
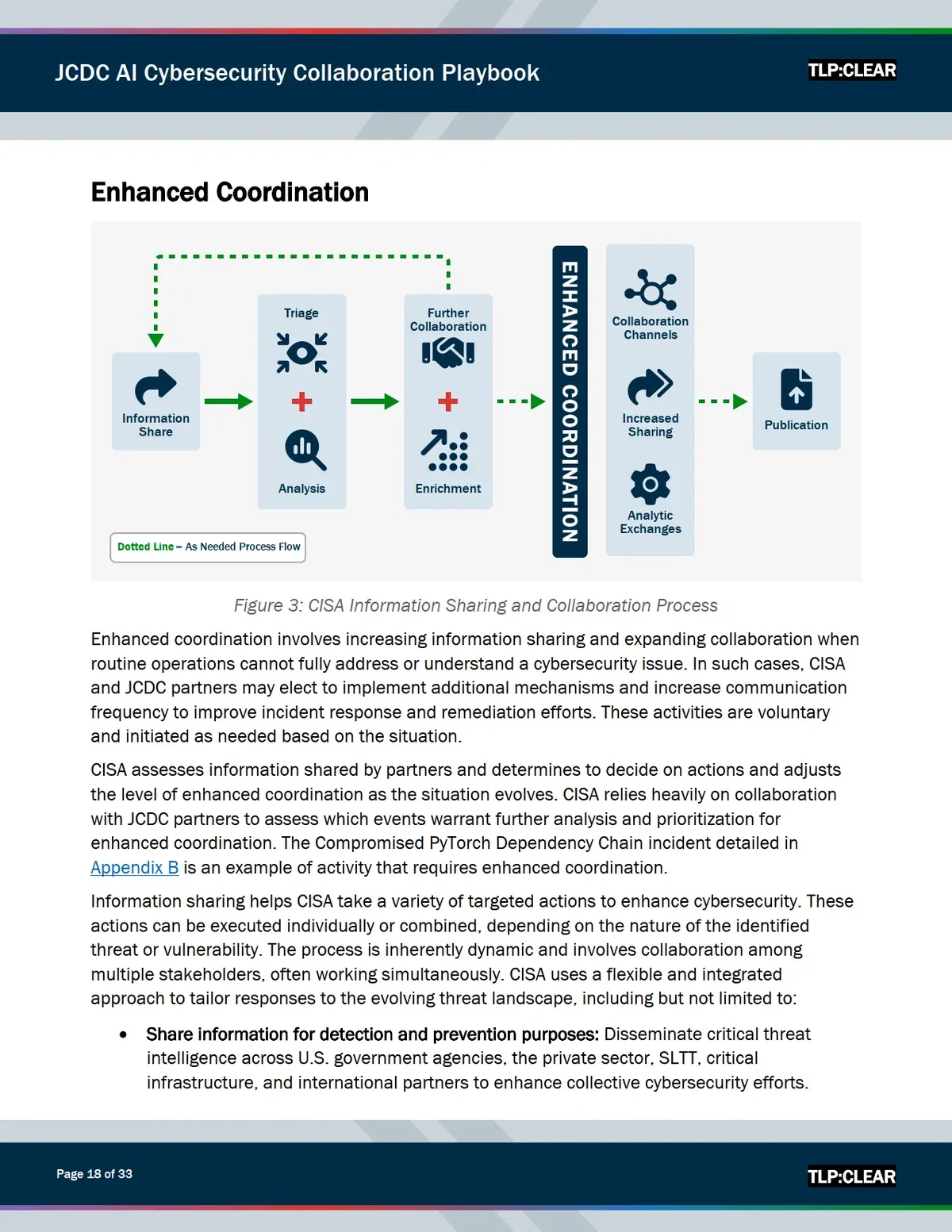
============================================================
In the world of algorithmic trading, especially in the high-stakes environment of perpetual futures markets, execution is critical. Perpetual futures, unlike traditional futures contracts, do not have an expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. This provides a unique set of challenges and opportunities that algorithmic traders must address to maximize their performance. In this execution guide, we will discuss the best practices, strategies, and tools for improving execution in perpetual futures trading.
Understanding Perpetual Futures and the Importance of Execution
Perpetual futures are contracts that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of assets (e.g., cryptocurrencies, commodities, or stocks) without worrying about expiration dates. This flexibility can lead to more opportunities, but also more complexity, as execution quality plays a significant role in determining profitability.
