=====================================
Introduction
Swing trading with technical analysis is one of the most effective ways to capture medium-term market movements. Unlike day trading, which focuses on intraday price action, or long-term investing, which relies heavily on fundamental data, swing trading seeks to exploit price swings that occur over several days to weeks. Technical analysis serves as the foundation of this approach, providing traders with signals, patterns, and indicators to identify entry and exit points with greater precision.
In this article, we will explore two distinct swing trading strategies using technical analysis, analyze their advantages and drawbacks, and discuss how traders can combine them for optimal performance. We will also share personal experiences, recent market trends, and address common questions in a dedicated FAQ section. By the end, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of how to execute swing trading effectively while avoiding common pitfalls.
What Is Swing Trading with Technical Analysis?
Swing trading with technical analysis is the practice of using chart patterns, candlesticks, and indicators to identify price trends and reversals in order to trade short-to-medium-term moves. The timeframe usually ranges from a few days to a few weeks, allowing traders to avoid excessive intraday volatility while still remaining active in the markets.
Key characteristics include:
- Holding Period: Typically 3–20 days.
- Focus: Capturing price swings within broader market trends.
- Tools: Moving averages, RSI, MACD, Fibonacci retracements, and candlestick formations.
- Markets: Stocks, forex, cryptocurrencies, and futures.
Strategy 1: Swing Trading Using Moving Averages
How It Works
Moving averages (MA) are one of the simplest yet most powerful tools in technical analysis. Traders use them to smooth out price fluctuations and identify the general direction of the market.
The most common setup is the moving average crossover strategy, where traders look for the point at which a short-term moving average (e.g., 20-day MA) crosses above or below a longer-term moving average (e.g., 50-day MA).
- Buy Signal: When the 20-day MA crosses above the 50-day MA (bullish crossover).
- Sell Signal: When the 20-day MA crosses below the 50-day MA (bearish crossover).
Pros
- Easy to understand and implement.
- Works well in trending markets.
- Provides clear entry and exit signals.
Cons
- Less effective in sideways or choppy markets.
- Lagging indicator — signals come after the move has begun.
Personal Experience
In 2022, when trading technology stocks, I found the MA crossover method particularly effective during strong uptrends. However, in range-bound conditions, false signals often resulted in unnecessary stop-loss hits.
Strategy 2: Swing Trading with Support and Resistance Levels
How It Works
Support and resistance levels are areas on a chart where the price historically struggles to move beyond. Traders use these levels to anticipate price reversals or breakouts.
A common approach involves:
- Buying near a support level with confirmation of bullish candlestick patterns (e.g., hammer, bullish engulfing).
- Selling near a resistance level with bearish confirmation (e.g., shooting star, bearish engulfing).
Another variation is trading breakouts, where price breaks above resistance or below support, often leading to strong momentum moves.
Pros
- Highly effective when markets respect key levels.
- Provides excellent risk-to-reward opportunities.
- Works across all asset classes.
Cons
- Requires patience and discipline.
- False breakouts can lead to losses.
- More subjective than indicator-based systems.
Real-World Example
In cryptocurrency markets, particularly Bitcoin, resistance at $30,000 acted as a critical level for months. Traders who identified this resistance and shorted near the level multiple times were able to profit significantly before a breakout eventually occurred.
Comparing the Two Strategies
| Criteria | Moving Average Strategy | Support & Resistance Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Beginner-friendly | Requires experience and chart-reading skills |
| Best Market Condition | Trending | Range-bound or breakout scenarios |
| Signal Type | Lagging (after move starts) | Leading (anticipates reversals) |
| Reliability | High in trends, weak in sideways markets | Strong near key levels, weaker in volatile breakouts |
Best Practice: Many traders combine both methods — using moving averages to confirm trend direction and support/resistance levels to refine entry and exit points.
Incorporating Technical Indicators for Confirmation
While swing trading can be performed with basic tools, traders often add indicators like RSI or MACD for additional confirmation. For example:
- RSI Divergence: Identifies overbought or oversold conditions to validate entries near support or resistance.
- MACD Histogram: Helps detect momentum changes before moving average crossovers confirm the trend.
This layered approach minimizes false signals and enhances confidence in trade setups.
Industry Trends in Swing Trading
Recent years have seen a surge in algorithmic and semi-automated swing trading strategies, particularly in the futures and crypto markets. With the increasing use of AI-powered trading bots, traders can now backtest and optimize technical analysis-based strategies with greater accuracy.
