
=====================================================
Introduction
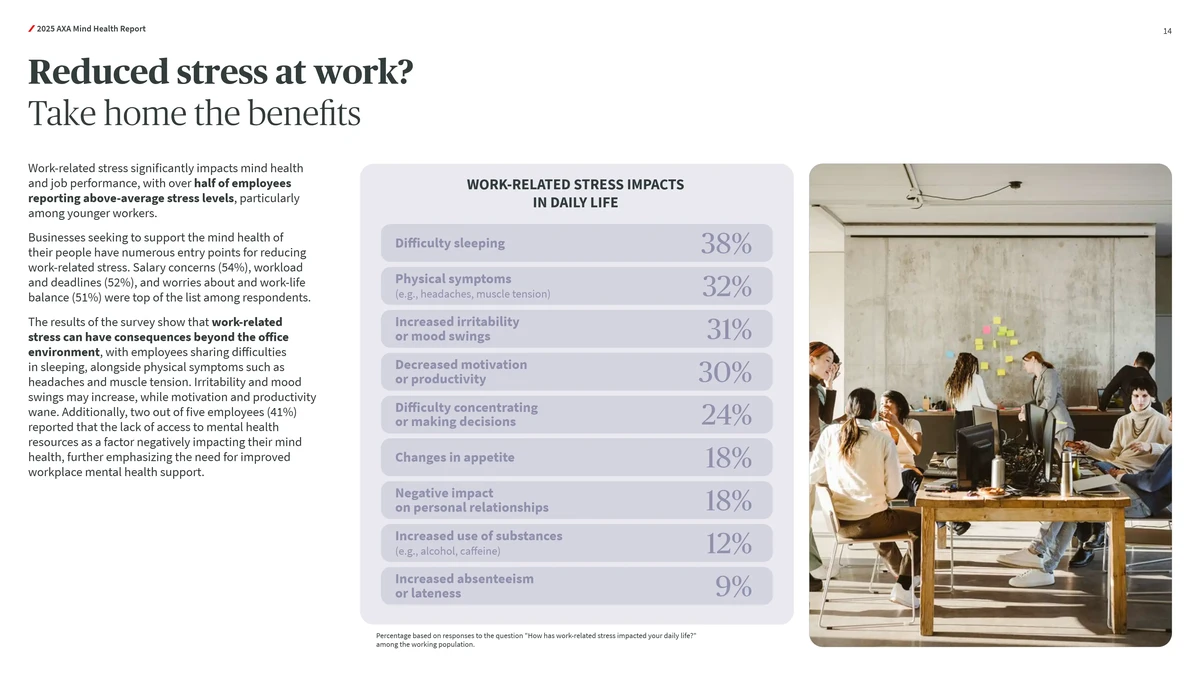
In the competitive world of futures trading, traders cannot rely on guesswork. The ability to test, refine, and validate trading strategies before risking capital is crucial for long-term success. This is where backtesting frameworks for successful futures trading play a transformative role. Backtesting involves simulating a trading strategy on historical market data to evaluate its potential performance. Done correctly, it provides traders with actionable insights into profitability, risk, drawdowns, and execution feasibility.
In this article, we will explore the importance of backtesting frameworks, compare different approaches, analyze key tools, and provide practical recommendations for building effective systems. Whether you are a beginner futures trader or a professional quant analyst, mastering backtesting is a cornerstone for consistent profitability.
The Importance of Backtesting Frameworks in Futures Trading
Why Backtesting Matters
Backtesting frameworks allow traders to:
- Validate strategies before risking money.
- Identify weaknesses in assumptions or models.
- Compare multiple approaches under identical market conditions.
- Quantify risk exposure using drawdown and volatility metrics.
- Improve confidence in execution by testing robustness.
In the futures market, where leverage amplifies both gains and losses, backtesting becomes indispensable. Without it, traders risk entering trades based on intuition rather than evidence.
How Backtesting Creates Discipline
One of the key psychological benefits of backtesting is discipline. A well-structured framework prevents traders from making impulsive decisions during market volatility. Instead, strategies are executed with consistency, reducing emotional bias.
{
“table”: [
{
"Topic": "Fiber Optics in Banking",
"Details": "Fiber optics technologies are transforming banking infrastructure, providing speed, reliability, and security for financial services."
},
{
"Topic": "Advantages of Fiber Optics",
"Subtopic": "Latency Reduction",
"Details": "Data travels at near-light speeds, reducing transmission delays."
},
{
"Topic": "Advantages of Fiber Optics",
"Subtopic": "Bandwidth Expansion",
"Details": "Supports massive transaction volumes and digital services without bottlenecks."
},
{
"Topic": "Advantages of Fiber Optics",
"Subtopic": "Security Enhancement",
"Details": "Fiber optics are harder to tap than copper, reducing cyber risks."
},
{
"Topic": "Why Banks Adopt Fiber Optics",
"Details": "To enhance high-frequency trading, digital banking, and improve customer experience."
},
{
"Topic": "The Rise of Fiber Optics",
"Details": "Fiber optics provide dramatically higher speeds, lower latency, and greater bandwidth than copper-based networks."
}
]
}
1. Historical Market Data
The quality and accuracy of historical futures data determine the reliability of results. Tick-by-tick data provides more granular insights but requires greater storage and computational power.
