
========================================================
Alpha is one of the most widely discussed performance metrics in modern investing. It represents a portfolio’s excess return relative to a benchmark, adjusted for risk. Knowing how to calculate alpha in trading accurately can make the difference between building a truly superior strategy and simply riding market beta. In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore alpha’s definition, calculation methods, advanced techniques, and practical tips for traders and portfolio managers.
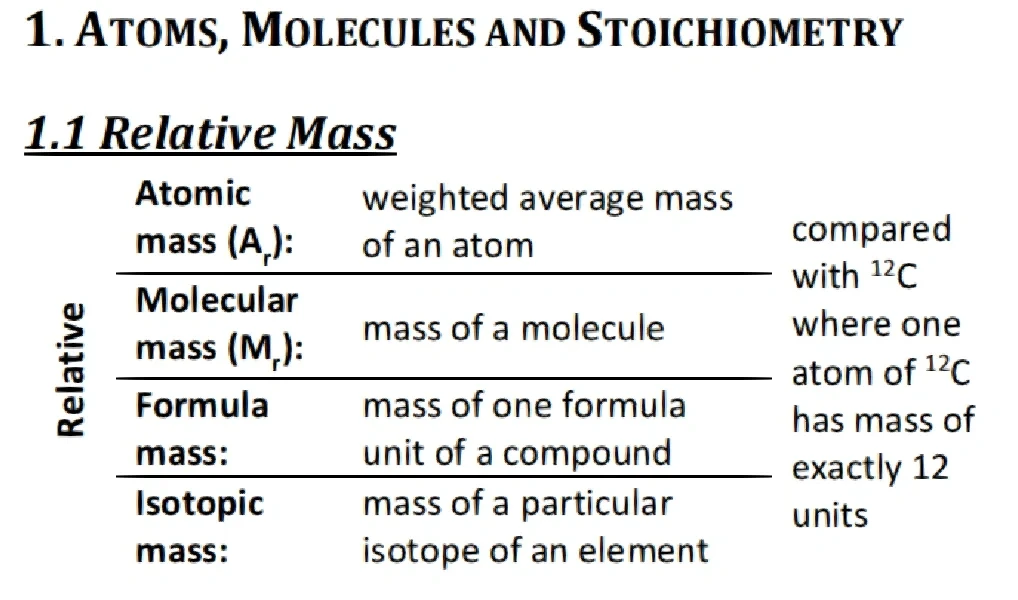
Understanding Alpha: The Basics
What Is Alpha in Trading?
In simple terms, alpha measures how much value an investment strategy adds beyond what could be explained by market movements (beta). If a strategy has an alpha of +2%, it means it outperformed its benchmark by 2% on a risk-adjusted basis.
Why Alpha Matters
Alpha is a cornerstone of quantitative investing, used to evaluate fund managers, hedge funds, and algorithmic strategies. It helps investors identify whether returns stem from genuine skill or from market exposure.
Alpha vs. Beta
- Beta measures sensitivity to market movements.
- Alpha measures skill-based excess return over the benchmark.
This distinction helps you compare strategies objectively and allocate capital more efficiently.
Visualizing Alpha vs. Beta on a performance chart
Core Formula: How to Calculate Alpha
Standard CAPM Formula
The most common method of calculating alpha uses the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM):
Alpha=Rp−[Rf+β(Rm−Rf)]\text{Alpha} = R_p - [R_f + \beta (R_m - R_f)]Alpha=Rp−[Rf+β(Rm−Rf)]
Where:
- RpR_pRp = Portfolio return
- RfR_fRf = Risk-free rate
- RmR_mRm = Market return
- β\betaβ = Portfolio beta
This formula gives you the excess return (alpha) over the expected return given your risk exposure.
Practical Steps
- Select a benchmark index that best represents your portfolio’s asset class.
- Calculate your portfolio’s beta using regression analysis.
- Plug in returns, risk-free rate, and beta into the CAPM formula.
- The residual is your alpha.
Method 1: Regression-Based Alpha
How It Works
This approach involves running a linear regression of portfolio returns versus benchmark returns. The intercept of the regression line represents alpha.
