
=================================================================
Introduction
In the world of trading and investing, risk and reward are two inseparable companions. For risk-averse investors, the challenge is not just achieving returns but ensuring that these returns are earned with the least possible risk. This is where Sharpe Ratio analysis for risk-averse investors becomes invaluable.
The Sharpe Ratio, developed by Nobel laureate William F. Sharpe, is one of the most widely used metrics for evaluating risk-adjusted performance. It helps investors measure how much excess return they are receiving for the volatility endured. In other words, it is a tool that turns raw numbers into actionable insights for cautious investors who want stability over speculation.
This article explores the concept in depth, discusses strategies, compares the Sharpe Ratio with other metrics, and provides practical tips to help risk-averse investors make better portfolio decisions. We will also naturally integrate related topics such as what is the importance of Sharpe Ratio in futures trading and how to calculate Sharpe Ratio in perpetual futures, ensuring the discussion remains both practical and SEO-friendly.
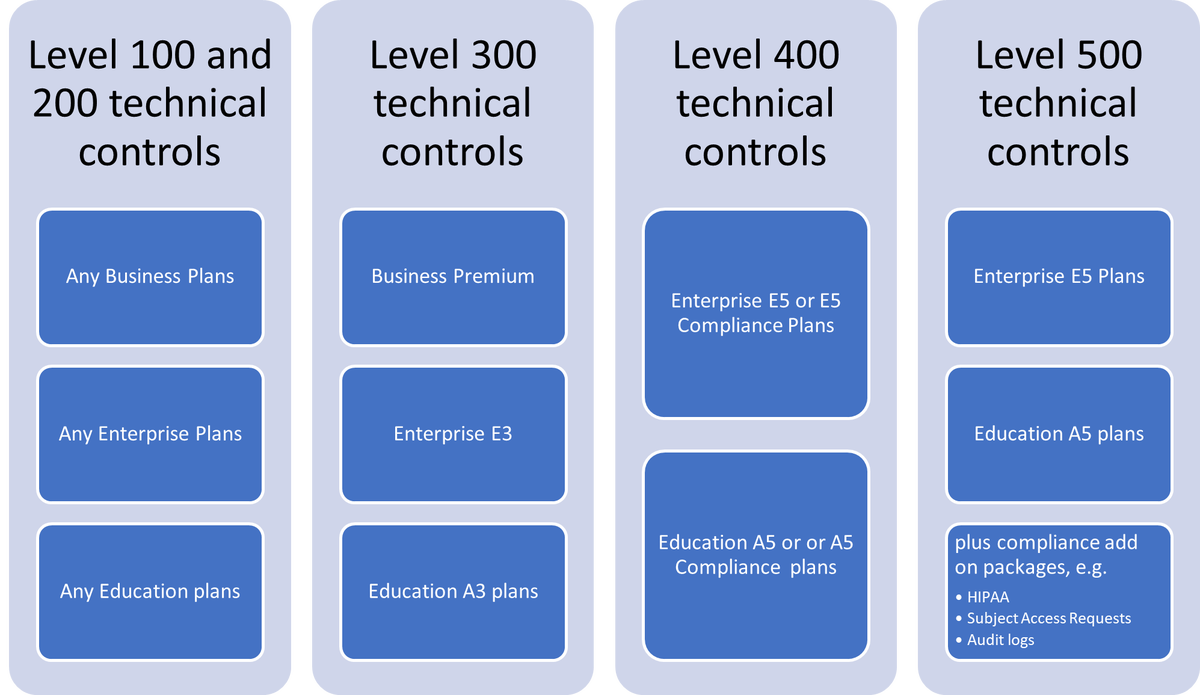
What is the Sharpe Ratio?
The Sharpe Ratio measures the excess return of an investment over the risk-free rate, divided by its volatility (standard deviation of returns).
Formula:
Sharpe Ratio=Rp−RfσpSharpe\ Ratio = \frac{R_p - R_f}{\sigma_p}Sharpe Ratio=σpRp−Rf
Where:
- RpR_pRp = Portfolio return
- RfR_fRf = Risk-free rate (e.g., treasury bonds)
- σp\sigma_pσp = Standard deviation of portfolio returns (risk/volatility)
For risk-averse investors, the Sharpe Ratio is crucial because it answers the question: Am I being adequately compensated for the risk I am taking?
Understanding the Sharpe Ratio formula helps investors quantify risk-adjusted returns.
Why Sharpe Ratio Matters for Risk-Averse Investors
1. Focus on Risk-Adjusted Returns
While many investors chase raw returns, risk-averse investors prioritize consistency and stability. The Sharpe Ratio eliminates the illusion of high returns by factoring in volatility.
2. Comparison Across Assets
Risk-averse investors often diversify into multiple asset classes. The Sharpe Ratio allows comparison between stocks, bonds, crypto, and even perpetual futures, ensuring fair benchmarking.
3. Portfolio Optimization
Sharpe Ratio analysis highlights which assets improve or weaken a portfolio’s efficiency, guiding investors toward optimal allocation decisions.
Two Approaches to Sharpe Ratio Analysis
Method 1: Static Historical Analysis
Description: This method uses historical returns and volatility data to compute the Sharpe Ratio over a fixed period (e.g., 1 year).
