
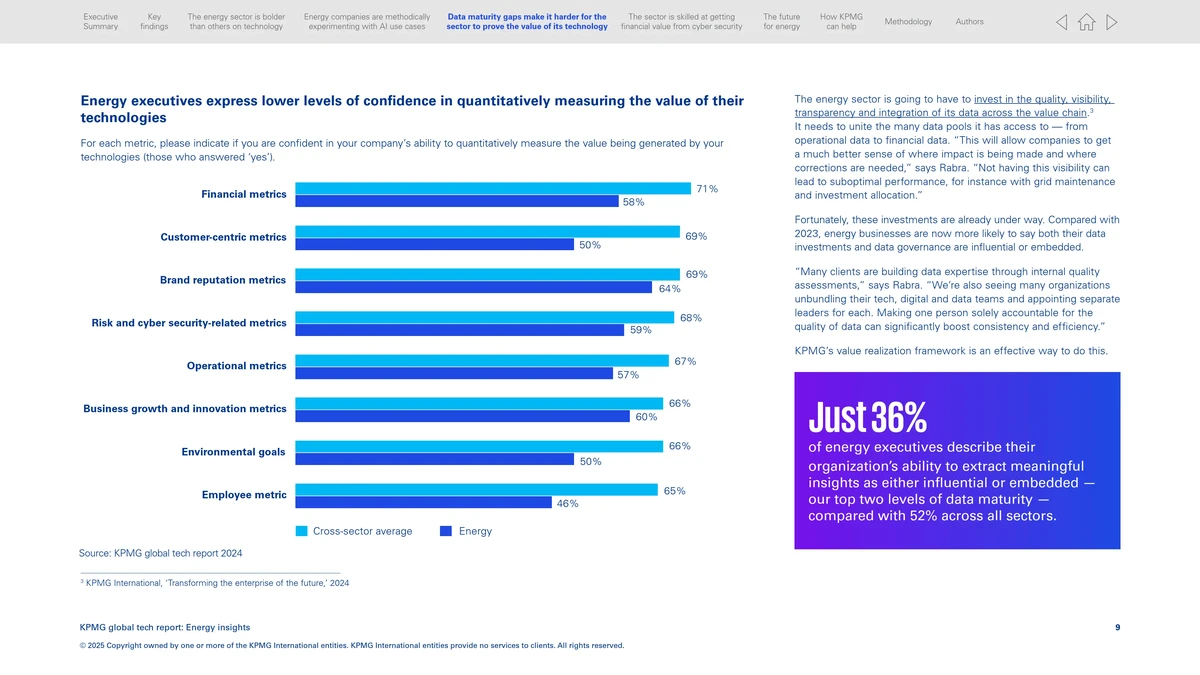
===============================================
Introduction: The Role of API in Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures trading has become one of the fastest-growing segments in global crypto and derivatives markets. Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual futures have no expiration date, allowing traders to maintain positions indefinitely. To succeed in this dynamic environment, traders and institutions increasingly rely on API integration solutions for perpetual futures.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provide seamless connections between trading platforms, analytical tools, and custom strategies. They enable real-time data flow, automated execution, and scalable infrastructure—making them essential for modern trading operations.
In this guide, I’ll draw from both professional trading experiences and current industry practices to explore integration solutions, compare different approaches, and highlight best practices for securing and optimizing APIs in perpetual futures.
Understanding API Integration for Perpetual Futures
What Is API Integration?
API integration is the process of connecting trading systems or tools with exchange platforms via standardized endpoints. In perpetual futures, this means connecting directly to the order book, market data, and account services of exchanges like Binance Futures, Bybit, or Deribit.
Why APIs Are Crucial
- Speed: Millisecond-level order execution.
- Automation: Hands-free trading using bots and algorithms.
- Scalability: Ability to manage thousands of trades simultaneously.
- Customization: Tailor trading systems to unique strategies.
