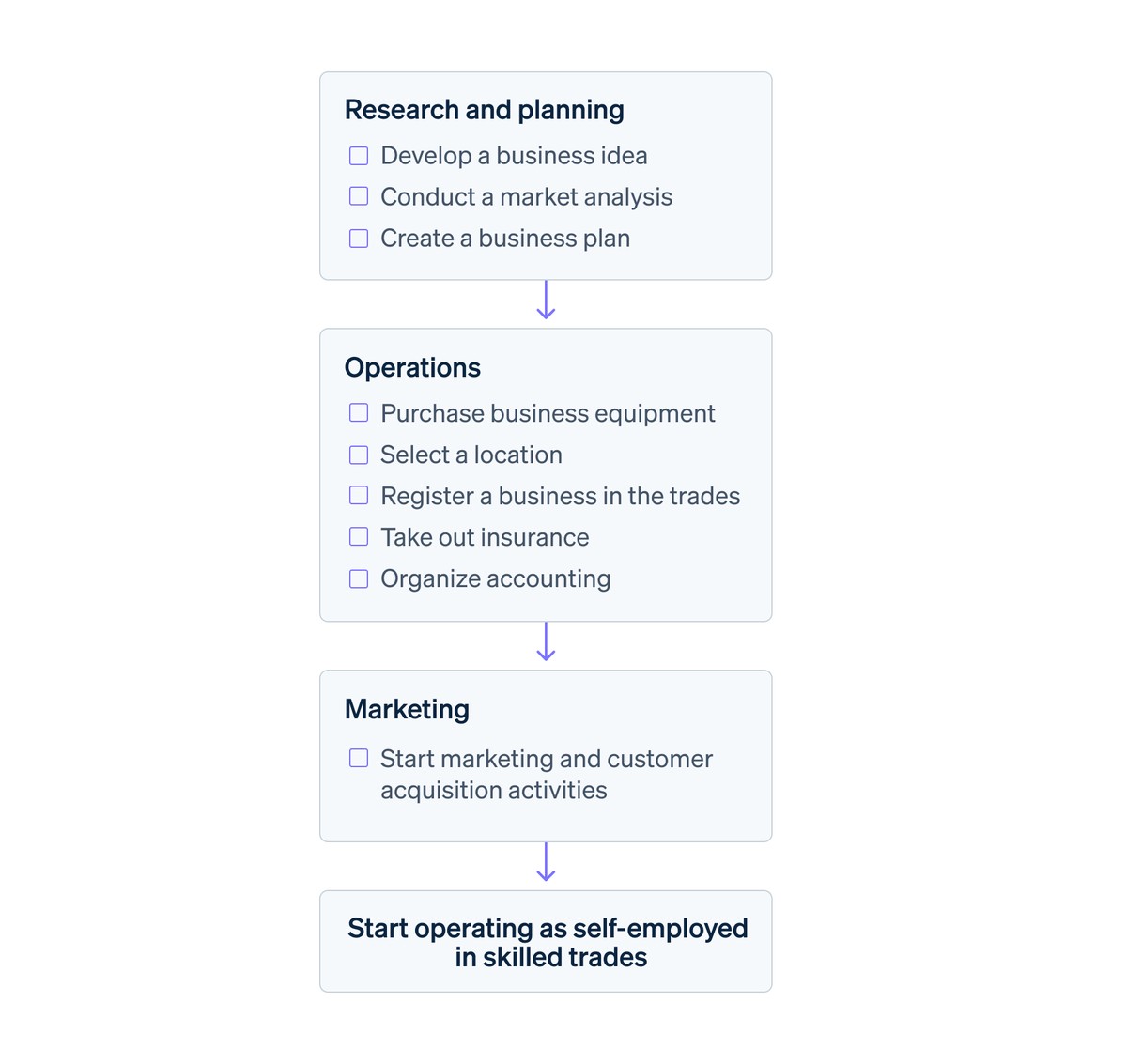
Step-by-step workflow for futures backtesting from historical data to performance analysis.
Key Components of a Robust Backtesting Process
1. High-Quality Historical Data
Accurate backtesting requires high-fidelity data, including tick-level or minute-level prices, volume, spreads, and execution costs.
Best Practices
- Use verified data providers to ensure accuracy.
- Include transaction costs, slippage, and margin requirements to reflect realistic conditions.
- Regularly update data sets to account for market structure changes.
