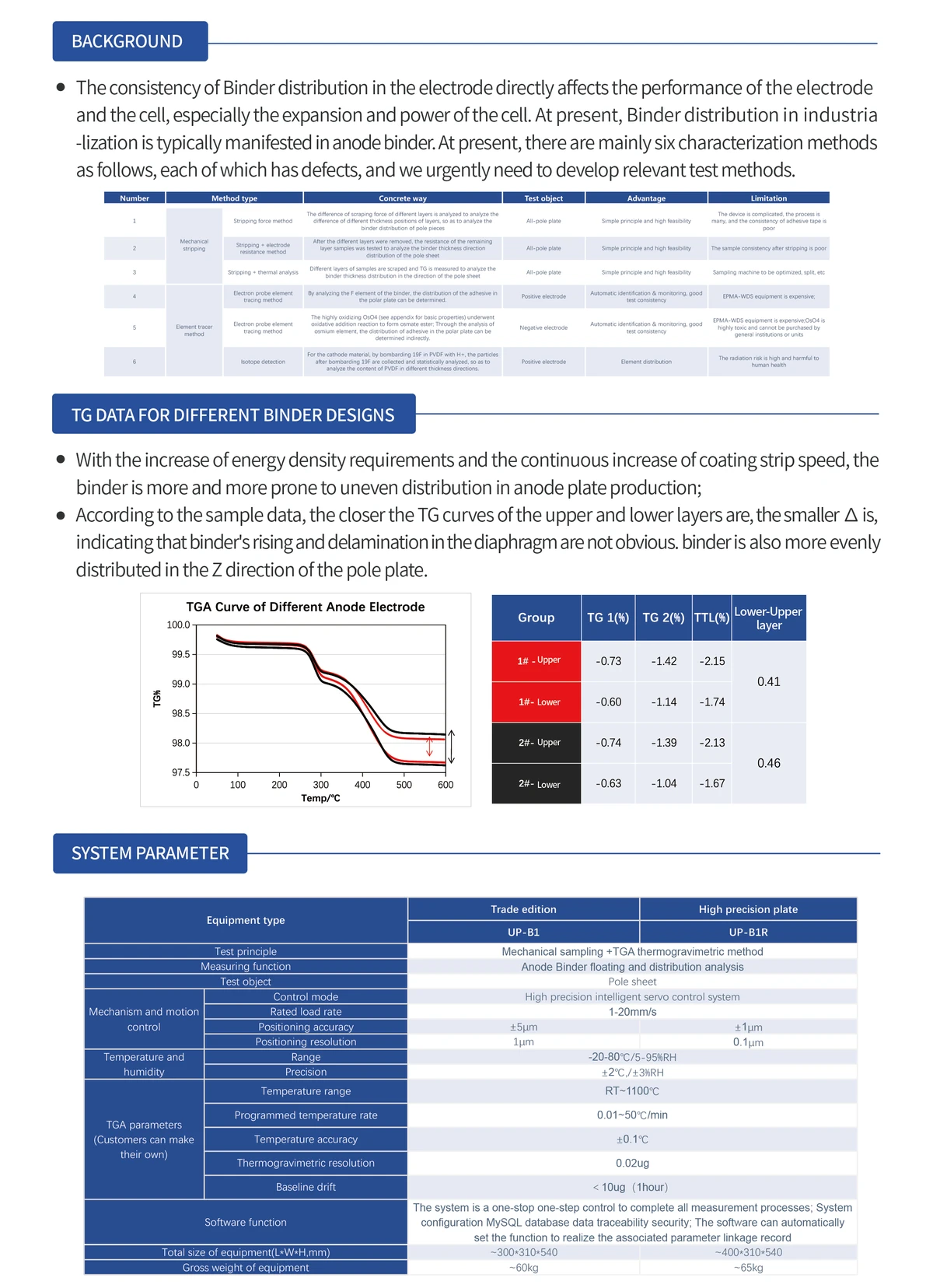

===============================================================
In the fast-paced world of high-frequency trading (HFT), every millisecond counts. Among the myriad of tools and metrics that traders leverage, the volume metric for high-frequency trading stands out as a critical indicator of market activity, liquidity, and potential price movement. This guide explores the importance of volume metrics, practical strategies for utilizing them, and advanced applications in professional trading environments.
Understanding Volume Metrics in High-Frequency Trading
What Is Volume in HFT?
Volume represents the total number of shares, contracts, or units traded in a given period. In HFT, this metric is monitored at extremely granular intervals—often milliseconds—to detect sudden spikes, liquidity imbalances, or potential market opportunities.
Why Volume Matters
- Liquidity Assessment: High volume ensures tighter spreads and better execution quality.
