

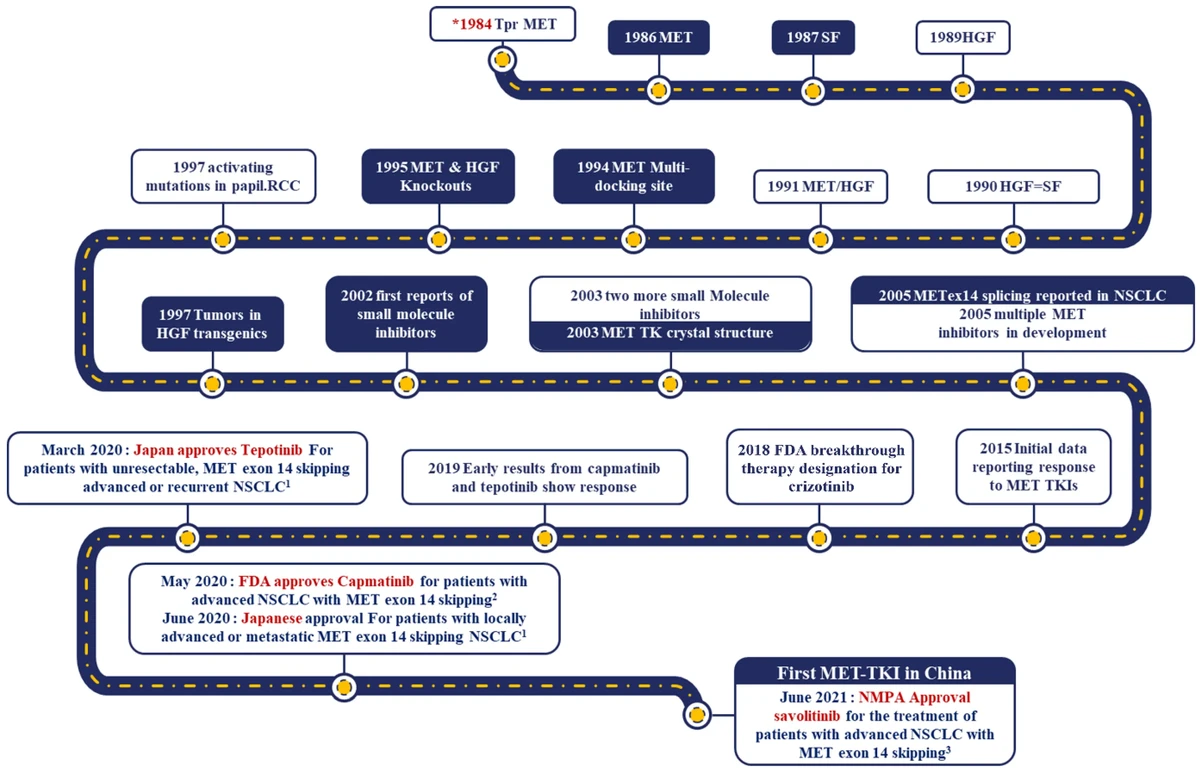
Understanding risk in perpetual futures trading requires more than analyzing charts or watching funding rates. One of the most reliable measures for capturing market sensitivity is beta, a statistical metric that evaluates how a perpetual futures contract moves in relation to its benchmark, usually Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH). This comprehensive step-by-step guide to beta calculation in perpetual futures will walk you through theory, methods, tools, and advanced applications—giving both beginners and professionals actionable insights.
What Is Beta in Perpetual Futures?
Beta measures the sensitivity of a perpetual futures contract’s returns relative to the market benchmark. A beta value helps traders and investors understand whether a position is more volatile (beta > 1), less volatile (beta < 1), or moves in the opposite direction (negative beta) compared to the chosen index.
For example:
- A perpetual futures contract with a beta of 1.5 moves 1.5% for every 1% move in Bitcoin.
- A beta of 0.5 means the asset is less volatile than Bitcoin.
- A beta of -1 suggests the position moves in the opposite direction of the benchmark.
Knowing this value answers critical questions such as How does beta affect perpetual futures trading?, especially in leveraged positions where risk is magnified.
Why Is Beta Important in Perpetual Futures?
Beta is not just an academic concept—it has practical applications in trading strategies:
- Risk Assessment – Traders can align their portfolio with desired volatility.
- Hedging – By knowing beta, traders can hedge exposure more precisely using inverse perpetual contracts.
- Portfolio Diversification – Beta reveals whether a contract moves independently or follows the benchmark too closely.
- Leverage Adjustments – Traders can modify leverage size based on contract volatility relative to the market.
Step-by-Step Guide to Beta Calculation
Step 1: Collect Price Data
To calculate beta, you need historical price data for both:
- The perpetual futures contract (e.g., ETH-USDT Perpetual).
- The market benchmark (e.g., BTC spot index).
Data frequency can vary—daily, hourly, or minute-by-minute—depending on your trading style. For intraday traders, high-frequency data is crucial.
Step 2: Calculate Returns
Returns are calculated as percentage changes in price:
\[ R_t = \frac{P_t - P_{t-1}}{P_{t-1}} \]
Where:
- \(R_t\) = return at time t
- \(P_t\) = price at time t
Both the perpetual contract and the benchmark require return series.
