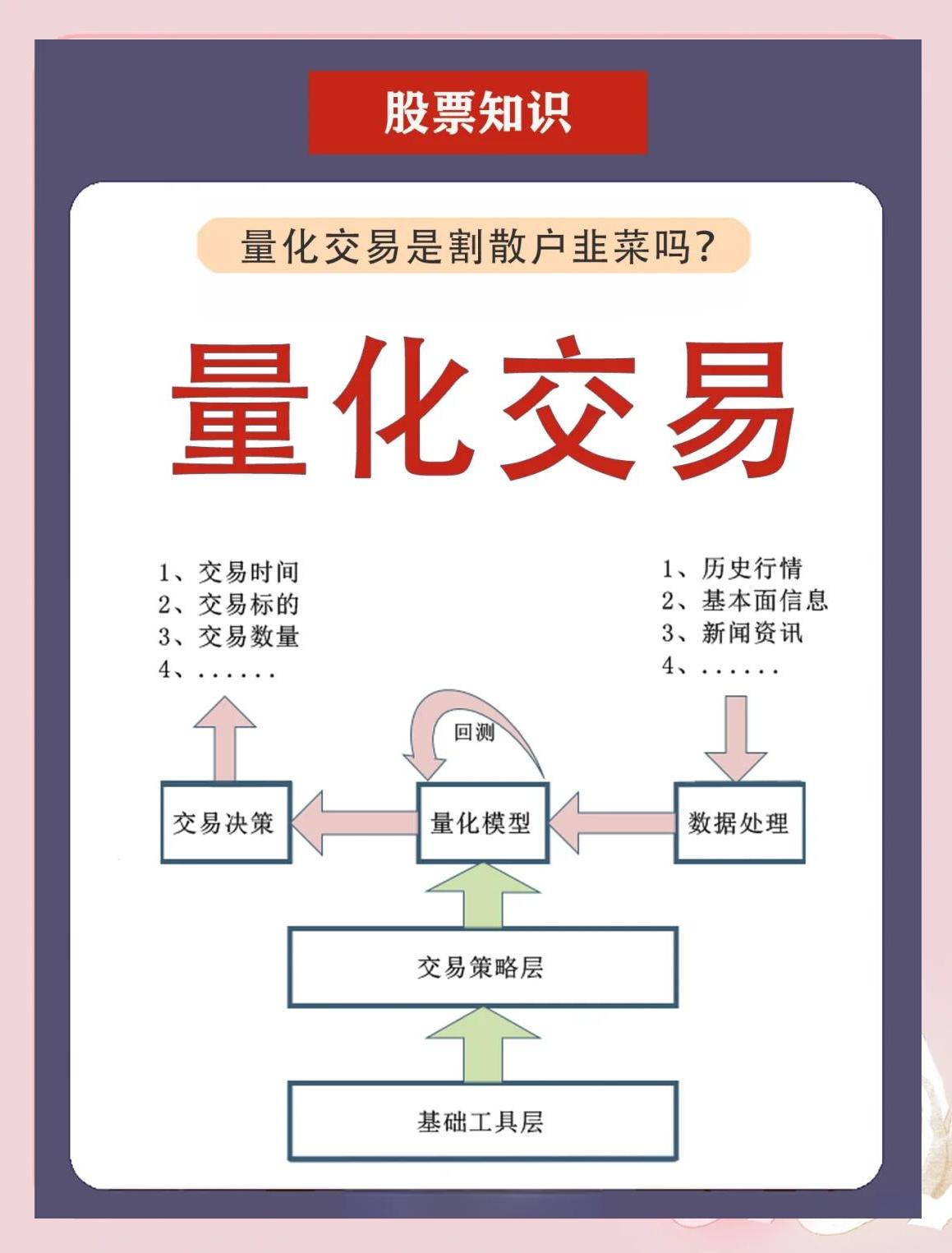

=================================================
Perpetual futures have revolutionized the derivatives market, offering traders a powerful way to speculate or hedge without worrying about contract expiration dates. For quantitative traders, 永续合约的量化交易模型 (quantitative trading models for perpetual futures) provide systematic frameworks to analyze, predict, and execute trades with precision. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the design principles, compare multiple strategies, discuss risk management, and present practical insights based on both personal experience and current market trends.
Understanding Perpetual Futures and Their Market Impact
What Are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual futures are derivatives contracts similar to traditional futures but without expiry dates. Traders can hold positions indefinitely, provided they maintain sufficient margin. Instead of settlement dates, these contracts use a funding rate mechanism to keep prices aligned with the spot market.
