
===========================================
Introduction
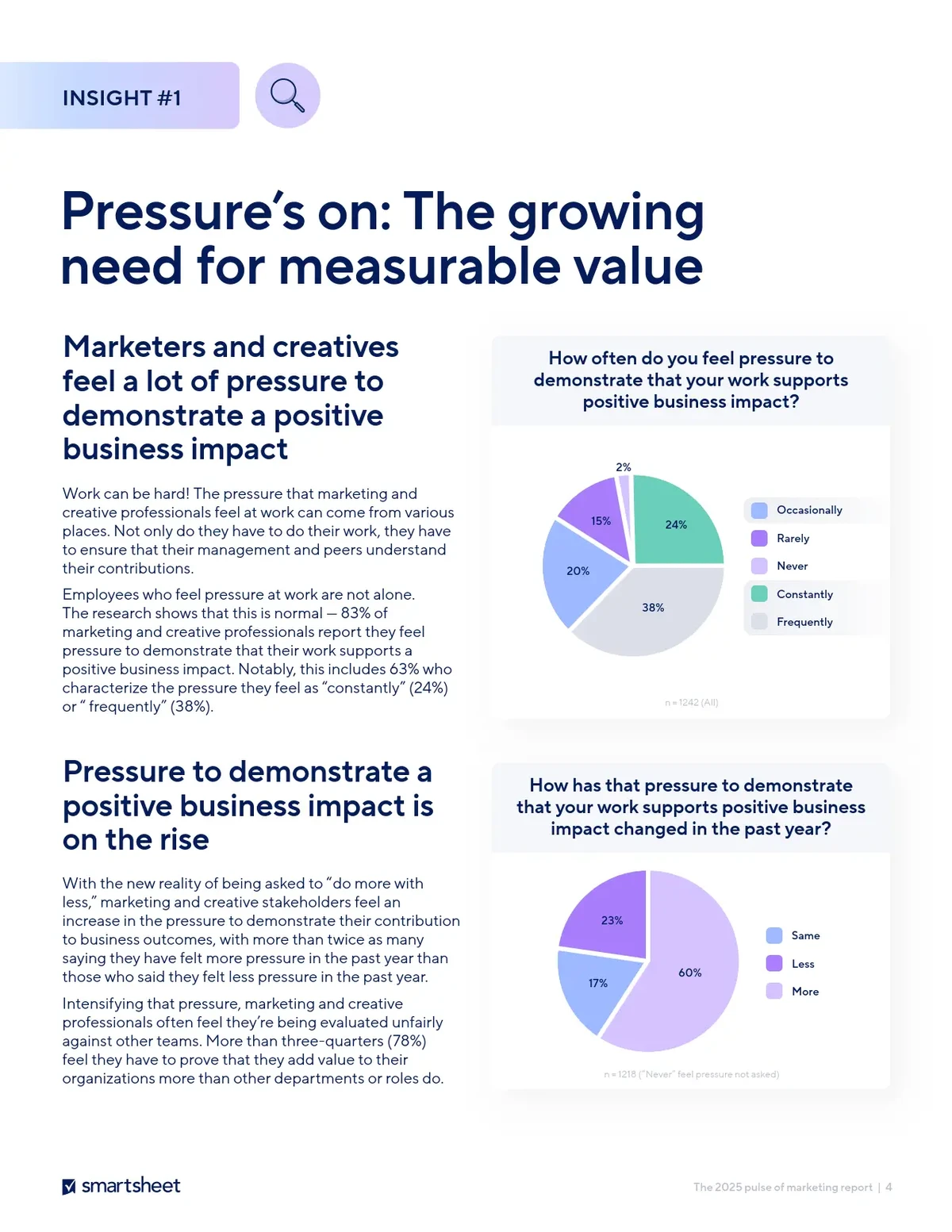
The rise of perpetual futures trading has transformed how both institutional and retail traders approach financial markets. While professional firms have historically relied on sophisticated infrastructure, recent developments have made advanced tools—particularly API for retail traders in perpetual futures—widely accessible.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) bridge the gap between traders and trading platforms, enabling automation, data retrieval, and strategy execution without manual intervention. For retail traders, this technology is no longer optional; it’s becoming an essential part of building a competitive edge in the fast-paced futures environment.
