
=====================================
Introduction: Understanding Swing Trading
Swing trading is a popular trading style that focuses on capturing short- to medium-term price movements in financial markets. Unlike day trading, which closes positions within a single day, swing traders typically hold positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on price swings. This swing trading guide for stock traders provides a structured approach for both beginners and experienced investors to maximize trading performance while managing risks effectively.
Swing trading is particularly effective in volatile markets, where price momentum creates frequent trading opportunities. By combining technical analysis, market psychology, and disciplined risk management, traders can generate consistent profits over time.
Core components of swing trading for stock traders.
Core Principles of Swing Trading
Principle 1: Identifying Trading Opportunities
Successful swing trading begins with recognizing market opportunities:
- Trend Analysis: Determine whether the market is trending up, down, or sideways.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Identify key price points where stocks historically reverse or break out.
- Volatility Assessment: Evaluate the potential magnitude of price swings to choose suitable trades.
Understanding these principles helps traders position themselves to enter trades at optimal points and exit with profits.
Principle 2: Risk Management
Managing risk is critical for swing traders to protect capital:
- Position Sizing: Adjust trade size relative to account balance and risk tolerance.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Place stops at levels that limit losses if the market moves against the trade.
- Diversification: Spread trades across sectors or instruments to reduce exposure.
Effective risk management ensures that losses do not erode profits, maintaining long-term sustainability.
Principle 3: Time Frame Selection
Swing traders focus on intermediate time frames, often using daily or 4-hour charts. Aligning analysis with the holding period ensures signals are relevant and actionable.
- Daily Charts: Useful for trend identification and swing boundaries.
- Intraday Charts: Can refine entry and exit points for more precise trades.
Choosing the appropriate time frame allows traders to balance trading frequency with analysis depth.
Principle 4: Discipline and Emotional Control
Emotional discipline is vital in swing trading:
- Avoid impulsive trades driven by fear or greed.
- Stick to predefined entry and exit rules.
- Maintain consistency in strategy application.
Discipline ensures systematic execution, which is key to long-term profitability.
Swing Trading Methods and Strategies
Method 1: Technical Analysis-Based Swing Trading
Technical analysis is the cornerstone of swing trading:
- Indicators: Moving Averages, RSI, MACD, Bollinger Bands
- Chart Patterns: Head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, triangles
- Momentum Trading: Enter trades when momentum signals align with trend direction
Advantages:
- Provides clear entry/exit signals
- Accessible to traders with limited quantitative background
Disadvantages:
- Can produce false signals in volatile or sideways markets
- Requires continual monitoring and adjustment
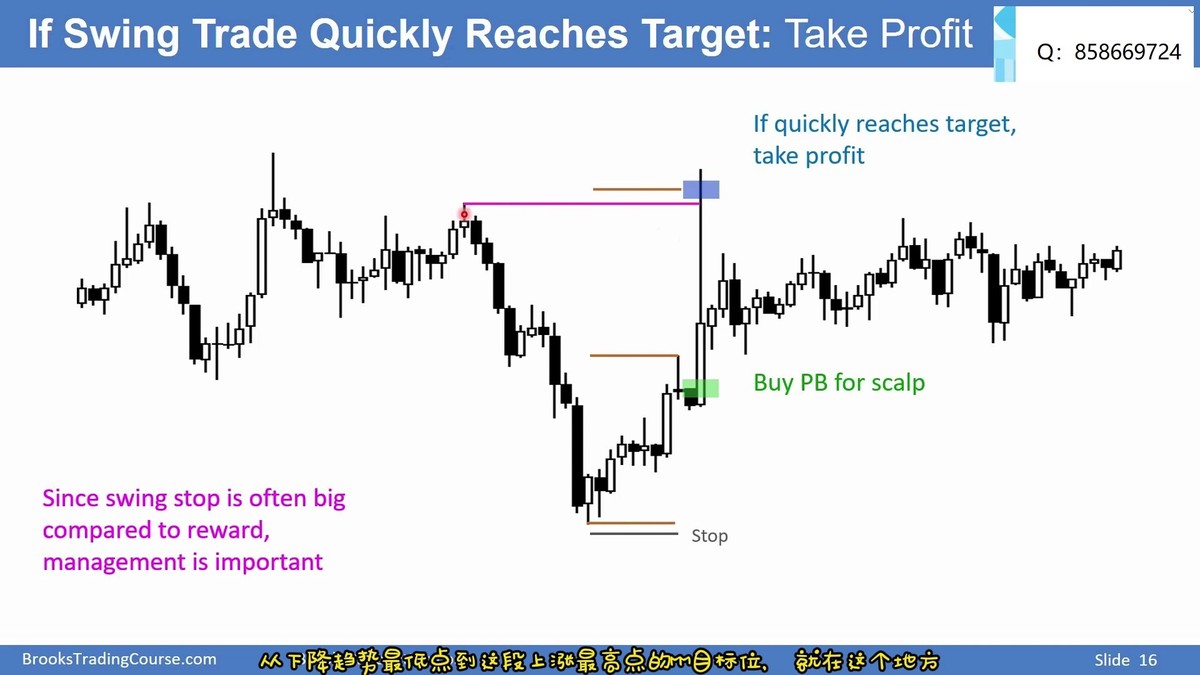
Example of a swing trade setup using moving averages and RSI.