Step 3: Run Regression Analysis
The standard formula for beta is derived from regression:
\[ R_{perp} = \alpha + \beta R_{benchmark} + \epsilon \]
- \(R_{perp}\): Return of perpetual futures
- \(R_{benchmark}\): Return of BTC/ETH index
- \(\beta\): Sensitivity coefficient
This regression gives you beta and alpha (the excess return not explained by the benchmark).
Step 4: Interpret Beta
- Beta > 1: High volatility, higher risk, and amplified returns/losses.
- Beta = 1: Moves in line with the benchmark.
- Beta < 1: Less sensitive, defensive behavior.
- Beta < 0: Inverse relationship, useful for hedging.
Step 5: Validate and Adjust
Recalculate beta using different time windows to confirm stability. For example, a 30-day rolling beta can reveal changes in market dynamics.
Methods for Calculating Beta
1. Covariance/Variance Method
\[ \beta = \frac{Cov(R_{perp}, R_{benchmark})}{Var(R_{benchmark})} \]
This method calculates beta directly from statistical formulas without regression.
Pros: Straightforward, quick calculation.
Cons: Less informative since it doesn’t provide alpha or error terms.
2. Regression Method
Regression provides both beta and alpha, making it more useful for professional analysis. Many platforms like RStudio, Python libraries (statsmodels), and Excel can run this.
Pros: More detailed insights.
Cons: Requires more data and statistical tools.
3. Rolling Beta Analysis
Traders often use rolling windows (e.g., 90-day beta) to track changes over time. This method adapts to volatility regimes.
Pros: Dynamic and adaptable to market conditions.
Cons: More complex and computationally demanding.
Step-by-step beta calculation framework with data collection, return calculation, regression, and interpretation.
Comparing Beta Calculation Methods
| Method | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Covariance/Variance | Quick checks | Simple, fast | Limited insights |
| Regression | Professional trading strategies | Provides alpha + confidence levels | Requires statistical knowledge |
| Rolling Beta | Dynamic markets (crypto, futures) | Adapts to volatility | Resource intensive |
Applications of Beta in Perpetual Futures
1. Portfolio Hedging
If your ETH perpetual contract has a beta of 1.2 relative to BTC, you can hedge exposure by shorting BTC perpetuals proportionally. This precise alignment makes hedges more efficient.
2. Risk-Adjusted Leverage
A trader with a 2x leverage position on a beta 1.5 contract is effectively taking 3x market risk. Beta allows adjusting leverage responsibly.
3. Alpha-Seeking Strategies
Beta helps filter systematic market risk. Traders looking for “alpha” (excess returns) adjust for beta to isolate performance not tied to market movement.
This is why guides like How to calculate beta in perpetual futures? remain essential for professionals seeking an analytical edge.
Advanced Beta Techniques for Experienced Traders
- Multifactor Beta Models – Instead of just BTC, use multiple benchmarks (ETH, altcoin index, volatility index).
- Beta with Funding Rates – Incorporate funding costs to calculate “net beta” in leveraged positions.
- Machine Learning Forecasting – AI models can predict beta shifts before they occur.
For institutions, resources such as Beta analysis for institutional investors in perpetual futures provide deeper frameworks for managing large portfolios.
Case Study: Retail vs. Institutional Use
- Retail Trader – Uses beta to size positions, avoiding excessive leverage. Example: Avoiding a beta 2.0 altcoin perpetual when trading on margin.
- Institutional Trader – Uses rolling beta and multifactor models to construct market-neutral strategies (long/short across correlated assets).

Beta applied in hedging, leverage adjustment, and alpha-seeking strategies.
Common Mistakes in Beta Calculation
- Short Data Windows – Using only a few days of data can produce misleading betas.
- Ignoring Non-Stationarity – Crypto markets evolve quickly; recalculation is essential.
- Benchmark Errors – Choosing the wrong benchmark (e.g., using ETH for a BTC perpetual) leads to misinterpretation.
- Blind Reliance – Beta is just one risk metric; it should complement, not replace, other tools.
FAQ: Beta in Perpetual Futures
1. Can beta change over time in perpetual futures?
Yes. Beta is dynamic and can shift rapidly due to liquidity changes, market volatility, or correlations breaking down. Rolling betas are best for tracking these shifts.
2. Should I calculate beta manually or use trading platforms?
Beginners can rely on beta calculators or exchange analytics. Advanced traders often use Python or R for custom calculations to adapt models to their strategies.
3. How does beta impact my leverage decisions?
If a perpetual contract has a beta of 2, trading it with 5x leverage means your effective market exposure is 10x. Understanding beta prevents unintended overexposure.
Conclusion: Why Beta Matters More Than Ever
In the volatile world of perpetual futures, beta is not just an academic measure—it’s a survival tool. By calculating and interpreting beta, traders gain clarity on risk, enhance hedging strategies, and build disciplined leverage management.
Whether you’re a beginner calculating covariance manually or an institutional desk deploying rolling regressions, mastering beta is essential for sustainable profits.
If this step-by-step guide to beta calculation in perpetual futures helped you, share it with your trading community, comment with your experiences, and join the discussion to refine collective knowledge.