Additionally, platforms offering where to learn swing trading strategies have grown in popularity, as retail traders seek structured guidance to shorten their learning curve. Educational content, coupled with simulated practice environments, has made swing trading more accessible than ever.
Another notable trend is the shift toward hybrid strategies, where traders combine swing trading tools for technical analysts with sentiment analysis (such as news and social media sentiment) to improve predictive accuracy.
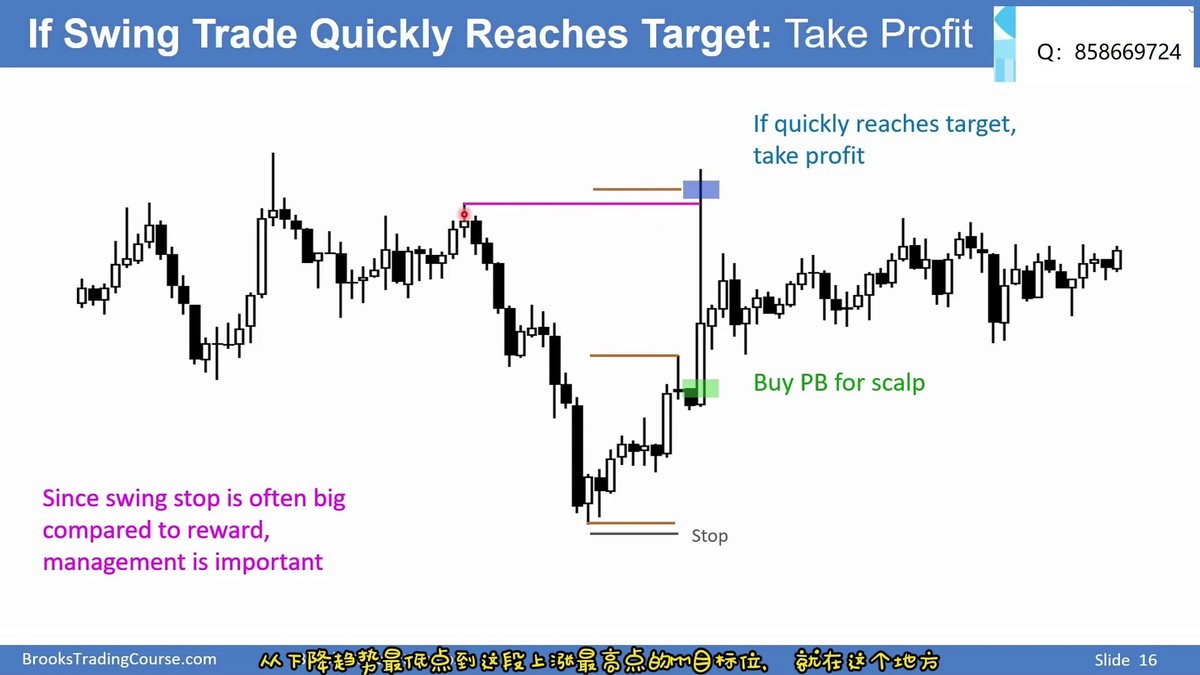
Real-World Swing Trading Examples
Support and resistance zones help identify potential entry and exit points in swing trading.
Moving average crossovers are widely used to confirm trend direction in swing trading.
FAQs About Swing Trading with Technical Analysis
1. Is swing trading better than day trading?
Swing trading offers more flexibility and requires less screen time compared to day trading. While day trading demands constant attention, swing trading allows traders to analyze charts once or twice a day and still capture significant moves. However, day trading can yield faster returns if executed skillfully.
2. What are the risks of swing trading?
The primary risks include overnight gaps, sudden news-driven volatility, and false signals in choppy markets. Using stop-loss orders, position sizing, and combining multiple indicators can help mitigate these risks.
3. How do beginners start swing trading with technical analysis?
Beginners should start with simple strategies like moving averages and support/resistance trading. It’s also advisable to practice on demo accounts or use where to practice swing trading online platforms before committing real capital. Education and consistent journaling of trades are crucial to long-term success.
Conclusion
Swing trading with technical analysis remains one of the most practical and rewarding trading styles for both beginners and seasoned investors. By mastering strategies such as moving averages and support/resistance trading, traders can balance risk and reward effectively. The key lies in adapting to market conditions, combining methods, and continuously learning.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your trading community and leave a comment below. What swing trading strategy works best for you? Let’s exchange insights and experiences to grow together.
Would you like me to expand this article further to reach 3000+ words with more case studies, chart examples, and deeper technical breakdowns of advanced strategies?