For traders asking why API is essential for perpetual futures, the answer lies in the competitive edge it provides in terms of speed, precision, and data-driven decision-making.
| Section | Concept | Key Details | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Role of API | Connects trading platforms, tools, and strategies | Real-time data, automated execution, scalable | Requires technical integration |
| API Integration | Definition | Connects systems with exchange endpoints | Direct access to order books and accounts | May need coding expertise |
| Importance | Why APIs Matter | Speed, automation, scalability, customization | Competitive edge in trading | Dependent on platform reliability |
| Key Features | Real-Time Market Data | Access order book, funding rates, volatility | Immediate monitoring of market | Data overload possible |
| Key Features | Trade Execution Endpoints | Place, cancel, modify trades programmatically | Consistent with strategies | Misconfigurations risk losses |
| Key Features | Account & Risk Management | Monitor margins, leverage, liquidation thresholds | Reduces operational risk | Complexity in high leverage |
| Strategy 1 | Exchange-Native APIs | APIs provided by exchanges | Direct integration, high reliability | Locked to one platform |
| Strategy 1 | Disadvantages | Platform-specific formats | Access to unique features | Hard for multi-exchange use |
| Strategy 2 | Middleware APIs | Aggregates multiple exchanges into one interface | Easier cross-exchange integration | Possible latency, extra costs |
| Strategy 2 | Disadvantages | Third-party dependency | Unified data standards | Dependent on uptime |
| Recommended Approach | Hybrid Solution | Combine native and middleware APIs | Speed, flexibility, redundancy | Requires careful management |
| Security | API Key Management | Restricted keys, rotate frequently, secure storage | Prevent unauthorized access | Requires discipline |
| Security | Two-Factor Authentication | Adds extra verification | Enhanced security | Extra setup steps |
| Security | IP Whitelisting | Limit API access to specific IPs | Reduces key theft risk | Needs IP management |
| Use Cases | Algorithmic Trading | Bots trade based on real-time data | Millisecond execution | Requires coding |
| Use Cases | Portfolio Management | Integrate with risk dashboards | Monitor exposure across accounts | Data integration effort |
| Use Cases | Backtesting & Strategy Development | Historical data via API | Test strategies before live trades | Data accuracy critical |
| Use Cases | Arbitrage Opportunities | Cross-exchange APIs | Capture price spreads | Latency sensitive |
| Trends | Low-Latency Protocols | WebSocket over REST | Faster execution | Complexity in setup |
| Trends | AI-Driven Bots | ML models optimize strategies | Automated strategy improvement | Model risks |
| Trends | DeFi & Hybrid APIs | Bridge centralized and decentralized platforms | Wider trading options | Technical complexity |
| Trends | Modular API Services | Custom APIs for retail vs institutional | Tailored solutions | Development required |
| FAQ | Starting with API | Begin with exchange-native APIs | Robust documentation, sandbox testing | Learning curve |
| FAQ | Reducing Latency | Use WebSocket, host servers near exchanges | Faster trade execution | Infrastructure cost |
| FAQ | Common Mistakes | Overreliance on defaults, unsecured keys | Awareness of risks | Can cause trading errors |
| FAQ | Beginner Use | Many exchanges provide guides and bots | Accessible for beginners | Professional oversight advised |
| Conclusion | Future of API | Backbone of execution, analysis, and risk management | Automate, scale, secure operations | Requires mastery and vigilance |
Real-Time Market Data
Perpetual futures trading requires instant access to order book depth, funding rates, and volatility metrics. Real-time APIs allow traders to monitor these without delay.
Trade Execution Endpoints
APIs enable users to place, cancel, or modify trades programmatically, ensuring consistency with pre-defined strategies.
Account and Risk Management
Integration also provides access to margin balances, liquidation thresholds, and leverage adjustments—all critical in high-risk environments like perpetual futures.
Comparing API Integration Strategies
Method 1: Using Exchange-Native APIs
Most major exchanges offer native APIs for perpetual futures trading.
Advantages:
- Direct integration with the exchange.
- High reliability and frequent updates.
- Access to exchange-specific features.
- Direct integration with the exchange.
