
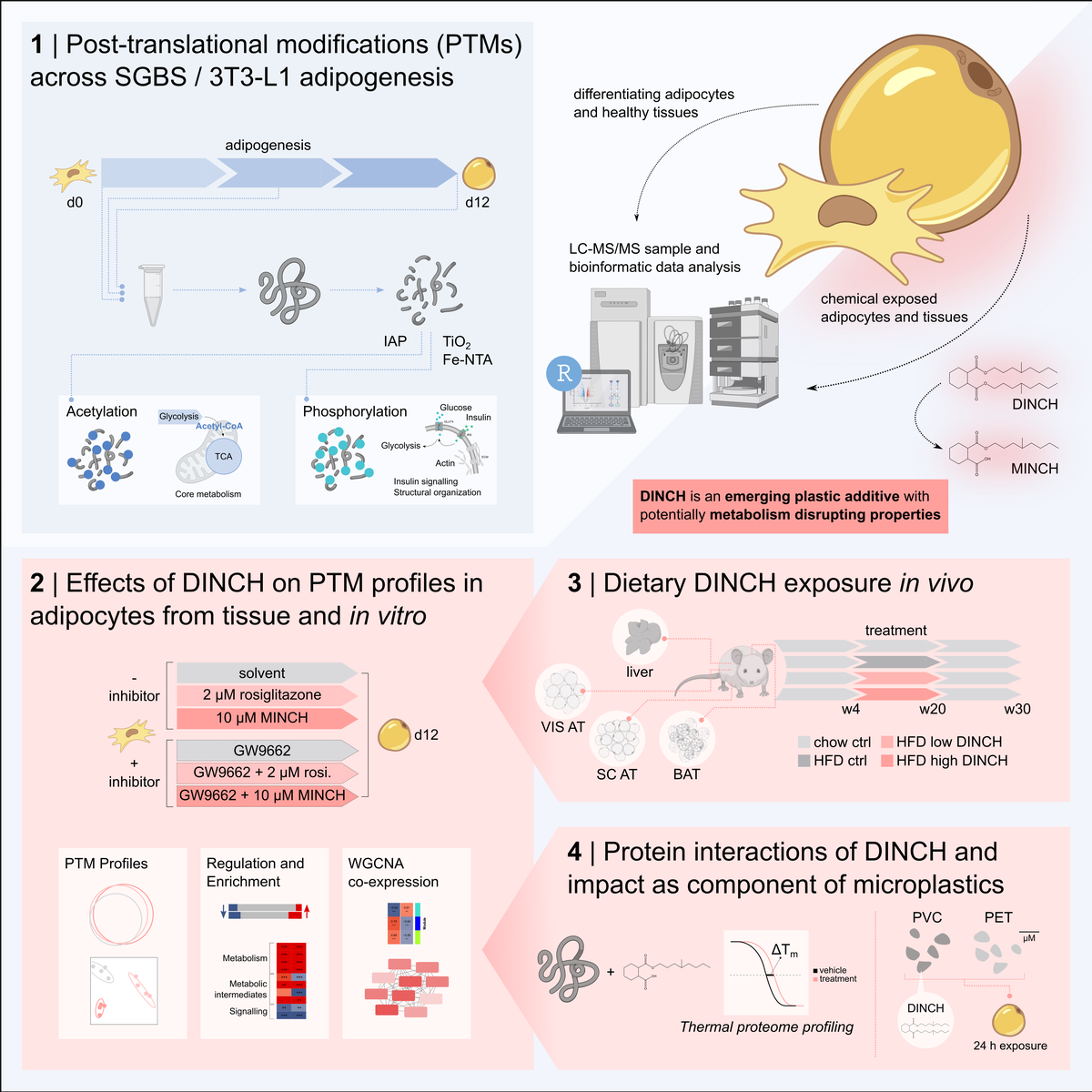
========================================
Perpetual futures have become one of the most dynamic trading instruments in the cryptocurrency and financial markets. Unlike traditional futures contracts that have fixed expiration dates, perpetual futures allow traders to hold leveraged positions indefinitely. To master this instrument, it is essential to understand not only the mechanics but also the strategies and tools involved. This tutorial on perpetual futures techniques will provide a structured guide for traders of all levels, backed by practical insights and professional analysis.
Introduction to Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures, sometimes called perpetual swaps, are derivative contracts that track the spot price of an asset without an expiry date. They are maintained through a funding rate mechanism, which balances long and short positions by periodically transferring payments between traders.
These instruments are especially popular in cryptocurrency markets because they allow high leverage, 24⁄7 trading, and hedging opportunities. Understanding how they function is the first step in learning advanced perpetual futures techniques.
Core Mechanics of Perpetual Futures
Funding Rates and Market Balance
Funding rates ensure that perpetual contracts track the underlying spot price. When the contract price trades above the spot market, longs pay shorts, and vice versa. This dynamic creates an incentive for market participants to correct the imbalance.