Pros
- Statistically rigorous.
- Incorporates time-series data.
- Useful for multi-factor models.
Cons
- Requires sufficient data history.
- Sensitive to outliers and market anomalies.
Method 2: Factor Model Alpha
How It Works
Instead of relying on a single benchmark, factor models (like Fama-French) decompose returns into multiple drivers—size, value, momentum, etc. Alpha becomes the residual unexplained by these factors.
Pros
- More comprehensive for complex strategies.
- Reduces false positives of skill-based returns.
- Helps identify hidden exposures.
Cons
- Data-intensive and complex.
- Requires specialized software or quant skills.
Factor model analysis showing alpha residuals
Comparing the Two Methods
| Method | Best For | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regression-Based Alpha | Traditional portfolios | Simple, widely understood | Less accurate for multi-factor exposures |
| Factor Model Alpha | Complex, quant strategies | More robust, accounts for style factors | Requires advanced analytics and data |
Recommendation: For retail or beginner traders, regression-based alpha is a great start. For institutional strategies or hedge funds, factor model alpha gives a clearer picture of true skill.
Advanced Techniques to Refine Alpha Calculation
Rolling Windows
Calculate alpha over rolling time frames (e.g., 12-month rolling) to detect performance persistence.
Adjusting for Nonlinear Risk
For options or leveraged products, beta may vary with market conditions. Advanced methods like conditional beta estimation can yield more accurate alpha.
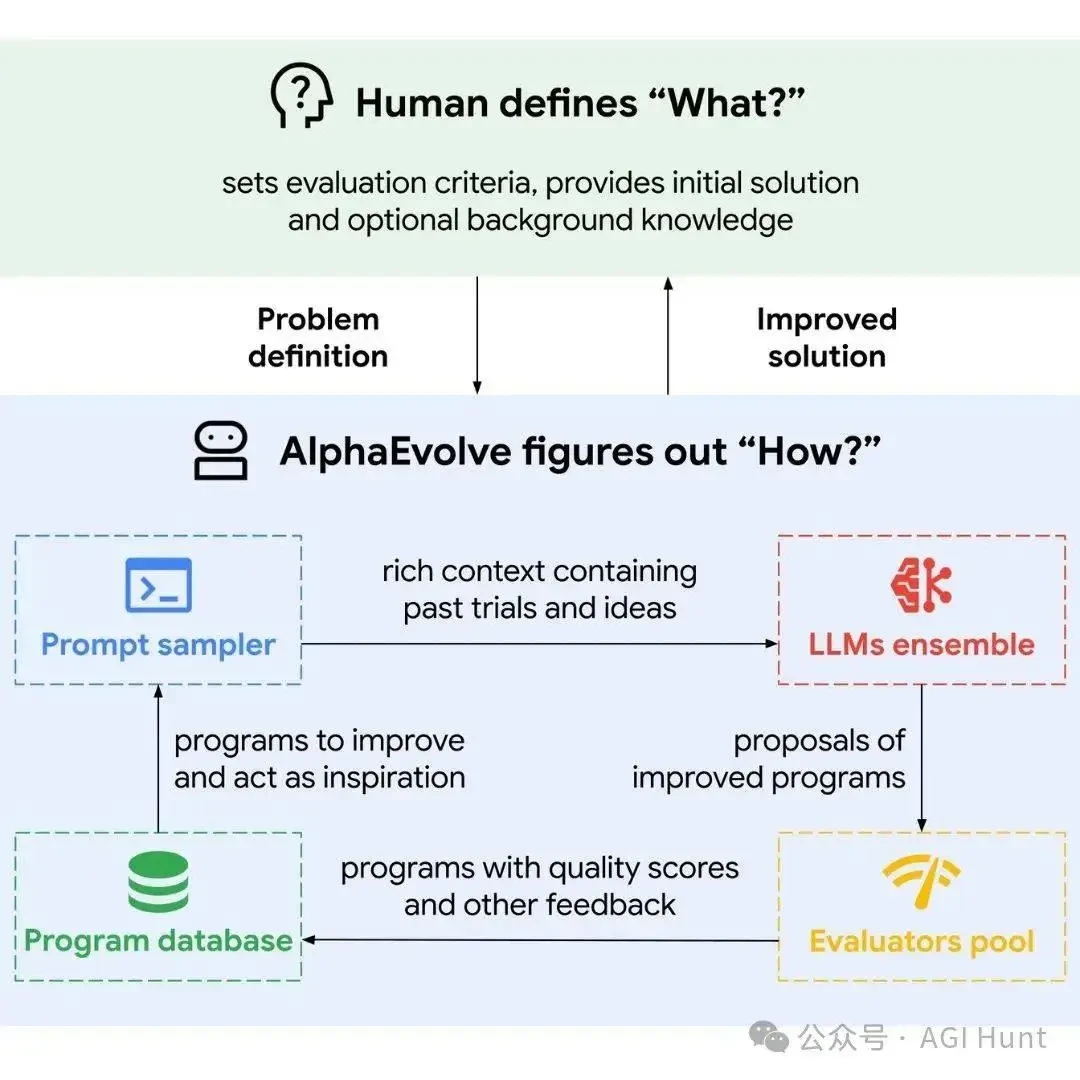
Integrating Alpha Into Strategy Design
Learning how to use alpha in perpetual futures or other derivatives helps traders identify mispricings and execute strategies with better risk-adjusted returns.
Common Pitfalls in Alpha Measurement
- Benchmark Mismatch: Choosing the wrong benchmark can distort alpha.
- Ignoring Fees and Slippage: Always use net-of-cost returns.
- Short Data Windows: Insufficient data may produce misleading alpha estimates.
- High Alpha Misinterpretation: Remember, why high alpha can be misleading—it could stem from hidden risks rather than skill.
Practical Example
Let’s say your strategy returned 12% over a year. The risk-free rate was 2%, the market returned 8%, and your beta is 1.1:
