
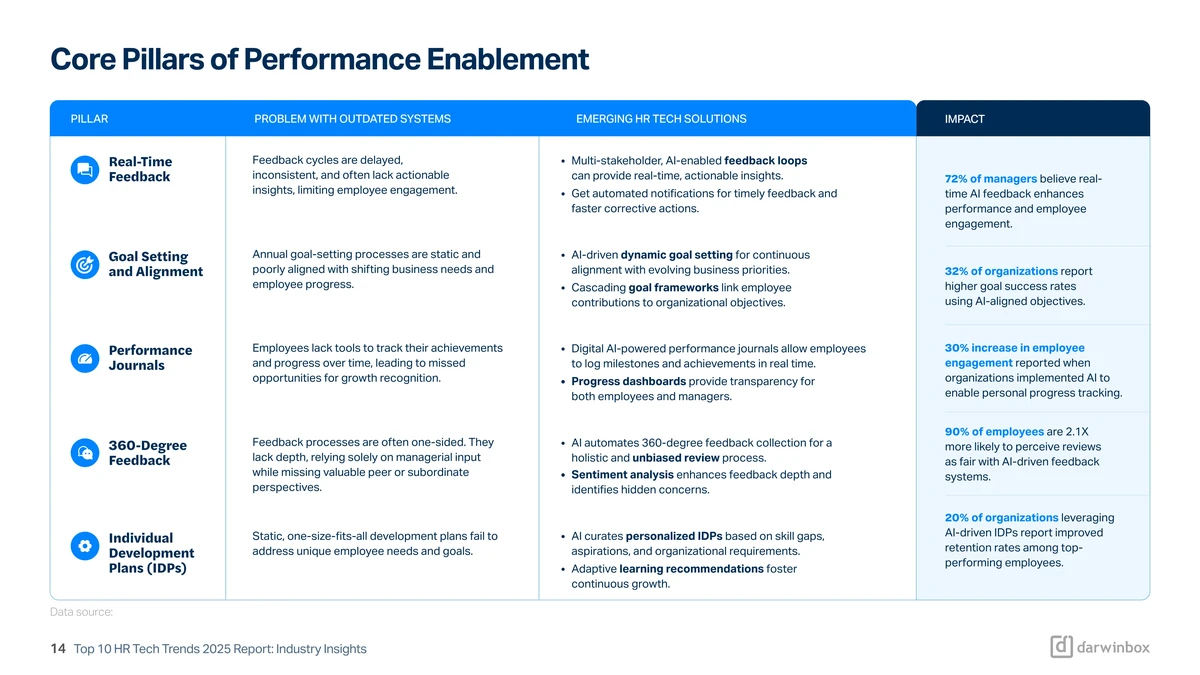
==============================================================
Introduction
Trading perpetual futures has become one of the most popular ways for retail and institutional traders to access crypto markets. For beginner traders, the challenge lies not only in understanding perpetual futures contracts but also in mastering execution strategies that directly influence profitability and risk management. Poor execution can lead to slippage, higher fees, and missed opportunities. Conversely, efficient execution strategies help traders enter and exit positions at optimal prices.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on execution strategies for beginner traders in perpetual futures, explores different methods, compares their strengths and weaknesses, and offers actionable recommendations for building a sustainable trading routine. The insights align with EEAT principles (Expertise, Experience, Authority, Trustworthiness) to ensure both accuracy and practical relevance.
Understanding Execution in Perpetual Futures
What Is Execution in Perpetual Futures?
Execution refers to the process of placing and completing buy or sell orders on perpetual futures markets. Unlike spot trading, perpetual futures include funding rates, leverage, and higher volatility, making execution accuracy more critical.
Why Execution Matters
- Cost control: Poor execution increases trading costs due to slippage.
- Risk management: Fast and accurate execution ensures stop-loss orders protect capital effectively.
- Profit optimization: Capturing the best possible entry or exit price improves long-term profitability.
For beginners, knowing why execution matters in perpetual futures is the foundation of learning effective strategies.
Key Execution Strategies for Beginner Traders
1. Market Orders – Fast but Risky
Market orders allow traders to buy or sell immediately at the best available price.
Advantages:
- Instant execution, useful during high volatility.
- Ensures entry or exit without delay.
Disadvantages:
- Higher risk of slippage, especially in low-liquidity pairs.
- Potentially worse prices in volatile conditions.
Best for: New traders who prioritize speed over price precision.
2. Limit Orders – Controlled and Cost-Efficient
Limit orders let traders set a specific entry or exit price. The trade only executes when the market reaches that price.