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of APIs for retail traders in perpetual futures, including methods of integration, strategies, pros and cons of different approaches, and practical advice on how to leverage APIs effectively.
Understanding APIs in Perpetual Futures
What Is an API in Trading?
An API allows traders to communicate directly with a trading platform’s server. Instead of placing trades manually through a web interface, APIs let you execute commands programmatically—such as placing orders, retrieving live prices, managing risk, and running algorithms.
Why APIs Are Important for Retail Traders
- Automation: Traders can implement strategies without being glued to their screens.
- Speed: Orders are executed faster than manual input, crucial in volatile perpetual futures markets.
- Customization: Tailor-made solutions can be developed to match specific trading styles.
- Scalability: Once an API setup is in place, traders can manage multiple markets and accounts simultaneously.
For this reason, many analysts argue that why API is essential for perpetual futures lies in its ability to democratize access to tools once exclusive to hedge funds and institutional players.
| Section | Key Point | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | API Importance | Enables automation, data retrieval, and strategy execution |
| Understanding APIs | Definition | Allows programmatic communication with trading platforms |
| Understanding APIs | Benefits | Automation, speed, customization, scalability |
| Types of APIs | REST API | Simple HTTP requests, beginner-friendly, slower for high-frequency |
| Types of APIs | WebSocket API | Real-time streaming, faster, requires stable internet |
| Types of APIs | FIX Protocol | High-performance, low-latency, complex setup, costly |
| API Strategies | Pre-Built Bots | Quick setup, no coding, limited customization, security risk |
| API Strategies | Custom Integration | Maximum flexibility, strategy optimization, coding required |
| API Strategies | Hybrid Approach | Start with bots, transition to custom solutions |
| Use Cases | Automated Scalping | Executes trades in milliseconds for small price moves |
| Use Cases | Risk Management | Automated stop-loss and take-profit orders |
| Use Cases | Portfolio Diversification | Manage multiple assets or contracts simultaneously |
| Use Cases | Backtesting | Test historical performance before live deployment |
| Workflow | API Workflow | Data flows between trader, broker API, and exchange |
| Reliable APIs | Sources | Binance, Bybit, OKX, TradingView, GitHub, forums |
| Security | Key Practices | API key management, 2FA, limited permissions, encryption |
| Advanced Strategies | Algorithmic Trading | Bots adjust positions automatically based on volatility |
| Advanced Strategies | Arbitrage Trading | Exploit price differences across exchanges instantly |
| Advanced Strategies | Machine Learning | Predict market movements via API-integrated models |
| Advanced Strategies | Real-Time Dashboards | Feed live data for faster decision-making |
| FAQ | Programming Skills | Not required for pre-built bots, needed for custom APIs |
| FAQ | REST vs WebSocket | REST for simple trades, WebSocket for high-frequency |
| FAQ | API Security | Use unique keys, enable 2FA, restrict permissions, rotate keys |
| Conclusion | Key Takeaway | APIs provide automation, speed, flexibility, and competitive edge |
1. REST APIs
These are the most common and beginner-friendly APIs. REST APIs are based on simple HTTP requests, making them accessible to non-programmers.
Advantages: Easy to set up, suitable for lightweight applications like retrieving prices or placing occasional trades.
Disadvantages: Slower compared to WebSocket APIs, limited for high-frequency trading.
2. WebSocket APIs
WebSocket APIs maintain a continuous connection between the client and server, delivering real-time streaming data such as order book depth and live price ticks.
Advantages: Faster, ideal for traders needing millisecond-level precision.
Disadvantages: Requires more programming knowledge and a stable internet connection.
3. FIX Protocol
Although primarily used by institutions, some brokers allow retail traders to access FIX APIs. These are high-performance, low-latency APIs designed for professional-grade trading.
