===================================================
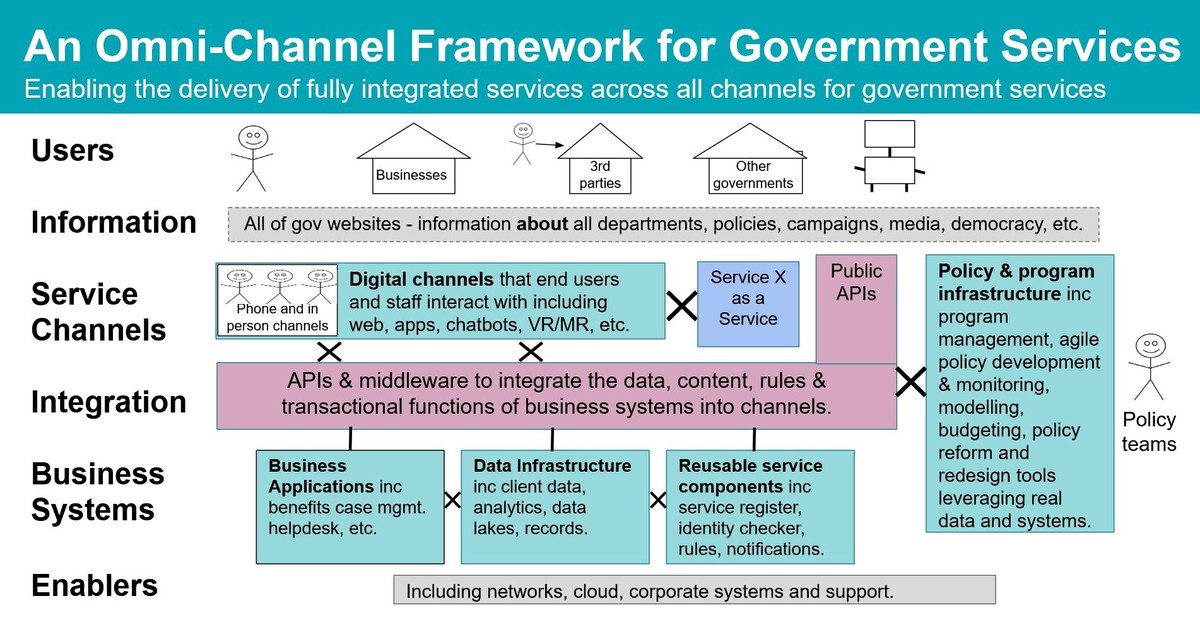
In the rapidly evolving crypto derivatives market, execution strategy comparison for perpetual futures has become a critical factor for both retail and institutional traders. Perpetual futures are unique instruments that allow traders to maintain leveraged positions indefinitely, but success depends heavily on how effectively trades are executed. Poor execution can erode profits, increase slippage, and even turn winning strategies into losing ones.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of execution strategies for perpetual futures, including algorithmic execution, manual trading, and hybrid approaches. It also examines the role of speed, accuracy, and risk management in building sustainable trading performance.