2. Realistic Trading Assumptions
Backtests must account for factors such as leverage, position sizing, and liquidity constraints. Unrealistic assumptions can lead to overestimated performance.
Common Pitfalls
- Ignoring slippage or latency effects.
- Overfitting strategies to historical patterns.
- Using perfect market fills that are not achievable in real-world trading.
Backtesting Methods for Futures Traders
Method 1: Walk-Forward Analysis
Walk-forward analysis involves dividing historical data into training and testing periods, optimizing the strategy on the training set, and validating on the testing set.
Advantages
- Reduces risk of overfitting.
- Provides insights into how strategies perform in unseen market conditions.
Drawbacks
- More computationally intensive.
- Requires careful segmentation of historical data to avoid bias.
Method 2: Monte Carlo Simulations
Monte Carlo simulations introduce randomness into historical data or trade execution to assess the robustness of a strategy under various scenarios.
Advantages
- Helps evaluate risk and probability of extreme drawdowns.
- Provides confidence intervals for expected returns.
Drawbacks
- Computationally intensive for high-frequency data.
- Requires statistical expertise to interpret results correctly.
Illustration of Monte Carlo simulations applied to a futures trading strategy.
Integrating Backtesting into Trading Workflow
Step 1: Define Strategy Rules
- Identify entry and exit criteria, stop-loss, take-profit, and position sizing.
- Ensure rules are codified clearly for algorithmic implementation.
Step 2: Choose Backtesting Framework
- Retail traders may use platforms like TradingView or NinjaTrader.
- Institutional traders often implement custom backtesting solutions integrated with execution systems.
Step 3: Analyze and Refine
- Evaluate performance metrics: Sharpe ratio, maximum drawdown, profit factor.
- Adjust strategy parameters based on insights without overfitting.
This article naturally incorporates internal links:
Advanced Techniques for Enhancing Backtesting Robustness
Multi-Asset and Correlation Testing
Incorporate correlations between multiple futures contracts to assess portfolio-level risks and hedging strategies.
Scenario-Based Stress Testing
Evaluate strategy performance under extreme market events, such as flash crashes, geopolitical crises, or liquidity shocks.
Automation and Continuous Monitoring
Automating the backtesting process allows for quick iteration and adaptation to changing market dynamics, ensuring strategies remain relevant.
Dashboard displaying backtesting results, including equity curves, drawdowns, and performance metrics.
Best Practices for Futures Backtesting
- Document Assumptions – Record all parameters and assumptions to ensure reproducibility.
- Test Across Multiple Timeframes – Avoid relying solely on one period of historical data.
- Stress Test Strategies – Use Monte Carlo and walk-forward analyses to validate robustness.
- Avoid Overfitting – Do not optimize too aggressively on historical data.
- Regularly Reassess – Update strategies based on recent market changes and new data.
FAQ: Robust Backtesting Processes for Futures Profitability
How do backtesting processes improve futures profitability?
Backtesting allows traders to identify the most effective entry and exit points, optimize risk management, and evaluate potential drawdowns. This reduces trial-and-error in live trading and increases probability of consistent profits.
Where to find perpetual futures backtesting tools?
Several platforms provide robust backtesting capabilities, including NinjaTrader, MetaTrader 5, and QuantConnect. Custom solutions can be developed for professional traders requiring advanced simulation features.
Why is backtesting essential in perpetual futures?
Perpetual futures involve continuous contracts without expiry, making it critical to test strategies under historical market fluctuations to understand risk, volatility, and execution performance.
Case Studies: Effective Backtesting in Action
- Retail Trader: Used walk-forward backtesting on BTC/USD perpetual futures to optimize short-term scalping strategy, achieving consistent risk-adjusted returns.
- Institutional Hedge Fund: Employed Monte Carlo simulations on multi-asset futures portfolio to stress-test strategies and allocate capital efficiently.
- Quantitative Researcher: Integrated high-frequency tick data into backtesting framework to develop predictive models for intraday trading.
Conclusion
Robust backtesting processes are indispensable for futures traders aiming for profitability and risk management. By combining high-quality data, realistic assumptions, and advanced methodologies such as walk-forward analysis and Monte Carlo simulations, traders can confidently deploy strategies that withstand real-world market conditions. Continuous monitoring, automation, and scenario analysis further enhance robustness, ensuring long-term success in futures trading.
Engage with this guide: share your experiences, discuss backtesting strategies, and forward this article to fellow traders seeking enhanced futures profitability.