Advantages: Extremely fast and reliable, favored by algorithmic traders.
Disadvantages: Complex setup, higher costs, and usually requires broker approval.
Comparing Two Key API Strategies
Method 1: Pre-Built Trading Bots Using APIs
Retail traders often rely on pre-built trading bots that connect to their broker via an API.
- Pros: Quick setup, no need for coding, affordable for beginners.
- Cons: Limited customization, reliance on third-party software, potential security risks.
Method 2: Custom API Integration
Tech-savvy traders or developers can build custom trading systems that connect directly via API.
- Pros: Maximum flexibility, ability to optimize strategies, integration with advanced analytics.
- Cons: Requires coding expertise, higher initial setup time, potential bugs if not properly tested.
Best Recommendation
A hybrid approach is often ideal: start with pre-built trading bots to gain familiarity, then transition into custom API solutions for perpetual futures traders. This ensures both accessibility and long-term growth potential.
Real-World Use Cases of APIs
- Automated Scalping: APIs execute trades in milliseconds, essential for capturing small price movements in perpetual contracts.
- Risk Management Tools: Automated stop-loss and take-profit orders prevent emotional decision-making.
- Portfolio Diversification: APIs allow monitoring and managing multiple currency pairs or perpetual contracts simultaneously.
- Backtesting and Strategy Validation: APIs help traders test historical performance before deploying strategies live.
Visual Example: API Workflow
API trading workflow for retail traders
This diagram illustrates how data flows between a retail trader’s system, the broker’s API, and the perpetual futures exchange.
Where to Find Reliable APIs
For retail traders, the challenge isn’t just knowing how to use API for perpetual futures trading?, but also knowing where to find reliable providers. Many major exchanges like Binance, Bybit, and OKX provide free API documentation. Additionally, third-party platforms like TradingView offer API integrations for signal automation.
For enhanced learning, communities like GitHub, Stack Overflow, and crypto trading forums provide real-world examples and troubleshooting solutions.
Security Considerations
When dealing with APIs, security cannot be overlooked. Key steps include:
- API Key Management: Store keys securely, avoid sharing them.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Always enable 2FA for accounts using APIs.
- Permission Settings: Use limited permissions (e.g., trading only, no withdrawals).
- Encrypted Connections: Ensure SSL/TLS encryption for all data exchanges.
Advanced Strategies with APIs
- Algorithmic Trading: Building bots that automatically adjust position sizes based on volatility.
- Arbitrage Trading: Using APIs to spot price discrepancies across exchanges and execute instant trades.
- Machine Learning Models: Integrating APIs with predictive models to forecast perpetual futures movements.
- Real-Time Monitoring Dashboards: APIs can feed live data into custom dashboards, giving traders an edge in decision-making.
FAQ: API for Retail Traders in Perpetual Futures
1. Do I need programming skills to use APIs?
Not necessarily. Many pre-built platforms allow you to connect via API without coding. However, having programming knowledge (Python, JavaScript) opens up advanced customization possibilities.
2. Which is better for retail traders: REST API or WebSocket API?
It depends on your strategy. REST APIs are suitable for simple trading and data requests, while WebSocket APIs are better for high-frequency and real-time strategies.
3. How do I secure my trading API?
Use unique API keys, restrict permissions, enable 2FA, and never share your keys. Additionally, rotate keys periodically and use IP whitelisting where supported.
Conclusion
APIs are no longer a tool reserved for institutional traders; they have become a cornerstone of modern trading for individuals. The right API for retail traders in perpetual futures empowers traders with automation, speed, and flexibility.
By combining structured learning, real-time experimentation, and security best practices, retail traders can build strategies that rival institutional approaches. Whether you choose pre-built bots or custom coding, the path forward involves embracing APIs as a critical component of trading success.
If you found this article helpful, share it with your network, comment below with your experiences using APIs, or join the discussion. Collaboration and shared insights can help every trader make better use of perpetual futures APIs.