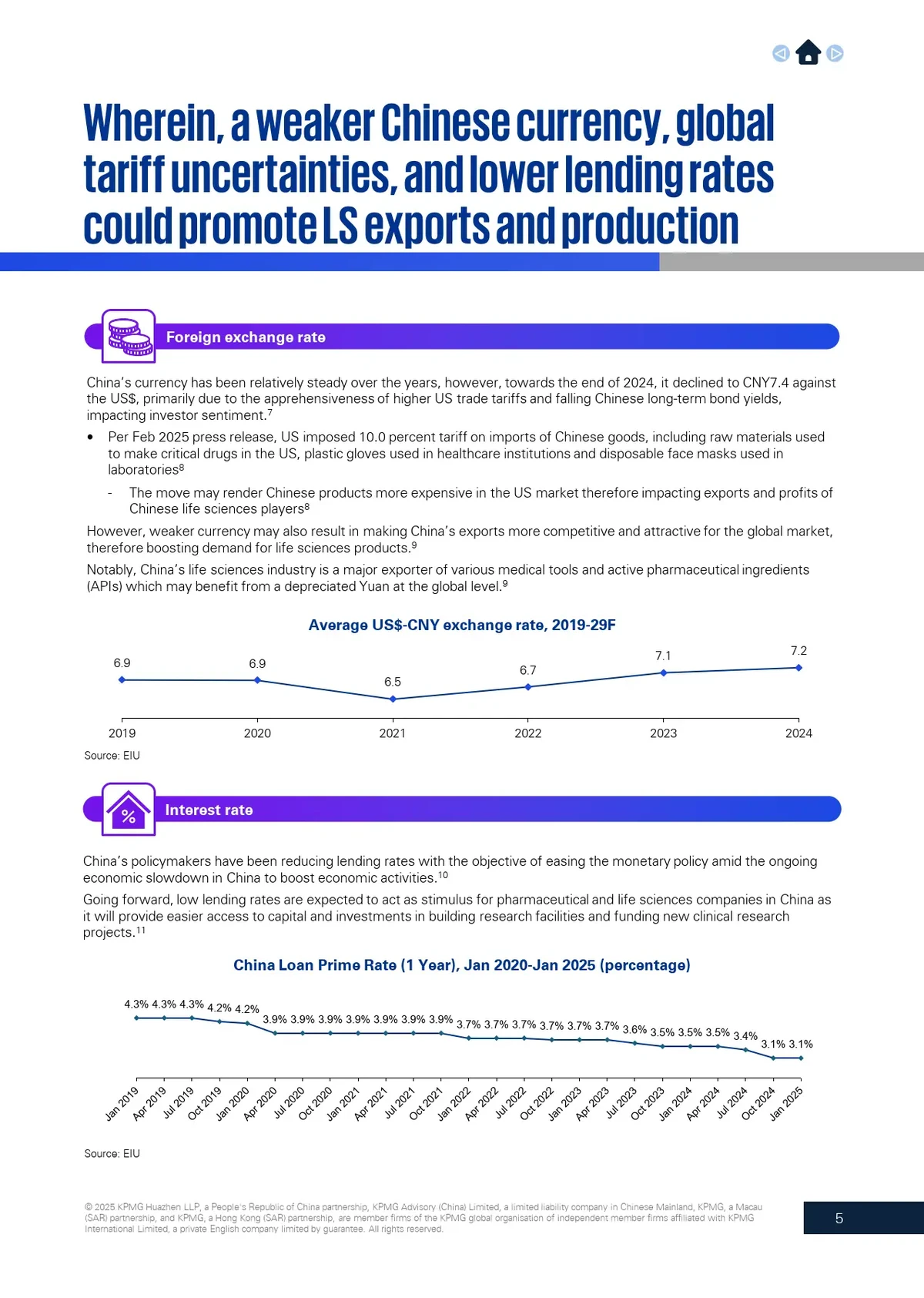
==============================================
In the world of perpetual futures trading, understanding how to calculate fee tier in perpetual futures is crucial for optimizing profitability. Fees can significantly impact your overall trading performance, and as a tech-savvy investor, knowing how to navigate fee tiers is a powerful tool. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps to calculate fee tiers in perpetual futures, discuss the importance of fee tiers, and provide you with strategies to optimize your trading costs.
What is a Fee Tier in Perpetual Futures?
Before diving into the specifics of how to calculate fee tier in perpetual futures, let’s first define what a fee tier is. A fee tier is essentially the structure that exchanges use to determine the fees charged to traders. These fees are typically based on the trading volume or activity of the trader over a set period.
How Fee Tiers Work
Exchanges generally use a maker-taker fee model, where:
- Maker fees are charged when you add liquidity to the market (i.e., you place a limit order that doesn’t immediately match with an existing order).
- Taker fees are charged when you remove liquidity from the market (i.e., you place a market order that immediately matches an existing order).
Fee tiers often have different levels:
- Tier 1: For traders with lower trading volume or activity.
- Tier 2 and beyond: For traders with higher trading volumes, often offering lower fees as a reward for higher activity.
These tiers incentivize traders to increase their activity in exchange for reduced fees.
Why Fee Tier Matters in Perpetual Futures Trading
Understanding fee tiers is not just about reducing your trading costs. The fee tier you belong to can have significant implications on your profitability in perpetual futures trading.