Pros:
- Easy to calculate.
- Provides a clear snapshot of past risk-adjusted performance.
- Useful for evaluating fund managers or ETFs.
Cons:
- Backward-looking; may not reflect future risk.
- Assumes volatility is constant, which may not hold true.
Method 2: Dynamic Forward-Looking Analysis
Description: Incorporates forecasted returns, implied volatility, and scenario analysis to predict Sharpe Ratios under future conditions.
Pros:
- Proactive approach suitable for uncertain markets.
- Can incorporate stress testing and probability models.
- Helps investors prepare for volatility shifts.
Cons:
- Requires more data and technical modeling.
- Forecasts may be inaccurate if assumptions are flawed.
Which Method Works Best?
For risk-averse investors, the best strategy is a hybrid approach—starting with historical analysis to establish a baseline, then layering forward-looking scenarios for proactive risk management. This balance ensures investors do not blindly rely on history while still grounding decisions in measurable data.
Comparing Sharpe Ratio with Other Metrics
While the Sharpe Ratio is powerful, it is not the only metric. Risk-averse investors should understand its strengths relative to alternatives:
- Sortino Ratio: Focuses only on downside volatility, making it more suitable for investors who care more about losses than upside deviations.
- Treynor Ratio: Uses beta instead of standard deviation, making it relevant for systematic risk analysis.
- Information Ratio: Useful for comparing active managers against benchmarks.
When considering what is the importance of Sharpe Ratio in futures trading, investors must also evaluate how it compares with these other metrics. Futures, by nature, carry high leverage and volatility, so using multiple metrics together provides a more complete picture.
Different ratios highlight different aspects of risk-adjusted returns.
Application in Futures and Perpetual Futures
The Sharpe Ratio has gained popularity in futures markets due to high volatility. For instance, how to calculate Sharpe Ratio in perpetual futures involves the same formula but requires careful adjustments:
- Returns are measured based on futures contracts’ PnL.
- Risk-free rate is often negligible in crypto perpetual futures but still included for accuracy.
- Volatility is calculated using rolling standard deviations of returns.
This allows risk-averse investors to evaluate whether perpetual futures strategies provide sufficient reward for the volatility taken on.
Practical Tips for Improving Sharpe Ratio
- Diversify Across Asset Classes
Adding low-correlation assets reduces volatility without sacrificing returns.
- Use Hedging Tools
Options, futures, or inverse ETFs can protect downside and stabilize returns.
- Reduce Trading Costs
Lower fees directly improve net returns, boosting the Sharpe Ratio.
- Avoid Over-Leverage
For futures and crypto, high leverage magnifies volatility and lowers Sharpe Ratio for risk-averse profiles.
- Implement Stop-Loss Rules
Disciplined risk management avoids extreme drawdowns.
Personal Experience and Industry Insights
From personal practice, Sharpe Ratio analysis has been a cornerstone for evaluating trading systems. I once compared two strategies:
- Strategy A delivered 20% annual returns with high volatility.
- Strategy B delivered 12% annual returns with far lower volatility.
While Strategy A looked better at first glance, its Sharpe Ratio was inferior. As a risk-averse investor, I chose Strategy B, which compounded steadily without sleepless nights.
Industry insights echo this preference: Hedge funds and institutional investors often require minimum Sharpe Ratios (e.g., >1.0) before approving allocations.
FAQs on Sharpe Ratio Analysis for Risk-Averse Investors
1. What is a “good” Sharpe Ratio for risk-averse investors?
A Sharpe Ratio above 1.0 is considered good, above 2.0 is very good, and above 3.0 is excellent. Risk-averse investors should target at least 1.5 to ensure stability.
2. Can the Sharpe Ratio be negative?
Yes. A negative Sharpe Ratio means the investment underperformed the risk-free rate, effectively punishing the investor for taking on unnecessary risk. Risk-averse investors should avoid assets with persistently negative Sharpe Ratios.
3. Is the Sharpe Ratio reliable in crypto markets?
It is useful but must be applied carefully. Crypto assets often experience extreme volatility, so supplementing Sharpe with Sortino or max drawdown metrics gives a more complete risk-adjusted picture.
4. How often should investors recalculate the Sharpe Ratio?
Quarterly updates are recommended for portfolios, though high-frequency traders may track it daily or weekly.
Conclusion
For risk-averse investors, the Sharpe Ratio is more than a statistic—it is a compass for navigating uncertain markets. By focusing on risk-adjusted returns, comparing across assets, and blending historical with forward-looking analysis, investors can build portfolios that provide steady, sustainable growth.
While no single metric guarantees success, the Sharpe Ratio offers a clear framework for evaluating whether your returns justify the risks. Combine it with diversification, hedging, and disciplined management, and it becomes a powerful ally for cautious investors.
Final Thoughts: Share and Engage
Have you applied the Sharpe Ratio in your investment strategy? Do you prefer it over other metrics like Sortino or Treynor? Share your experiences in the comments below, and don’t forget to share this guide with fellow risk-averse investors who want to build smarter, more resilient portfolios.
Risk-averse investors use Sharpe Ratio analysis to make better-informed portfolio decisions.