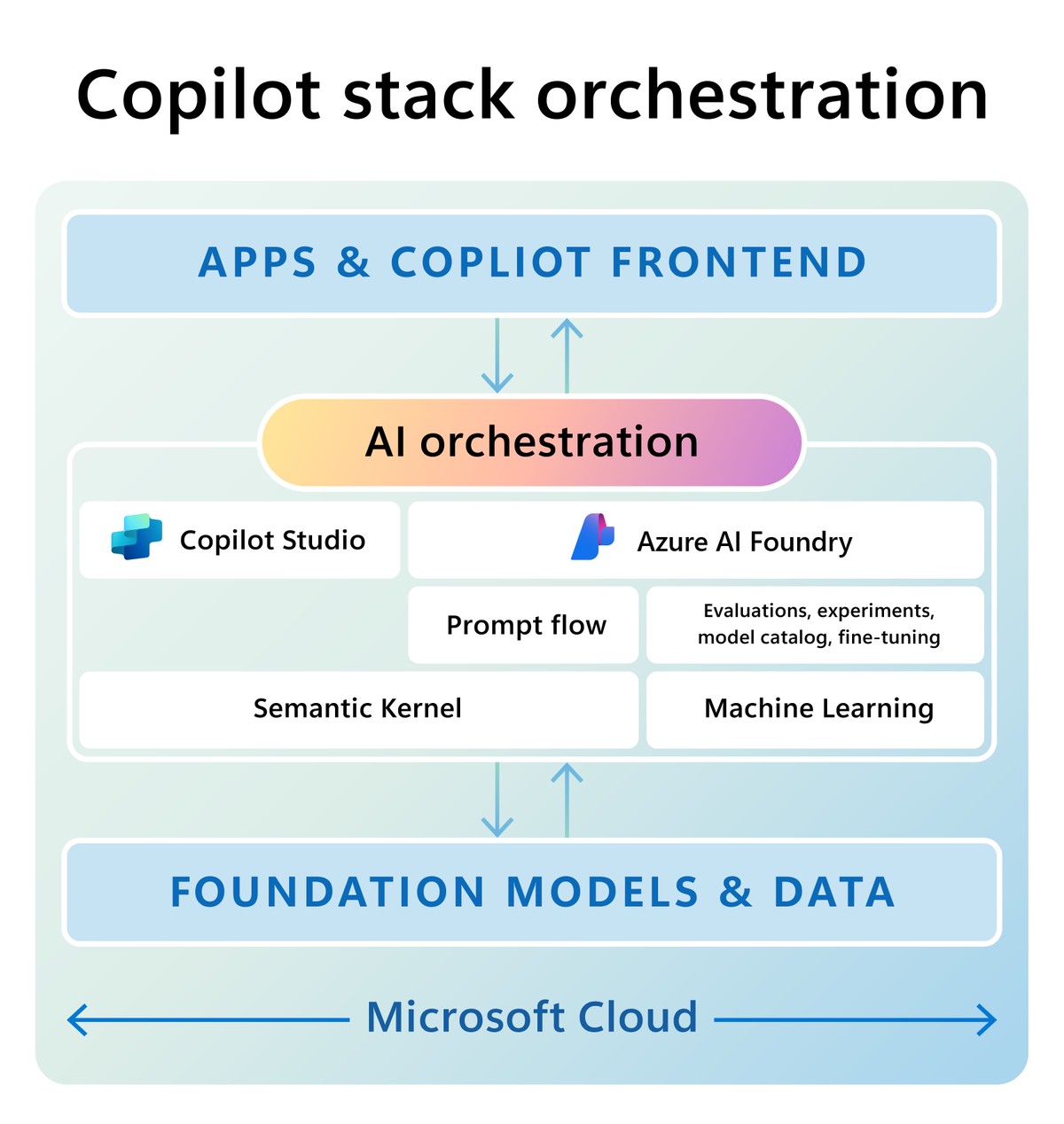
Understanding Execution in Perpetual Futures
Execution refers to the process of turning a trading idea into an actual position in the market. In perpetual futures, execution is more complex than in traditional markets due to factors like funding rates, high leverage, and fragmented liquidity across exchanges.
Traders must evaluate their execution strategy in terms of:
- Speed: How quickly orders reach the market.
- Accuracy: Whether orders are filled at the intended price.
- Cost efficiency: How much slippage and fees affect profitability.
- Scalability: Ability to handle larger orders without significant market impact.
For a deeper dive, many professionals explore how execution affects perpetual futures trading, which highlights the direct link between execution quality and strategy performance.
Core Execution Strategies in Perpetual Futures
1. Manual Execution
Manual execution involves placing trades directly through an exchange interface. This is common among beginners and discretionary traders.
Advantages:
- Full control over entry and exit decisions.
- Easy to adapt to sudden market changes.
- No additional software or infrastructure costs.
Disadvantages:
- Prone to human error and emotional decision-making.
- Slower than algorithmic execution, leading to slippage.
- Inefficient for handling high-frequency or large-volume trades.
Best Use Case: Short-term discretionary trades or low-frequency strategies.
2. Algorithmic Execution
Algorithmic execution relies on trading bots and advanced software to automate order placement. These systems can use strategies like TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price), VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price), or Smart Order Routing to optimize fills.
Advantages:
- Faster and more precise execution than manual methods.
