============================================================
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of perpetual futures trading, credit risk assessment is a critical element for both retail and institutional investors. With perpetual futures contracts, traders speculate on the future price of an asset without any set expiration date, making these instruments highly leveraged and, therefore, highly risky. For retail traders, the concept of credit risk becomes especially crucial as it directly impacts their ability to maintain positions, margin calls, and even their overall profitability.
In this article, we will delve into how to assess credit risk for retail perpetual futures customers, explore various strategies for risk evaluation, and provide insights on effective mitigation methods. Additionally, we will compare different risk assessment strategies, their pros and cons, and recommend the most reliable practices for retail traders.
What is Credit Risk in Perpetual Futures?
Understanding Credit Risk
Credit risk refers to the possibility of a counterparty failing to meet its financial obligations, either due to insolvency, a lack of liquidity, or other financial difficulties. In the context of perpetual futures trading, credit risk can occur if the trader or the exchange involved fails to meet margin calls or liquidate positions in a timely manner.
For retail traders, the counterparty risk is associated with both the exchange and the brokerage firm handling their trades. Therefore, assessing credit risk for retail customers involves evaluating the reliability of these parties and the financial infrastructure that supports the perpetual futures market.
Why Credit Risk is Crucial for Perpetual Futures Traders
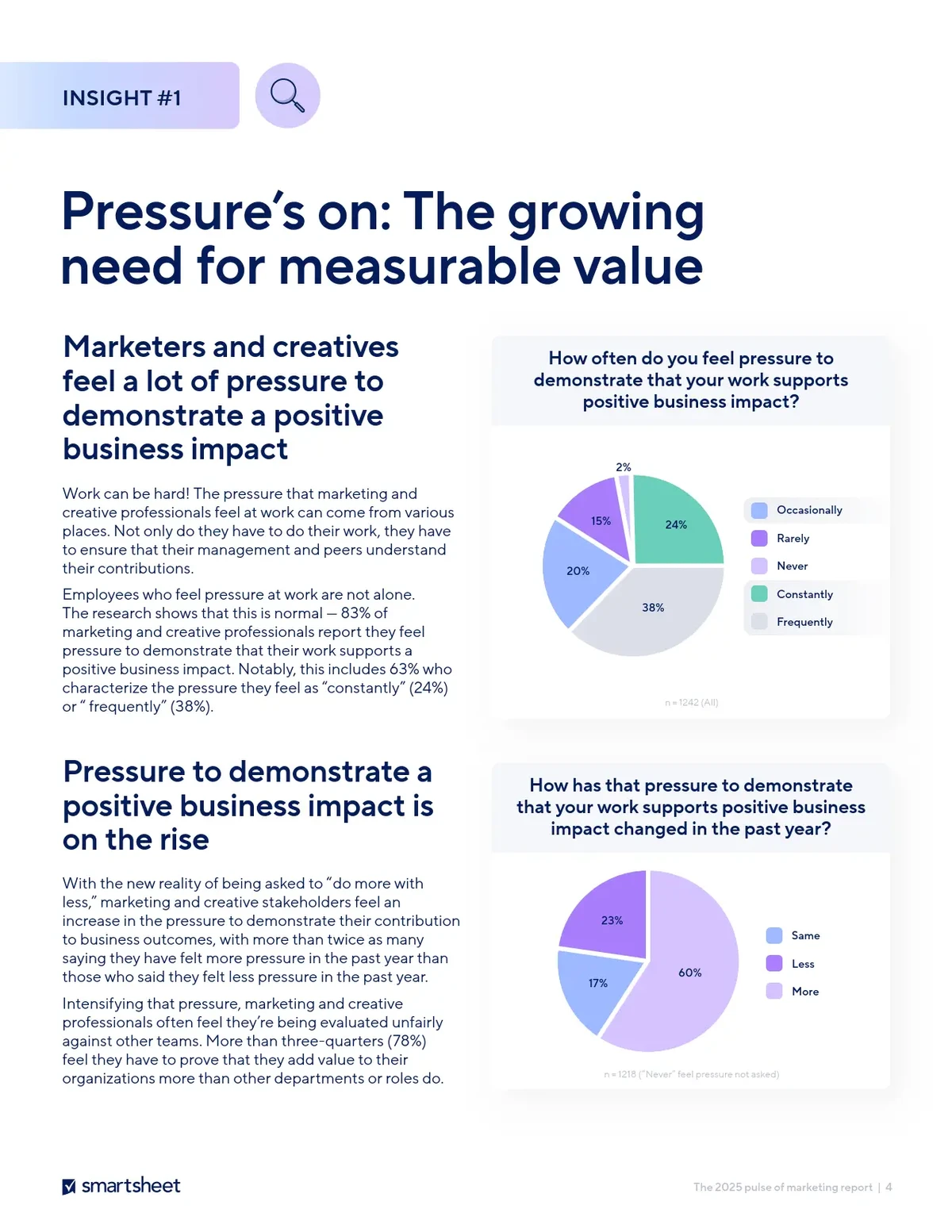
Retail traders using perpetual futures contracts typically employ significant leverage, which increases both potential gains and losses. The risk of losing more than the initial margin is always present, and without proper risk management, this could lead to substantial financial losses. As these contracts do not have an expiration date, they continue to accrue costs, making timely risk management more crucial.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition of Ratios | Numerical relationships measuring risk, reward, leverage, and performance |
| Importance for Amateurs | Provide structure, prevent impulsive trades, support long-term growth |
| Key Ratios | Risk-Reward Ratio, Leverage Ratio, Win Rate, Profit Factor, Sharpe Ratio |
| Risk-Reward Ratio | Compares potential profit to possible loss; simple to calculate |
| Leverage Ratio | Shows borrowed capital relative to equity; amplifies gains/losses |
| Win Rate & Profit Factor | Win rate = % of winning trades; profit factor = total profit ÷ total loss |
| Sharpe Ratio | Adjusts returns relative to volatility; evaluates risk-adjusted performance |
| Strategy 1 | Fixed Risk-Reward Scalping: 1:2 ratio, short timeframes, quick trades |
| Strategy 2 | Leverage Ratio Swing Trading: moderate leverage, multi-day positions, chart-based |
| Strategy Comparison | Scalping = high risk, day traders, RRR focus; Swing = moderate risk, amateurs, leverage & RRR |
| Common Mistakes | Ignoring risk management, overusing leverage, misinterpreting ratios, inconsistency |
| Best Practices | Start with risk-reward ratios, apply leverage cautiously, build consistency |
| Recommended Starting Ratio | 1:2 risk-reward ratio for beginners |
| Leverage Guidelines | Limit to 2x–5x for novices until risk control is mastered |
| Profit Guarantee | Ratios guide decisions but cannot eliminate risk; use with analysis and discipline |
1. Credit Rating of Trading Platforms
One of the first steps in assessing credit risk for retail perpetual futures traders is evaluating the creditworthiness of the trading platform or broker. This can be achieved through a detailed credit rating analysis. Many exchanges are publicly rated by independent financial rating agencies that assess their operational risk, liquidity, and overall financial health.
