

=============================================================================================
The Efficient Frontier is one of the most important concepts in modern portfolio theory (MPT) and continues to be a core principle for investors looking to optimize their portfolios. It represents the set of portfolios that maximizes expected return for a given level of risk, or alternatively, minimizes risk for a given level of return. Understanding and applying the Efficient Frontier has become essential for both institutional and individual investors aiming to improve portfolio performance and risk management. This article explores the concept of the Efficient Frontier, how it is applied, and the strategies and tools used by professional investors to optimize their portfolios.
What is the Efficient Frontier?
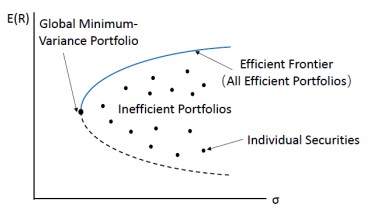
The Efficient Frontier is a graphical representation of the trade-off between risk and return. In the context of investment portfolios, it shows the optimal portfolios that offer the highest expected return for a given level of risk, or conversely, the lowest risk for a given return. The Efficient Frontier was introduced by Harry Markowitz in 1952 as part of his Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT), which revolutionized the way investors view portfolio construction.
Key Characteristics of the Efficient Frontier
- Risk-Return Tradeoff: Portfolios on the Efficient Frontier balance the risk of investment (usually measured by standard deviation) and the expected return. Investors can select a portfolio that suits their risk tolerance and return expectations.
- Diversification: The Efficient Frontier emphasizes the importance of diversification, where combining different assets or asset classes can reduce risk without sacrificing return.
- Portfolios Below the Frontier: Any portfolio below the Efficient Frontier is considered suboptimal, as it means the portfolio is not taking full advantage of the potential return for its level of risk.
How the Efficient Frontier is Calculated
To calculate the Efficient Frontier, investors use the following variables:
- Expected Returns: The average return an investor expects from each asset.
- Covariances and Correlations: The relationship between the returns of different assets, which shows how they move relative to one another.
- Standard Deviations: The measure of volatility or risk of an asset.
Using these inputs, an optimization model is built that maximizes returns for a given level of risk or minimizes risk for a desired return. The result is a curve that represents the Efficient Frontier, with the ideal portfolio being a point on that curve.
Strategies to Optimize the Efficient Frontier
Optimizing the Efficient Frontier involves selecting the right mix of assets that maximize return while minimizing risk. There are several strategies employed by institutional investors and quantitative analysts to achieve this optimization.
1. Mean-Variance Optimization (MVO)
One of the most common approaches for finding the Efficient Frontier is Mean-Variance Optimization (MVO). This method uses historical data on asset returns, variances, and covariances to calculate the portfolio that offers the highest expected return for a given level of risk. MVO relies on the assumption that investors are risk-averse, meaning they prefer lower risk for a given level of return.
Pros:
- Systematic Approach: Provides a structured framework for optimizing portfolios.
- Widely Used: It is the foundation of many asset management strategies and software tools.
Cons:
- Relies on Historical Data: MVO assumes that future returns will follow similar patterns to historical data, which may not always hold true.
- No Consideration of Extreme Events: MVO does not account for outliers or “black swan” events, which can have a significant impact on portfolios.
2. Black-Litterman Model
The Black-Litterman Model is an extension of the Mean-Variance Optimization method. Developed by Fischer Black and Robert Litterman, this model incorporates investor views or market opinions on asset returns to adjust the Efficient Frontier. The model combines subjective opinions with historical data to generate more balanced portfolio allocations.
Pros:
- Flexible and Intuitive: Allows investors to express views on market conditions and adjust the portfolio accordingly.
- Better Results: It often produces more realistic and stable portfolio allocations than traditional MVO.
Cons:
- Complexity: The model requires advanced understanding of statistical methods and market forecasting.
- Subjectivity: The inclusion of subjective views can lead to bias in the final portfolio.
3. Risk Parity
The Risk Parity approach is another popular method for optimizing portfolios. This strategy focuses on balancing the risk contributions from each asset class, rather than equally weighting the assets. The idea is to allocate capital in a way that each asset class contributes equally to the overall risk of the portfolio, which can lead to better risk-adjusted returns.
Pros:
- Risk Diversification: It helps ensure that no single asset class dominates the risk exposure in the portfolio.
- Stable Risk Exposure: By focusing on risk rather than return, Risk Parity portfolios can deliver more consistent results.
Cons:
- Lower Expected Return: This strategy may lead to lower overall returns compared to traditional asset allocation methods.
- Requires Active Monitoring: It requires ongoing adjustments to maintain the desired risk balance.
4. Machine Learning and AI for Portfolio Optimization
Recent advancements in machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) have opened up new opportunities for optimizing the Efficient Frontier. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of market data, identify patterns, and optimize portfolios with greater precision than traditional methods.
Pros:
- Data-Driven Insights: AI models can process large datasets and uncover hidden relationships between assets.
- Adaptability: Machine learning models can adapt to changing market conditions, improving portfolio optimization in dynamic environments.
Cons:
- Complexity: The development and implementation of machine learning models can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Overfitting Risk: There is a risk that machine learning models may overfit to historical data, leading to poor performance in live markets.
The Importance of the Efficient Frontier in Modern Investing
The Efficient Frontier is crucial for institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and private equity firms, as it allows them to optimize risk and return for large portfolios. Additionally, understanding the Efficient Frontier can help individual investors select the most appropriate mix of assets that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Applying the Efficient Frontier in Perpetual Futures
In the context of perpetual futures, the Efficient Frontier can be an invaluable tool for managing risk and maximizing returns. By using perpetual futures contracts, investors can take advantage of leveraged positions, which can amplify both potential returns and risks. The Efficient Frontier helps determine the optimal amount of leverage and asset allocation that minimizes risk while maximizing the expected return.
How to Calculate the Efficient Frontier with Perpetual Futures
When calculating the Efficient Frontier for perpetual futures, investors must consider:
- Volatility of the futures market.
- Leverage used.
- Correlation between the underlying asset and the futures contract.
By applying the Efficient Frontier model, traders can identify the ideal mix of spot positions and futures contracts to achieve the highest return for a given level of risk.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between the Efficient Frontier and traditional asset allocation?
The Efficient Frontier focuses on optimizing portfolios based on the risk-return trade-off, while traditional asset allocation typically involves selecting a fixed percentage of assets in different categories (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.). The Efficient Frontier provides a more sophisticated approach by identifying the best possible combinations of assets that yield the highest return for the lowest risk.
2. Can individual investors use the Efficient Frontier?
Yes, individual investors can use the Efficient Frontier as part of their portfolio optimization process. Many online investment tools and financial advisors offer Efficient Frontier analysis, allowing individual investors to create portfolios that are better aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
3. What tools are available to calculate the Efficient Frontier?
There are several tools available for calculating the Efficient Frontier, including financial modeling software such as MATLAB, R, and Python. Many brokers and asset managers also offer portfolio optimization tools that use the Efficient Frontier to help investors optimize their portfolios.
Conclusion
The Efficient Frontier is an essential concept in portfolio optimization, helping investors achieve the best possible return for a given level of risk. With the rise of modern strategies such as machine learning, Risk Parity, and Black-Litterman Models, institutional investors can enhance their portfolio performance and gain a competitive edge. Whether you are a professional investor or an individual looking to optimize your portfolio, understanding the Efficient Frontier is crucial for making informed and data-driven investment decisions.