Alpha=12%−[2%+1.1(8%−2%)]=12%−[2%+6.6%]=3.4%\text{Alpha} = 12\% - [2\% + 1.1(8\% - 2\%)] = 12\% - [2\% + 6.6\%] = 3.4\%Alpha=12%−[2%+1.1(8%−2%)]=12%−[2%+6.6%]=3.4%
Your strategy generated an alpha of 3.4%, meaning it outperformed on a risk-adjusted basis.
Alpha calculation example with formula breakdown
Using Alpha Metrics in Practice
For Portfolio Managers
Evaluate strategies, allocate capital, and reward managers based on risk-adjusted alpha.
For Quant Traders
Backtest alpha factors, optimize position sizing, and build alpha-driven algorithms.
For Retail Investors
Compare fund performance beyond headline returns. Identify whether managers truly add value.
FAQ: How to Calculate Alpha in Trading
1. How do I find reliable alpha metrics?
Look for platforms offering clean historical data and analytics, such as Bloomberg, Morningstar, or specialized quant platforms. These sources make it easier to know where to get reliable alpha metrics without manual calculation.
2. How can I improve alpha in my strategies?
Focus on improving execution quality, diversifying factors, and reducing costs. Many traders build custom signals or use proprietary data to enhance alpha—this is at the heart of how to improve alpha in strategies.
3. Why is alpha important for investment decisions?
Alpha shows whether a strategy’s returns are due to genuine skill. Knowing why alpha matters in investment decisions can help investors avoid paying high fees for beta exposure and instead allocate to true outperformers.
Conclusion: Mastering Alpha Calculation
Knowing how to calculate alpha in trading empowers traders, analysts, and investors to evaluate performance accurately. Start with the CAPM formula and regression-based alpha, then graduate to factor models for a deeper view of your strategy’s drivers. Avoid common pitfalls, select appropriate benchmarks, and use rolling analyses to monitor alpha stability.
By mastering alpha, you can make smarter investment decisions, design stronger trading systems, and clearly separate skill from luck.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your network or comment below with your experiences calculating and using alpha in your own strategies. Your feedback helps refine best practices for the entire trading community.