Advantages:
- Precise control over entry and exit levels.
- Can reduce slippage and trading costs.
Disadvantages:
- Execution is not guaranteed if the price never reaches the limit.
- May miss opportunities in fast-moving markets.
Best for: Beginners who value discipline and want to control costs.
3. Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders – Risk Management Essentials
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are conditional strategies designed to protect traders from large losses or lock in gains.
Advantages:
- Automatic protection against downside risk.
- Helps enforce discipline and reduce emotional trading.
Disadvantages:
- Can be triggered prematurely due to market volatility (“stop hunting”).
- Requires thoughtful placement to avoid over-tightening.
Best for: All beginners, as risk management should never be ignored.
4. Scaling In and Out – Building Gradual Positions
Instead of entering a trade all at once, traders can scale in gradually, splitting their orders into smaller portions. Similarly, scaling out means taking profit in stages.
Advantages:
- Reduces timing risk by averaging entry or exit prices.
- Provides flexibility in volatile markets.
Disadvantages:
- Requires more active management.
- May increase transaction fees due to multiple orders.
Best for: Beginners who want to reduce emotional pressure and smooth out market entry points.
Comparing Execution Strategies
| Strategy | Speed | Cost Efficiency | Risk Control | Suitability for Beginners |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market Orders | Very High | Low | Low | Quick entry/exit, but risky |
| Limit Orders | Moderate | High | Medium | Great for disciplined trading |
| Stop-Loss/Take-Profit | Conditional | High | Very High | Essential risk management |
| Scaling In/Out | Moderate | Medium | High | Good for learning patience |
From a beginner’s perspective, combining limit orders with stop-loss orders offers a balance between cost control and risk management. Market orders should only be used in fast-moving scenarios, while scaling strategies can help build confidence over time.
How to Improve Execution in Perpetual Futures
Improving execution is not just about choosing strategies—it involves refining skills and using the right tools.
- Use trading platforms with low latency: Faster execution minimizes slippage.
- Monitor liquidity: Trade during peak volume hours for tighter spreads.
- Leverage order book analysis: Watching depth charts can guide better entry points.
- Automate when possible: Simple bots or alerts can help execute without emotional bias.
Learning how to improve execution in perpetual futures gives beginners an edge in markets dominated by experienced traders and algorithms.
Common Mistakes Beginners Should Avoid
- Overusing Market Orders – Leads to unnecessary slippage.
- Ignoring Stop-Loss Placement – Exposes traders to liquidation risks.
- Chasing Prices – Emotional trading results in poor entries.
- Over-Leveraging – Amplifies both gains and losses, leading to execution pressure.
Practical Example: A Beginner’s Trade Setup
Imagine a beginner wants to long Bitcoin perpetual futures at $60,000:
- They set a limit order at $59,800 to reduce entry cost.
- They place a stop-loss order at $58,500 to manage risk.
- They define a take-profit order at $61,500 to lock in gains.
- They scale out by selling half the position at \(61,000 and the rest at \)61,500.
This combination demonstrates discipline, risk management, and gradual profit realization.
Execution flow in perpetual futures trading
FAQ – Execution in Perpetual Futures
1. What is the safest execution strategy for beginners?
The safest approach combines limit orders with stop-loss orders. This ensures controlled entry at a good price while protecting against unexpected volatility.
2. How can I reduce slippage in perpetual futures?
Slippage can be reduced by trading during high-volume sessions, using limit orders instead of market orders, and choosing trading platforms with strong liquidity pools.
3. Should beginners use leverage when learning execution strategies?
It’s recommended to start with low leverage (1x–3x). High leverage magnifies execution mistakes, leading to faster losses. Building skill and discipline first is more important than chasing high returns.
Conclusion
For beginner traders in perpetual futures, mastering execution strategies is as important as understanding the contracts themselves. Market orders provide speed, but limit orders and risk management tools like stop-loss orders offer a safer path. Scaling strategies help smooth market entries, while consistent improvements in platform choice, liquidity awareness, and automation enhance execution efficiency.
If you’re new to trading, focus on building a disciplined approach with limit orders and protective stop-losses. Over time, layer in more advanced execution techniques as your confidence grows.
💡 What execution strategy do you find most effective in your perpetual futures trading journey? Share your thoughts in the comments, and don’t forget to pass this guide along to fellow traders!
Would you like me to create a downloadable execution strategy checklist (PDF) that beginners can use as a quick reference while trading?