Why Perpetual Futures Are Popular Among Traders
The combination of leverage, liquidity, and 24⁄7 trading makes perpetual futures one of the most traded products in crypto and derivatives markets. This explains 为什么永续合约流行于交易市场 — they offer:
- Continuous exposure without rolling contracts
- Access to leverage up to 100x on some exchanges
- High liquidity and tight spreads on major trading platforms
Perpetual Futures Market Structure
Foundations of Quantitative Trading Models
The Role of Quantitative Models
Quantitative trading models use mathematical formulas, historical data, and algorithmic execution to make systematic decisions. For perpetual futures, they:
- Identify market inefficiencies
- Manage leverage exposure
- Automate entries and exits to avoid emotional bias
Key Model Components
- Signal Generation: Determines when to go long or short
- Position Sizing: Adjusts exposure based on volatility and account size
- Execution Layer: Minimizes slippage and transaction costs
- Risk Management: Ensures drawdowns remain within acceptable limits
Two Leading Quantitative Models for Perpetual Futures
1. Mean Reversion Model
Concept:
Prices tend to oscillate around a fair value. When prices deviate significantly, the model takes a position anticipating a return to the mean.
Example:
If BTC perpetual futures trade at a 2% premium to spot, the model might short futures and buy spot, profiting when prices converge.
Pros:
- High win rate in range-bound markets
- Clear mathematical threshold for trade signals
Cons:
- Poor performance during strong trends
- Requires constant recalibration of “fair value”
2. Trend-Following Model
Concept:
“Ride the wave” — when a strong trend is detected, the model enters in the direction of momentum and rides it until reversal signals appear.
Example:
If BTC breaks a major resistance with volume confirmation, the model enters long and uses a trailing stop-loss to lock profits.
Pros:
- Captures large moves during trending markets
- Simple to implement with moving averages or breakout signals
Cons:
- Frequent stop-outs in choppy conditions
- Lower win rate compared to mean reversion models
Recommended Model Combination
The most robust approach is often a hybrid system that detects market regimes and switches between mean reversion and trend-following models. For example:
- Use volatility filters to detect ranging vs. trending environments
- Allocate capital dynamically based on regime probability
This dynamic approach maximizes profitability across diverse market conditions and aligns with 如何分析永续合约交易趋势 for a data-driven decision-making process.
Model Optimization Techniques
1. Parameter Tuning
Backtest multiple parameter combinations (e.g., moving average lengths, z-score thresholds) to identify optimal settings. Avoid overfitting by using out-of-sample testing.
2. Leverage Control
Dynamic leverage adjustment based on volatility ensures consistent risk exposure. For example, reduce leverage during high funding rate periods to avoid unnecessary costs.
3. Execution Algorithms
Use smart order routing or TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) to minimize slippage, especially for high-frequency strategies.
Quantitative Model Optimization Workflow
Risk Management in Perpetual Futures Quant Models
Margin and Liquidation Risk
Perpetual contracts are leveraged instruments. Always size positions to avoid liquidation during normal volatility fluctuations.
Funding Rate Impact
Monitor funding rates closely. A high positive rate erodes profits for long positions; hedging or switching to short exposure can neutralize this cost.
Portfolio Diversification
Do not rely solely on one model or asset. Diversify across different contracts and strategies to smooth returns.
Advanced Strategies: High-Frequency and Market Making
Professional firms and algorithmic traders often deploy 永续合约的高频交易技巧 such as:
- Market-making bots that profit from bid-ask spreads
- Arbitrage between perpetual futures and spot markets
- Statistical arbitrage across multiple exchanges
While highly profitable, these strategies require significant infrastructure, co-location servers, and risk monitoring.
Tools and Platforms for Building Models
- Backtesting Frameworks: Python libraries like Backtrader, Zipline
- Data Providers: Kaiko, CryptoCompare, Binance API
- Execution Platforms: CCXT for API trading, custom-built execution engines
For beginners, consider exploring 初学者的永续合约交易指南 to understand the basics before implementing complex models.
Common Mistakes in Perpetual Futures Quant Models
- Overfitting: Models that perform well in backtests but fail in live trading.
- Ignoring Fees and Funding: Transaction costs can erode profitability.
- Underestimating Tail Risk: Sudden market crashes can wipe out accounts if stops fail.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
- AI-Powered Models: Machine learning increasingly used for signal generation
- Institutional Adoption: Hedge funds are building crypto-native quant desks
- Regulatory Oversight: Models must adapt to new compliance requirements
FAQ: Quantitative Trading Models for Perpetual Futures
1. Can retail traders successfully run quant models for perpetual futures?
Yes, but start small. Use simple models like moving average crossovers and gradually progress to multi-factor systems.
2. How much capital is required for effective model trading?
While some models can work with small capital, meaningful diversification usually requires at least \(5,000–\)10,000 for crypto perpetuals due to margin requirements.
3. How often should models be re-optimized?
Review performance monthly or quarterly. If market volatility shifts dramatically, recalibrate parameters sooner.
Conclusion: Building Smarter Perpetual Futures Strategies
The 永续合约的量化交易模型 is more than just a buzzword — it is a structured way to approach trading with discipline and consistency. By combining mean reversion, trend-following, and risk management techniques, traders can create robust systems that thrive across market cycles.
Take the next step: design your own quant model, backtest it thoroughly, and refine based on real-world performance. Share this article with fellow traders, comment with your favorite strategy, and join the conversation to make perpetual futures trading smarter and safer for everyone.
要不要我帮你整理一份 永续合约量化交易模型的参数优化清单(PDF 版),包含回测模板、风险计算公式和策略切换逻辑,方便你直接应用到实盘?