Method 2: Price Action and Market Psychology
Some swing traders rely on price action, focusing on market behavior rather than indicators:
- Observe candlestick patterns, trend lines, and support/resistance zones.
- Analyze market sentiment to anticipate reversals or breakouts.
- Combine with volume analysis to confirm strength of moves.
Advantages:
- Flexible and adaptable across different market conditions
- Helps understand underlying market dynamics
Disadvantages:
- Requires experience to interpret patterns accurately
- Subjective analysis may lead to inconsistent results
Method 3: Hybrid Approach
A hybrid approach combines technical indicators with price action and sentiment analysis:
- Use technical tools to identify potential trades
- Confirm with price action and volume analysis
- Apply risk management rules rigorously
Benefits: Balances quantitative precision with qualitative market insights.
Drawbacks: Complexity increases, demanding more analytical skills.
Real-World Swing Trading Example
- Identify a stock in an uptrend using moving averages.
- Check RSI to confirm it is not overbought.
- Enter position at a support level, place stop-loss slightly below support.
- Exit at resistance or trend reversal signal.
This systematic approach exemplifies the principles outlined above.
Practical Tips for Swing Traders
Developing a Swing Trading Plan
- Define risk tolerance, target returns, and holding periods.
- Choose trading instruments aligned with strategy and market volatility.
- Establish clear entry and exit criteria, including stop-loss and take-profit rules.
Tools and Resources
- Trading platforms with charting and backtesting capabilities (e.g., TradingView, ThinkorSwim)
- News feeds and market sentiment analysis tools
- Educational resources and swing trading courses for continuous learning
Automation and Advanced Techniques
- Algorithmic swing trading can automate pattern recognition and order execution.
- Backtesting historical data ensures strategy viability before deploying capital.
Integration Tip: Combine automated alerts with manual oversight for enhanced control.
A structured swing trading plan showing entry, exit, and risk management zones.
FAQ: Swing Trading Guide for Stock Traders
1. How to start swing trading as a beginner?
Begin with education on chart patterns and indicators, practice on demo accounts, and develop a simple trading plan. Gradually increase trade complexity as confidence and skills grow.
2. Why is swing trading effective?
Swing trading captures short- to medium-term trends, allowing traders to profit from price volatility without the need for constant market monitoring like day trading.
3. How to identify swing trading opportunities?
Look for trends, support and resistance levels, momentum indicators, and confirm with volume or price action patterns. Combining multiple signals increases accuracy.
4. Where to find swing trading tips?
Reliable sources include trading communities, educational websites, webinars, and mentor programs. Practical experience through simulated trading platforms is invaluable.
5. How to manage risk in swing trading?
Apply strict stop-loss orders, diversify positions, size trades appropriately, and avoid overleveraging. Consistency in applying risk rules is essential for preserving capital.
Conclusion
This swing trading guide for stock traders provides a comprehensive roadmap to mastering short- to medium-term trading. By combining technical analysis, price action, and disciplined risk management, traders can enhance their profitability while minimizing risk.
Practical application, continuous learning, and consistent execution are the keys to success. Swing trading offers flexibility and opportunities across market conditions, making it suitable for beginners and experienced traders alike.
Engage with the community, share your experiences, and refine your strategy for sustainable long-term growth.