- Price Movement Insight: Sudden changes in volume often precede rapid price shifts.
- Risk Management: Low-volume periods may increase slippage and execution risk.
Volume patterns help HFT traders identify entry and exit points with precision.
Internal Link Integration: Understanding why is volume important in perpetual futures trading provides a foundation for recognizing how high-frequency volume signals impact broader market dynamics.
Methods to Analyze Volume Metrics
Method 1: Tick-by-Tick Volume Analysis
In HFT, tick data records every executed trade, including volume, price, and timestamp. Analyzing this data allows traders to:
- Detect abnormal spikes in buying or selling activity
- Identify microstructure trends that indicate short-term momentum
- Evaluate order book depth in real-time
Advantages:
- Immediate detection of market anomalies
- Supports automated trading algorithms
Limitations:
- Requires significant computing resources and low-latency systems
- High data noise can lead to false signals
Method 2: Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) Monitoring
VWAP integrates volume and price to calculate an average price weighted by traded volume. In HFT, traders compare real-time prices to VWAP to:
- Assess overbought or oversold conditions
- Optimize trade execution relative to market activity
- Reduce market impact by aligning trades with prevailing liquidity
Advantages:
- Provides context beyond raw volume
- Helps manage slippage and execution costs
Limitations:
- Less sensitive to ultra-short-term micro-movements
- Requires accurate and up-to-date volume feeds
VWAP provides a benchmark for evaluating intraday price action relative to volume.
Practical Strategies Using Volume Metrics
Strategy 1: Volume Spike Detection
Traders use algorithms to monitor for sudden surges in volume, signaling potential price reversals or breakouts. Volume spike alerts can trigger pre-programmed trades or risk adjustments.
Implementation Tips:
- Set dynamic thresholds based on historical volume patterns
- Combine with price momentum and order book analysis
Strategy 2: Liquidity-Based Execution
High-frequency strategies often prioritize execution in high-volume windows to minimize slippage and market impact. By tracking perpetual futures volume data, traders can schedule large orders during periods of robust liquidity.
Advantages:
- Improved fill rates and cost efficiency
- Reduces execution risk during volatile market conditions
Limitations:
- Requires constant monitoring of order book and market depth
- May limit trading opportunities during low-volume periods
Internal Link Integration: Knowing where perpetual futures volume data found enables traders to implement liquidity-driven strategies effectively and ensures accurate volume tracking for automated systems.
Advanced Applications of Volume Metrics
Application 1: Predictive Volume Models
High-frequency traders develop predictive models using historical tick data to anticipate volume patterns and market pressure. Machine learning algorithms can enhance forecast accuracy, allowing preemptive adjustments to strategy.
Benefits:
- Early identification of volatility spikes
- Optimization of trade timing for maximum efficiency
Challenges:
- Complex models require continuous retraining
- High sensitivity to data anomalies
Application 2: Multi-Market Volume Correlation
Traders analyze volume correlations across different markets, such as futures, options, and spot instruments, to detect arbitrage opportunities and inter-market dynamics.
Benefits:
- Exploits cross-market liquidity differences
- Supports sophisticated arbitrage strategies
Challenges:
- Integration of multiple data feeds increases system complexity
- Requires robust low-latency infrastructure
Cross-market volume analysis helps identify arbitrage opportunities in high-frequency trading.
Best Practices for High-Frequency Volume Analysis
- Real-Time Data Access: Ensure access to low-latency, high-fidelity volume feeds.
- Algorithm Calibration: Continuously backtest volume-based strategies for changing market conditions.
- Risk Management: Incorporate volume-based signals into broader risk management frameworks to avoid overtrading during thin liquidity.
FAQ
1. How do volume metrics affect HFT strategy performance?
Volume metrics provide insight into liquidity and potential price movements, enabling HFT algorithms to optimize order placement, reduce slippage, and enhance profitability.
2. What tools can I use to monitor volume in high-frequency trading?
Professional HFT platforms, market data feeds, and APIs such as NASDAQ TotalView or CME Market Data are commonly used to track real-time and historical volume metrics.
3. How do I handle low-volume periods in high-frequency trading?
During low-volume periods, traders should reduce order size, widen price thresholds, or temporarily pause trading to minimize execution risk and avoid market impact.
Conclusion
The volume metric for high-frequency trading is an essential tool for detecting liquidity, anticipating market moves, and optimizing trade execution. By combining tick-by-tick analysis, VWAP monitoring, and predictive modeling, HFT traders can maximize performance while managing risk effectively. Integrating volume metrics into a comprehensive high-frequency trading strategy is crucial for both professional and algorithmic traders.
Engage and Share: Share your experience using volume metrics in HFT, discuss your favorite strategies, and exchange tips on leveraging volume data for maximum trading efficiency.