Pros:
- Provides an overall financial health check of the platform.
- Offers transparency on counterparty reliability.
Cons:
- Some platforms may not have available ratings or are newer and untested.
- Rating agencies might have limited scope in assessing all operational risks related to cryptocurrency or derivatives platforms.
2. Margin and Leverage Limits
Another important factor is understanding the margin and leverage limits set by the trading platform. Credit risk is directly influenced by the leverage that a retail trader uses to enter a perpetual futures position. Platforms that offer excessive leverage can pose a higher credit risk to traders, especially if they are not able to manage their positions effectively.
Pros:
- Allows traders to control risk exposure by limiting leverage.
- Platforms that have more stringent margin requirements can be less risky for retail traders.
Cons:
- Traders might face margin calls and forced liquidation if they fail to meet margin requirements, increasing the risk.
- Some platforms offer high leverage, attracting traders but increasing the risk of credit exposure.
3. Counterparty Risk Assessment
Counterparty risk refers to the risk that the platform or broker, as the intermediary in the trade, fails to settle trades or meet financial obligations. This risk can be evaluated by analyzing the exchange’s liquidity, the financial health of the institution managing the platform, and its track record of fulfilling its financial commitments.
Pros:
- Provides a clear view of the risk involved with the exchange itself.
- Ensures that users are trading with trustworthy parties.
Cons:
- Evaluating counterparty risk can be difficult, especially if the platform does not disclose financial data publicly.
- Newer or less-established platforms may lack transparency.
Key Strategies for Managing Credit Risk in Perpetual Futures
1. Diversification of Trading Positions
One of the best strategies for managing credit risk in perpetual futures is to diversify positions across multiple assets or exchanges. This helps spread the potential risk, reducing the impact of a single default or margin call.
Pros:
- Lowers the overall exposure to one specific asset or platform.
- Allows traders to balance risk more effectively across multiple instruments.
Cons:
- Requires more time and effort to manage multiple positions.
- Diversifying across different platforms can introduce additional operational risks.
2. Risk Monitoring Tools
Using risk management tools is essential for any retail trader, especially when dealing with leveraged products like perpetual futures. Tools like stop-loss orders, auto-liquidation mechanisms, and real-time risk dashboards help in monitoring and managing credit risk effectively. These tools automatically adjust positions to prevent traders from being exposed to unnecessary risks.
Pros:
- Automates risk management and helps in timely decision-making.
- Protects traders from emotional decision-making during volatile market conditions.
Cons:
- Not all platforms offer advanced risk management tools.
- Can lead to potential losses if the risk parameters are set too tightly.
Comparing Credit Risk Assessment Strategies
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Rating Analysis | Transparent assessment of platform health. | May not be available for newer platforms. |
| Margin & Leverage Limits | Direct control over leverage and risk exposure. | Potential for margin calls and forced liquidations. |
| Counterparty Risk Evaluation | Provides detailed analysis of financial stability. | May be hard to evaluate for new or decentralized platforms. |
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What factors influence credit risk in perpetual futures?