Impact on Profitability
Perpetual futures contracts, by nature, allow traders to hold positions for an extended period, which can rack up substantial fees over time. Even small differences in fees can accumulate and affect your net returns, especially for frequent traders.
Why Brokers Offer Different Fee Tiers
Exchanges provide different fee tiers as an incentive for traders to execute larger volumes of trades. Higher volume traders provide liquidity, which helps markets function more efficiently. The tiered fee structure helps exchanges reward these traders while attracting new ones with lower fees for starting out.
For professional and institutional traders, fee structures are a critical element of their strategy. Retail traders should also pay attention to fee tiers, as they can increase profitability by moving up the tiers with higher volume.
How to Calculate Fee Tier in Perpetual Futures
Step 1: Identify the Exchange’s Fee Structure
The first step in calculating the fee tier in perpetual futures is to understand the exchange’s fee structure. Most exchanges like Binance, Bybit, or FTX will have detailed information on how they calculate trading fees.
- Look for the Fee Schedule on the exchange’s website.
- Make sure to understand the distinction between maker fees and taker fees.
- Check if the exchange offers discounts based on trading volume or the use of the platform’s native token.
For example, Binance offers a tiered discount system, where fees are reduced as your 30-day trading volume increases.
Step 2: Calculate Your 30-Day Trading Volume
Many exchanges base your fee tier on your 30-day trading volume. This volume can be either in terms of USD value or number of contracts traded. For example:
- Tier 1: < $50,000 trading volume
- Tier 2: \(50,000 – \)500,000 trading volume
- Tier 3: > $500,000 trading volume
Check your trading history or your account’s performance statistics to determine your current trading volume.
Step 3: Identify the Correct Tier Level
Once you know your trading volume, you can compare it to the exchange’s fee schedule to see which tier you fall under. For example, if your trading volume is above $50,000 in the last 30 days, you may qualify for Tier 2 fees, which will be lower than Tier 1.
Step 4: Apply Fee Structure to Your Trades
Once you’ve determined your fee tier, apply the relevant fee rates (maker and taker) to your trades. The fees will depend on whether you’re adding liquidity (maker) or taking liquidity (taker).
Here’s an example:
- Tier 1 (Low Volume): Maker Fee = 0.1%, Taker Fee = 0.2%
- Tier 2 (Medium Volume): Maker Fee = 0.08%, Taker Fee = 0.16%
- Tier 3 (High Volume): Maker Fee = 0.05%, Taker Fee = 0.1%
Step 5: Factor in Discounts or Promotions
Many exchanges offer promotions or discounts based on using their native tokens or specific strategies. For instance, Binance offers discounts when using BNB tokens to pay for trading fees.
Strategies to Optimize Your Fee Tier in Perpetual Futures
1. Increase Your Trading Volume
The most direct way to optimize your fee tier is by increasing your trading volume. Higher volumes may push you to a lower fee tier, thus reducing the total fees you pay over time.
How to Increase Volume Efficiently:
- Trade More Frequently: Consider adjusting your trading strategy to increase the number of trades you make. However, be mindful of market conditions to avoid unnecessary trades.
- Use Multiple Pairs: Spread your trading volume across different trading pairs to quickly accumulate volume on the platform.
- Leverage: Using leverage allows you to trade larger positions with less capital, thus increasing your overall trading volume.
2. Use Limit Orders to Benefit from Maker Fees
Limit orders help you add liquidity to the market and benefit from maker fees. If you consistently place limit orders and avoid market orders, you will benefit from lower trading costs.
- Limit orders generally have lower fees because they provide liquidity to the market.
- You can set your limit orders at prices that are likely to be filled based on historical price data and technical analysis.
3. Leverage Fee Tier Discounts
Some exchanges allow traders to use native tokens to pay for trading fees. For instance, Binance allows users to pay fees with BNB (Binance Coin), which can grant you significant discounts.
- Keep an eye on exchange promotions and make sure you are taking advantage of any discounts available.
- Consider staking the platform’s native token to access exclusive fee discounts and other benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How do I know if I qualify for a higher fee tier in perpetual futures?
To determine your qualification for a higher fee tier, check your 30-day trading volume. If your volume exceeds a certain threshold (usually listed in the exchange’s fee schedule), you’ll automatically qualify for the next tier, which offers lower fees.
2. Can I manually move to a higher fee tier in perpetual futures?
You cannot manually move to a higher fee tier; however, you can increase your trading volume to qualify for better fee tiers. By executing more trades or using higher leverage, you can achieve the necessary volume to move to a higher tier.
3. Do all exchanges offer the same fee tier structure?
No, each exchange has its own fee structure. Some platforms, like Binance and Bybit, use a tiered fee system based on trading volume, while others may offer flat fee rates regardless of trading volume. Always check the fee schedule of your chosen exchange to understand how fees are calculated.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate fee tier in perpetual futures is essential for optimizing your trading strategy and reducing costs. By calculating your 30-day trading volume, applying the right fee structure, and using strategies like limit orders and leveraging discounts, you can minimize fees and maximize your profitability in perpetual futures trading.
As the market evolves, continuously monitor your fee tier and adjust your strategies accordingly to ensure you’re always operating at the most favorable cost structure.
For more insights and strategies, feel free to explore additional resources on fee tier reduction methods and best practices for optimizing trading fees in perpetual futures.
Share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about fee tiers in perpetual futures in the comments below! Let’s continue the conversation!