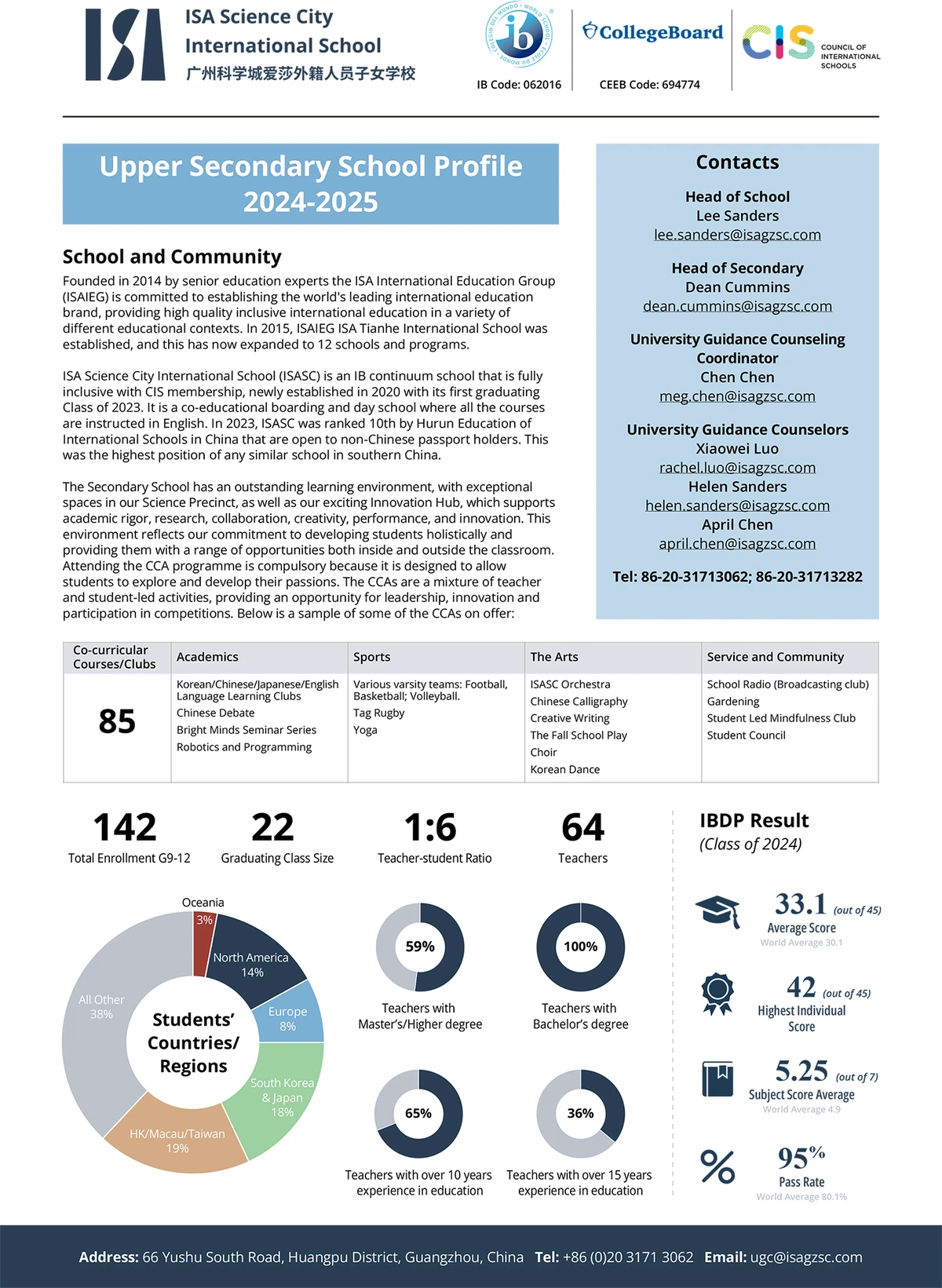
============================================
Perpetual futures are one of the most fascinating financial instruments in the crypto market, particularly attractive to young traders, learners, and aspiring finance professionals. For students exploring trading, investing, or risk management, understanding perpetual futures is essential. This guide provides a deep perpetual futures understanding for students, built with clear explanations, practical strategies, comparisons, and real-world insights to ensure beginners and advanced learners gain confidence in applying these tools effectively.
What Are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual futures are derivative contracts that allow traders to speculate on the price of an asset—such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies—without owning it. Unlike traditional futures, perpetual futures have no expiration date, meaning traders can hold their positions indefinitely, provided they maintain margin requirements.
These contracts mirror spot prices through a unique mechanism called the funding rate, which balances the contract price with the underlying asset’s market value.