Several factors affect credit risk in perpetual futures, including the platform’s financial health, margin requirements, leverage levels, and counterparty reliability. The higher the leverage and the more volatile the market, the greater the risk to the trader. It is essential to consider the reputation and stability of the platform before trading.
2. How can traders mitigate credit risk in perpetual futures?
Traders can mitigate credit risk by using risk management tools like stop-loss orders and diversifying their positions across different assets or exchanges. Additionally, choosing a platform with strong security features and lower leverage limits can help reduce exposure to credit risk.
3. Why is credit risk important for retail perpetual futures investors?
Credit risk is crucial for retail investors in perpetual futures as these contracts are highly leveraged. A failure to assess the creditworthiness of the platform or the counterparty can result in significant financial loss. Proper credit risk assessment ensures that the investor is not exposed to unnecessary risks, including margin calls and platform insolvency.
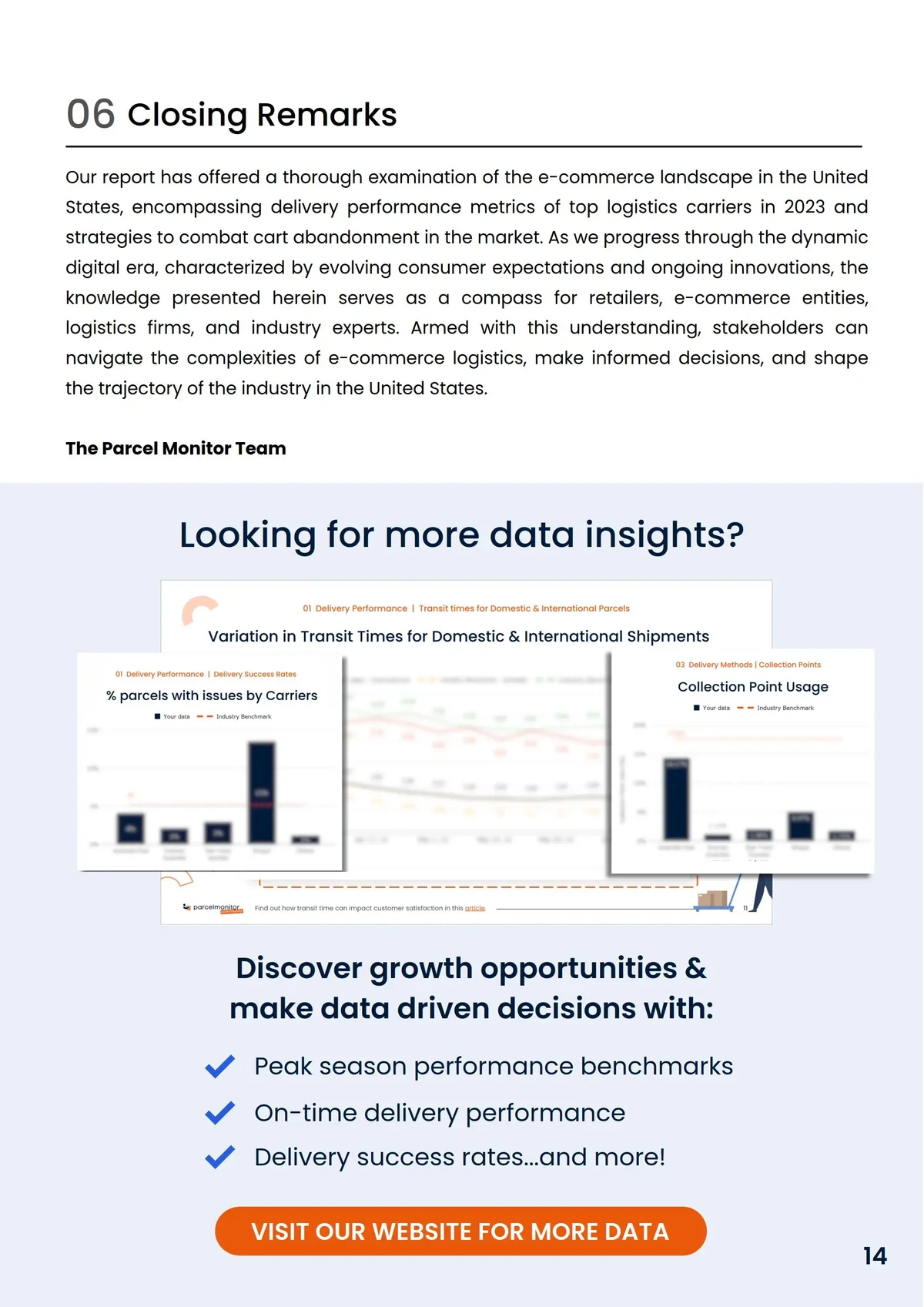
Conclusion
Assessing credit risk in perpetual futures trading is a complex but essential task for retail investors. By evaluating the financial stability of trading platforms, understanding leverage limits, and utilizing advanced risk management tools, traders can better protect themselves from potential losses. Diversification and using stop-loss strategies are key practices that can help manage credit risk more effectively.
By implementing these strategies, retail traders can reduce their exposure to unexpected financial setbacks and navigate the high-risk world of perpetual futures with greater confidence and security.