2. Trading Rules and Logic
A framework must codify entry, exit, and risk management rules. For example:
- Entry rule: Buy when the 20-day moving average crosses above the 50-day average.
- Exit rule: Sell when the 20-day moving average falls below the 50-day average.
3. Performance Metrics
Robust backtesting frameworks analyze multiple performance dimensions:
- Net Profit and Loss (PnL)
- Sharpe Ratio
- Maximum Drawdown
- Win/Loss Ratio
- Risk-Adjusted Returns
4. Transaction Costs and Slippage
Ignoring costs leads to inflated performance metrics. Futures traders must account for:
- Exchange fees
- Bid-ask spreads
- Market impact
Comparing Two Backtesting Approaches
Method 1: Event-Driven Backtesting
Event-driven frameworks simulate trading based on actual market events (ticks, orders, or trades).
Pros:
- High accuracy with tick-level simulation.
- Realistic modeling of slippage and latency.
- Well-suited for high-frequency and algorithmic futures trading.
Cons:
- Computationally expensive.
- Requires detailed historical tick data.
Method 2: Bar-Based Backtesting
Bar-based frameworks use time-aggregated data (minute, hourly, or daily bars).
Pros:
- Less resource-intensive.
- Faster for testing long-term strategies.
- Easier to implement for swing and position traders.
Cons:
- Less accurate for intraday scalping.
- Misses granular market dynamics.
Recommended Approach
For professional futures traders seeking accuracy, event-driven frameworks are superior. However, for beginners and long-term investors, bar-based backtesting provides a practical starting point. A hybrid approach can also be adopted—starting with bar-based testing for initial validation, followed by event-driven testing for refinement.
Modern Backtesting Tools and Frameworks
Open-Source Solutions
- Backtrader: Python-based, flexible, with integrated risk and performance metrics.
- QuantConnect: Cloud-based, supports futures, equities, and crypto.
- Zipline: Originally developed by Quantopian, good for prototyping strategies.
Proprietary Platforms
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5): Popular among retail futures traders.
- NinjaTrader: Widely used for futures-specific backtesting.
- MultiCharts: Offers robust testing with professional charting tools.
These frameworks integrate with execution platforms, allowing traders to transition seamlessly from testing to live trading.
How Backtesting Improves Futures Profitability
One of the most overlooked advantages of backtesting is its ability to highlight strategy robustness across different market conditions. For example, by learning how to perform backtesting in perpetual futures, traders can assess whether their strategy holds up during high volatility events such as FOMC announcements or geopolitical shocks.
Backtesting also helps identify overfitting—when a strategy works on past data but fails in live markets. By testing across multiple futures contracts (e.g., crude oil, S&P 500, and gold), traders can distinguish between genuine edge and data mining bias.
Common Pitfalls in Backtesting
Overfitting
Designing a strategy that perfectly matches historical data but fails in real markets.
Ignoring Execution Realities
Backtests that don’t include slippage or commissions are misleading.
Limited Data Sets
Testing on a small time window leads to biased conclusions.
Survivorship Bias
Only considering contracts that exist today without accounting for expired ones can distort results.
Practical Example of a Futures Backtest
A trader designs a trend-following strategy for the E-mini S&P 500 futures:
- Entry Rule: Go long when price closes above 20-day high.
- Exit Rule: Close position when price closes below 10-day low.
- Stop Loss: 2% of capital per trade.
Results (2005–2023 backtest):
- Annualized Return: 12%
- Sharpe Ratio: 1.4
- Max Drawdown: 18%
- Win Rate: 48%
This illustrates how structured frameworks reveal realistic expectations.
Advanced Trends in Backtesting
Machine Learning Integration
AI-driven models allow dynamic adjustments to strategies based on changing market conditions.
Cloud-Based Scalability
Platforms like QuantConnect enable running hundreds of backtests simultaneously with scalable computing power.
Data-Driven Customization
Custom datasets (such as order book depth or sentiment analysis) improve predictive accuracy.
By leveraging robust backtesting processes for futures profitability, traders can refine execution and reduce systemic risk.
FAQ: Backtesting in Futures Trading
1. How much historical data do I need for reliable backtesting?
Ideally, at least 10 years of futures data across different market regimes. For intraday strategies, tick data covering multiple volatility cycles is recommended.
2. What is the best backtesting framework for beginners?
For newcomers, Backtrader or NinjaTrader is ideal. They balance simplicity with powerful features. As traders progress, they can adopt event-driven frameworks or cloud-based tools.
3. How do I know if my strategy is overfitted?
If your backtest shows unusually high performance (e.g., Sharpe Ratio above 3) but fails in live trading, it’s likely overfitted. Testing across multiple instruments and timeframes helps reduce this risk.
Conclusion
Backtesting frameworks for successful futures trading are not optional—they are essential. By simulating strategies on historical data, traders gain insights into profitability, risks, and robustness. While bar-based testing is suitable for beginners, professional traders benefit from event-driven frameworks for precision.
As the futures market evolves with new technologies, machine learning, and cloud-based platforms, backtesting remains the foundation of evidence-based decision-making.
If you are serious about trading, it’s time to integrate structured backtesting into your workflow. Share this article with fellow traders, comment with your experiences, and let’s build a community of disciplined, data-driven futures professionals.
Futures backtesting workflow explained through data analysis and testing pipelines