- Capable of breaking large orders into smaller chunks to minimize market impact.
- Eliminates emotional bias.
- Suitable for high-frequency strategies.
Disadvantages:
- Requires technical expertise to build and maintain algorithms.
- Higher infrastructure costs (servers, low-latency connections).
- Vulnerable to system failures or coding errors.
Best Use Case: High-frequency traders, institutions, and advanced retail traders.
3. Hybrid Execution
Hybrid execution combines manual decision-making with algorithmic order placement. For example, a trader may decide when to enter but use a bot to execute the order gradually.
Advantages:
- Balances human intuition with algorithmic efficiency.
- Provides flexibility for discretionary strategies while reducing slippage.
- Allows traders to scale without fully automating everything.
Disadvantages:
- Requires both market knowledge and technical tools.
- Still slower than fully automated execution in fast-moving markets.
Best Use Case: Swing traders or institutions balancing discretionary analysis with systematic order flow.
Execution strategies framework: manual, algorithmic, and hybrid

Comparing Execution Strategies
| Factor | Manual Execution | Algorithmic Execution | Hybrid Execution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow | Very Fast | Moderate |
| Accuracy | Medium | High | High |
| Cost Efficiency | Low (slippage risk) | High | Medium |
| Scalability | Poor | Excellent | Good |
| Best For | Beginners, low-frequency traders | High-frequency, institutions | Swing traders, semi-automated |
From this comparison, algorithmic execution clearly dominates in terms of speed and scalability, but manual and hybrid strategies still have niches where they excel.
Industry Trends in Execution
- Institutional Adoption: Hedge funds and trading firms increasingly deploy advanced algorithms and smart order routers.
- Decentralized Platforms: DeFi perpetual futures (e.g., dYdX, GMX) introduce unique execution challenges like liquidity fragmentation and on-chain latency.
- Execution Optimization Tools: Professional traders now leverage specialized analytics to evaluate slippage, latency, and fill rates.
To better adapt, many traders study how to optimize execution in perpetual futures, which offers practical ways to fine-tune both manual and algorithmic strategies.
Risk Management in Execution
Execution risk is often underestimated but critical in perpetual futures due to high leverage.
- Slippage Control: Use limit orders when possible.
- Exchange Selection: Choose platforms with deep liquidity and reliable infrastructure.
- Redundancy Planning: Backup internet connections and APIs prevent catastrophic failures.
- Position Sizing: Keep leverage and order sizes in line with liquidity conditions.
Order book dynamics showing execution impact in perpetual futures
Practical Insights from Experience
From my own trading experience, execution strategy can be the difference between consistent profits and frustrating losses:
- Manual trading felt intuitive but often led to missed entries during high volatility.
- Algorithmic execution dramatically improved consistency, especially for scalping strategies.
- Hybrid execution proved most effective for longer-term positions where precision mattered less than decision-making flexibility.
FAQs on Execution Strategy Comparison for Perpetual Futures
1. Which execution strategy is best for beginners in perpetual futures?
Beginners should start with manual execution to build intuition about order books and market behavior. As skills develop, transitioning to hybrid or algorithmic execution makes sense.
2. How do I measure execution efficiency in perpetual futures?
You can measure execution by tracking metrics such as slippage, fill rate, and latency. Detailed analysis of these metrics helps evaluate whether your strategy is underperforming due to poor execution.
3. Why does execution speed matter so much in perpetual futures?
Because perpetual futures markets are highly volatile and leveraged, even a 100ms delay can result in worse prices. This is why execution speed is crucial in perpetual futures, especially for scalpers and arbitrageurs.
Conclusion
A successful trader must look beyond strategy design and focus on execution quality. Through this execution strategy comparison for perpetual futures, we’ve seen that manual, algorithmic, and hybrid approaches each have their place.
- Manual: Best for beginners or low-frequency trades.
- Algorithmic: Superior for speed, precision, and scale.
- Hybrid: Balanced choice for swing traders and semi-automated approaches.
The optimal choice depends on experience, resources, and trading style.
If this article helped clarify your understanding, feel free to share it with fellow traders and drop a comment below: Which execution strategy do you use most often in perpetual futures, and why?
Perpetual futures trading interface showing execution dynamics