Why Perpetual Futures Matter for Students
For students, perpetual futures offer a hands-on way to understand market dynamics, leverage, and risk management while practicing with demo accounts or small capital. Many universities and crypto communities recommend perpetual futures trading because it combines theoretical finance with real-world applications, such as hedging strategies and liquidity management.
Key Features of Perpetual Futures
No Expiry Date
Students often ask, “why perpetual futures have no expiry?” The main reason is flexibility. Unlike quarterly or monthly futures contracts, perpetual futures allow traders to maintain their positions indefinitely, which aligns better with fast-moving crypto markets.
Leverage Opportunities
Perpetual contracts offer leverage ranging from 2x up to 100x on many exchanges. While this can amplify gains, it also magnifies risks, making risk control strategies essential.
Funding Rate System
The funding rate ensures perpetual futures remain close to spot market prices. Traders either pay or receive funding depending on whether they hold long or short positions, teaching students a practical lesson in market equilibrium.
Cross-Comparisons: Perpetual Futures vs. Regular Futures
| Feature | Perpetual Futures | Regular Futures |
|---|---|---|
| Expiry Date | None | Fixed (weekly, monthly, quarterly) |
| Funding Rate | Yes | No |
| Popular in | Crypto markets | Traditional commodities, stocks |
| Strategy Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Risk Management | Requires constant monitoring | Defined by contract expiry |
This direct comparison helps students grasp how perpetual futures differ from regular futures while making them more relevant to crypto trading.
Strategies for Students Learning Perpetual Futures
1. Scalping Strategy
Scalping involves making many small trades to capture tiny price differences.
- Advantages: Quick results, suitable for students with limited time.
- Disadvantages: Requires intense focus and high discipline.
2. Swing Trading with Perpetual Futures
Swing traders hold positions for days or weeks to capture medium-term trends.
- Advantages: Lower stress compared to scalping, better for students balancing academics.
- Disadvantages: Requires technical analysis knowledge and patience.
3. Hedging Strategy
Students investing in crypto portfolios can hedge against downside risks by shorting perpetual futures.
- Advantages: Reduces risk exposure, valuable learning tool.
- Disadvantages: Funding fees can reduce long-term profitability.
How Perpetual Futures Generate Profits
Profits are generated in two primary ways:
- Directional Trading – Taking long or short positions depending on whether you expect the market to rise or fall.
- Funding Rate Arbitrage – Exploiting funding rate discrepancies between different exchanges.
For students, the directional strategy is easier to start with, while arbitrage requires advanced knowledge and more capital.
Risk Management in Perpetual Futures
Margin and Liquidation
Students must understand that positions can be liquidated if margin requirements are not met. Learning this teaches real-world lessons about leverage discipline.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Implementing stop-losses ensures that one wrong trade does not wipe out your capital. This is a cornerstone of risk management education.
Diversification of Trades
Combining perpetual futures with spot investments or other derivatives helps students practice portfolio risk control.
Practical Learning Path for Students
- Step 1: Start with a demo account on a crypto exchange offering perpetual futures.
- Step 2: Focus on small trades with low leverage (2x–5x).
- Step 3: Use perpetual futures for hedging, not just speculation.
- Step 4: Join communities or take structured courses—where to learn about perpetual futures is just as important as practicing.
Understanding perpetual futures: how funding rates, leverage, and perpetual contracts interact in the crypto market
Industry Trends in Perpetual Futures
- Increased Institutional Adoption: Hedge funds and banks are entering perpetual futures markets.
- AI-Powered Trading: Advanced algorithms are improving execution speed for perpetual contracts.
- Education for Students: More universities are including perpetual futures understanding for students in their finance and blockchain programs.
FAQs: Perpetual Futures for Students
1. How do perpetual futures work in trading?
Perpetual futures work by mimicking spot market prices through a funding rate system. Traders open long or short positions and keep them open indefinitely, as long as they maintain required margin balances.
2. Are perpetual futures suitable for students with small capital?
Yes. Many exchanges allow trading with as little as \(10–\)50. However, it’s recommended that students use low leverage and prioritize risk management solutions in perpetual futures to avoid large losses.
3. What is the best strategy for students starting with perpetual futures?
The safest strategy is combining spot holdings with hedging perpetual futures positions. This protects against losses and helps students learn market mechanics without excessive risk. Scalping and arbitrage should only be attempted once experience is gained.
Final Thoughts
Developing a solid perpetual futures understanding for students is about combining theory with practice. By experimenting with small trades, focusing on risk management, and studying real-world case examples, students can transform perpetual futures from an intimidating concept into a powerful learning tool.
If you found this guide helpful, feel free to share it with classmates, trading groups, or student finance communities. Let’s build a more financially literate generation together—comment below with your thoughts, experiences, or questions on perpetual futures!