==============================================================
Limit orders are one of the most essential tools in modern trading, allowing traders to set specific prices at which they are willing to buy or sell assets. Understanding how to modify a limit order effectively can significantly improve trading efficiency, reduce slippage, and optimize profits. This article explores strategies, practical techniques, and expert insights for modifying limit orders across different markets, including equities, futures, and cryptocurrencies.
Understanding Limit Orders
What Is a Limit Order?
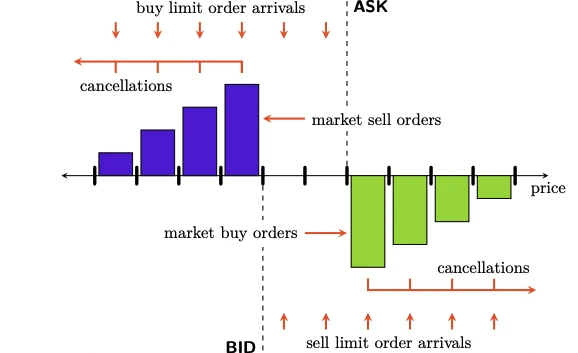
A limit order is an instruction to buy or sell an asset at a specified price or better. Unlike market orders, which execute immediately at the current market price, limit orders give traders control over the execution price.
Key Features of Limit Orders:
- Price control
- No guarantee of execution
- Flexibility in trading strategy
Limit Order Concept
Why Limit Orders Matter
Limit orders are crucial because they help traders:
- Avoid paying more than desired
- Protect profits in volatile markets
- Strategically enter or exit positions
How to Modify a Limit Order
Modifying a limit order involves adjusting its parameters after placing it. This can be necessary due to market movement, trading strategy adjustments, or risk management considerations.
Method 1: Price Adjustment
Changing the order price is the most common modification.
Steps:
- Access your trading platform’s order management system.
- Locate the open limit order.
- Update the desired execution price.
- Confirm the modification.
Advantages:
- Quick adaptation to market changes
- Improves chances of execution at favorable prices
Disadvantages:
- Frequent adjustments may incur platform fees
- Can lead to overtrading if not disciplined
Method 2: Quantity Adjustment
Traders may also need to modify the order quantity to manage exposure.
Steps:
- Open the limit order in your trading interface.
- Adjust the order size according to risk management.
- Submit changes for execution.
Advantages:
- Aligns position size with risk tolerance
- Reduces potential losses in volatile markets
Disadvantages:
- Smaller orders may miss price opportunities
- Large reductions can affect portfolio strategy
Modify Limit Order Example
Advanced Techniques for Professionals
Time-in-Force Adjustments
Adjusting time-in-force parameters (e.g., GTC, IOC) can influence how long a modified limit order remains active.
- GTC (Good Till Cancelled): Stays active until filled or manually canceled.
- IOC (Immediate or Cancel): Executes immediately for the available quantity; unfilled portion is canceled.
Conditional Modifications
Some platforms allow conditional limit orders that automatically adjust based on market triggers, such as price movement or volume thresholds.
Embedded Insight: Learn how to optimize limit orders to enhance efficiency in dynamic trading environments.
Platforms and Tools
Choosing the Right Platform
- Check whether the platform allows easy modifications.
- Evaluate latency and order execution reliability.
- Look for visual order book integration for precise adjustments.
Useful Tools
- Order Management Systems – Track and modify multiple orders efficiently.
- Interactive Simulations – Test modification strategies without financial risk.
- Analytics Dashboards – Monitor order performance and adjust parameters dynamically.
Limit Order Tools for Traders
Comparing Strategies for Different Traders
| Trader Type | Recommended Modification Strategy | Key Advantage | Risk Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Simple price adjustment | Easy to manage | May miss fast market moves |
| Day Trader | Conditional limit orders | Automation and speed | Requires platform understanding |
| Institutional | Quantity and time-in-force modification | Precision control | Complex setup |
| Retail Investor | Basic price + quantity updates | Flexibility | Needs monitoring |
FAQs
Q1: Can I modify a limit order after partial execution?
A1: Yes. Most platforms allow modification of the unfilled portion. Traders should consider remaining quantity and updated price levels to optimize execution.
Q2: How does modifying a limit order affect fees?
A2: Some exchanges charge fees for multiple modifications. Understanding platform-specific rules is essential to avoid excessive costs.
Q3: Is it better to cancel and create a new limit order or modify an existing one?
A3: It depends. For small changes, modification is efficient. For major changes in price or quantity, canceling and placing a new order may be preferable.
Best Practices
- Plan Before Placing Orders – Avoid frequent reactive changes.
- Monitor Market Conditions – Modify only when market movement justifies adjustment.
- Use Analytics Tools – Incorporate order book and trading signals to guide modifications.
- Limit Emotional Decisions – Stick to pre-defined risk parameters and profit targets.
Embedded Insight: Explore how to set limit order in perpetual futures to integrate advanced order modification techniques for leveraged trading markets.
Conclusion
Effectively modifying limit orders is a key skill for successful trading. By understanding price and quantity adjustments, leveraging advanced tools, and integrating quantitative strategies, traders can enhance execution efficiency and reduce risk exposure. Whether you are a beginner or an institutional investor, mastering limit order modifications improves your trading precision and profitability.
Call to Action: Share your limit order modification experiences in the comments and explore more strategies to optimize your trading performance.
Optimized Limit Orders for Better Trading Results