Leverage and Position Sizing
Traders can use leverage ranging from 2x up to 100x on some exchanges. Proper leverage selection is critical for managing risk. Excessive leverage can magnify profits but also lead to rapid liquidation.
Price Discovery Mechanism
Perpetual contracts use an index price, derived from multiple spot exchanges, to prevent manipulation and maintain a fair market value. This ties into how perpetual futures are priced, which is crucial for accurate trading decisions.
Perpetual futures price mechanism
Key Perpetual Futures Techniques
1. Trend-Following Strategy
This technique involves identifying long-term or short-term trends and entering positions in the same direction.
Advantages:
- Works well in strongly directional markets
- Easier to follow with standard indicators like moving averages
- Works well in strongly directional markets
Disadvantages:
- Can result in losses during range-bound markets
- Requires patience and discipline
- Can result in losses during range-bound markets
2. Mean Reversion Strategy
This strategy assumes prices will revert to their average after deviating significantly.
Advantages:
- Profitable in sideways or choppy markets
- Works with oscillators like RSI or Bollinger Bands
- Profitable in sideways or choppy markets
Disadvantages:
- High risk in trending markets
- May require strict stop-loss rules
- High risk in trending markets
3. Arbitrage Techniques
Arbitrage in perpetual futures often involves exploiting differences between:
Spot and perpetual prices (cash-and-carry arbitrage)
Funding rate inefficiencies across exchanges
Price discrepancies between similar perpetual pairs
Advantages:
- Lower directional risk
- Often consistent returns in efficient setups
- Lower directional risk
Disadvantages:
- Requires large capital and advanced execution tools
- Profit margins are thinner compared to speculative strategies
- Requires large capital and advanced execution tools
4. Hedging with Perpetual Futures
Many investors use perpetuals to hedge against price fluctuations in their spot holdings. For instance, holding Bitcoin in a wallet and shorting BTC perpetuals helps offset downside risk. This demonstrates why choose perpetual futures for hedging is a practical question for portfolio managers.
Risk Management in Perpetual Futures
Risk management is perhaps the most important perpetual futures technique. Without it, even the best strategies can lead to losses.
Position Sizing
Using proper position sizing prevents overexposure. A common rule is to risk no more than 1–2% of account equity per trade.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Setting predefined exit levels reduces emotional decision-making and protects capital.
Funding Rate Awareness
Monitoring funding rates avoids unnecessary losses, especially for long-term positions.
Diversification
Spreading risk across multiple currency pairs or strategies minimizes exposure to a single market shock.
Risk management in perpetual futures
Comparing Techniques: Trend-Following vs. Mean Reversion
| Feature | Trend-Following Strategy | Mean Reversion Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Market Type | Trending | Sideways/Range-bound |
| Risk Level | Moderate to High | High in trends |
| Tools Used | Moving Averages, MACD | RSI, Bollinger Bands |
| Suitability | Swing/Day Traders | Scalpers, Range Traders |
From personal experience, trend-following tends to outperform in crypto markets because of their frequent directional moves. However, combining it with mean reversion strategies in lower timeframes provides a more balanced trading approach.
Where to Learn Perpetual Futures Techniques
Aspiring traders can access structured learning materials such as:
- Exchange educational hubs (Binance Academy, Bybit Learn)
- Online trading communities and Discord groups
- Professional blogs and newsletters
- Practice on demo accounts before risking real funds
This aligns closely with where to learn about perpetual futures, a common concern for beginners looking to build a foundation in trading.
Advanced Tools for Perpetual Futures Traders
- TradingView: Technical charting with community strategies
- CoinGlass: Funding rate and liquidation data
- QuantConnect: Algorithmic trading frameworks
- 3Commas: Automated bots and portfolio management
These tools enhance both manual and automated perpetual futures techniques.
FAQ: Tutorial on Perpetual Futures Techniques
1. What is the best perpetual futures technique for beginners?
For beginners, trend-following with low leverage (2x–5x) is recommended. It’s simpler to learn and aligns with market momentum, reducing the risk of premature liquidation.
2. How do professionals manage risks in perpetual futures trading?
Professionals use strict position sizing, hedging strategies, and real-time monitoring of funding rates. They also diversify across multiple instruments and avoid excessive leverage.
3. Can perpetual futures be profitable long-term?
Yes, perpetual futures can be profitable long-term if traders combine effective strategies, robust risk management, and continuous learning. However, over-leveraging and neglecting funding costs are the main pitfalls that erode profitability.
Conclusion
This tutorial on perpetual futures techniques has covered the essential mechanics, strategies, risk management principles, and advanced tools for traders. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, mastering these techniques can help you navigate the complex yet rewarding world of perpetual futures.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your network and join the discussion below—your experience and insights could help others refine their trading journey.
Would you like me to also generate a meta description (SEO-optimized) and a title tag for this article so you can publish it directly with full on-page SEO?