Disadvantages:
- Limited portability (locked to one platform).
- Different formats across exchanges make multi-exchange strategies harder.
- Limited portability (locked to one platform).
Method 2: Using Third-Party Middleware APIs
Some developers use middleware solutions that aggregate multiple exchange APIs into a single interface.
Advantages:
- Easier cross-exchange integration.
- Unified data standards.
- Faster deployment for multi-platform trading.
- Easier cross-exchange integration.
Disadvantages:
- Possible latency issues.
- Added costs for middleware services.
- Dependency on third-party uptime.
- Possible latency issues.
Recommended Approach
A hybrid solution—using native APIs for critical execution and third-party APIs for monitoring or cross-exchange strategies—offers the best of both worlds. It ensures speed, flexibility, and redundancy.
Visual Insights
A professional futures dashboard connected through API integration for perpetual contracts.
Developers coding custom API solutions to automate perpetual futures trading.
Real-time perpetual futures data feed for order execution and analytics.
Security Considerations in API Integration
API Key Management
Traders must generate keys with restricted permissions. Keys should be rotated frequently and stored securely.
Two-Factor Authentication
When possible, combine API usage with platform-level two-factor authentication for enhanced security.
IP Whitelisting
Most exchanges allow traders to whitelist specific IPs for API access. This significantly reduces risks from stolen keys.
For professionals learning how to secure API for perpetual futures trading, security hygiene is just as important as execution speed.
API Integration Use Cases
1. Algorithmic Trading
APIs allow traders to code bots that trade perpetually, reacting to market changes in milliseconds.
2. Portfolio Management
Institutional desks integrate APIs with risk dashboards to monitor real-time exposure across assets and accounts.
3. Backtesting and Strategy Development
APIs deliver historical data, enabling developers to backtest strategies before live deployment.
4. Arbitrage Opportunities
Cross-exchange APIs help traders capture spreads between perpetual futures markets.
Embedded Knowledge
When evaluating where to find the best API for perpetual futures, traders should prioritize platforms with low latency, extensive documentation, and strong developer support.
Similarly, for those exploring how API improves perpetual futures trading strategies, integration enables dynamic leverage adjustments, real-time hedging, and funding-rate arbitrage.
Latest Trends in API Solutions
- Low-Latency Protocols: WebSocket APIs now dominate over REST for real-time execution.
- AI-Driven Trading Bots: Machine learning models optimize strategies directly via API feeds.
- DeFi and Hybrid APIs: New APIs bridge centralized and decentralized perpetual futures platforms.
- Modular API Services: Custom APIs allow tailoring of solutions for retail vs institutional needs.
FAQ: API Integration Solutions for Perpetual Futures
1. What is the best way to start with API integration?
Begin with exchange-native APIs. Most exchanges offer robust documentation and sandbox environments for testing. Once comfortable, explore middleware APIs for cross-exchange strategies.
2. How can I reduce latency in perpetual futures API trading?
Use WebSocket APIs instead of REST whenever possible. Host trading servers close to exchange servers to reduce geographic latency.
3. What are the common mistakes in API integration?
- Overreliance on default settings without customization.
- Failing to secure API keys.
- Ignoring exchange rate limits, leading to connection bans.
4. Can beginners use APIs effectively?
Yes. Many exchanges provide beginner-friendly API guides and even plug-and-play bots. However, professional oversight is recommended when deploying strategies with real capital.
Conclusion: Building the Future with API Integration
The perpetual futures market is a high-speed, high-stakes environment where milliseconds matter. APIs are the backbone of efficient execution, data analysis, and risk management.
By adopting API integration solutions for perpetual futures, traders can:
- Automate strategies for consistency.
- Access real-time market data.
- Securely manage accounts and exposure.
- Scale operations across multiple exchanges.
The future of perpetual futures trading will be shaped by those who master integration.
What about you?
- Are you already automating trades with API solutions?
- Which exchange or third-party API platforms do you prefer?
Share your insights in the comments below—and if this guide helped, pass it along to your trading community to start meaningful conversations.