Why Execution Matters in Perpetual Futures
Execution refers to the process of carrying out buy or sell orders in the market. In the context of perpetual futures, execution becomes crucial for several reasons:
- Speed and Timing: In fast-moving markets, slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price) can significantly impact profit margins. A delay in execution can turn a profitable trade into a losing one.
- Liquidity: Perpetual futures markets can experience periods of low liquidity, which makes it difficult to execute large orders without causing significant price movements.
- Cost Efficiency: Poor execution can lead to higher transaction costs due to excessive slippage or unfavorable market conditions, thus reducing overall profitability.
The ability to execute efficiently in perpetual futures is often the differentiator between success and failure for algorithmic traders.
Strategies for Optimizing Execution in Perpetual Futures
Optimizing execution in perpetual futures requires a combination of strategic approaches, algorithmic techniques, and market knowledge. Below, we’ll explore two effective execution strategies: Smart Order Routing (SOR) and Slippage Control.
1. Smart Order Routing (SOR)
Smart Order Routing (SOR) involves using advanced algorithms to determine the optimal trading venues and routes for executing orders. This strategy is essential for navigating highly fragmented markets, where the same asset can be traded across multiple exchanges.
How SOR Works in Perpetual Futures
SOR algorithms analyze various factors such as order book depth, liquidity, and transaction costs across multiple exchanges and liquidity providers. By evaluating these parameters, SOR directs orders to the best possible venues for execution, reducing slippage and improving overall fill prices.
Benefits of Using SOR:
- Reduced Slippage: SOR ensures that orders are executed at the best available prices across various platforms.
- Lower Transaction Costs: By choosing the most cost-effective venues, SOR can help minimize hidden fees and commissions.
- Faster Execution: SOR algorithms can execute orders faster, reducing the impact of market volatility on the execution price.
Drawbacks of Smart Order Routing
While SOR is an effective strategy, it requires high-quality data feeds and sophisticated infrastructure. Additionally, while SOR improves execution speed and reduces slippage, it may not always be able to handle extremely large orders without market impact.
2. Slippage Control Techniques
Slippage occurs when there is a difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is actually executed. In volatile markets, such as those often found in perpetual futures, slippage can be particularly pronounced, resulting in substantial losses.
How to Control Slippage in Perpetual Futures
Several techniques can be employed to minimize slippage:
- Limit Orders: Instead of using market orders, traders can use limit orders to set a specific price at which they are willing to execute their trades. This prevents slippage but risks not getting the trade executed if the market price doesn’t reach the limit.
- Partial Fill Orders: By breaking large orders into smaller portions and executing them sequentially, traders can reduce the market impact and minimize slippage. This method is often used in combination with limit orders.
- Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP): This algorithm executes an order evenly over a specified time period, helping to reduce market impact by ensuring that large orders do not flood the market all at once.
- Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP): VWAP strategies aim to execute orders in line with the market’s average volume, reducing the risk of slippage by spreading the order out in line with the asset’s trading volume.
Advantages of Slippage Control:
- Minimized Execution Costs: By controlling slippage, traders can ensure that their trades are executed at optimal prices.
- Improved Trade Outcomes: Effective slippage control often results in better overall trade outcomes, as the trader avoids being filled at unfavorable prices.
Disadvantages of Slippage Control:
- Execution Speed: Some slippage control techniques, such as TWAP and VWAP, may slow down execution. In fast-moving markets, this could result in missed opportunities.
Advanced Execution Techniques for Professional Traders
While Smart Order Routing and slippage control are essential strategies, professional algorithmic traders often implement more advanced techniques to further optimize execution in perpetual futures markets. Below are two additional methods:
1. High-Frequency Execution Algorithms
High-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms are designed to execute a large number of trades in fractions of a second. These algorithms are typically used to take advantage of tiny price discrepancies across different markets or exchanges.
How HFT Improves Execution
HFT algorithms execute multiple orders in the market at lightning speed, capturing small price movements before they dissipate. This execution speed ensures that traders can capitalize on even the most fleeting opportunities.
Benefits of High-Frequency Execution:
- Ultra-fast Execution: Trades are executed in microseconds, reducing the impact of price volatility and increasing the likelihood of favorable fills.
- Volume Advantage: HFT strategies rely on large trade volumes, which help offset small profit margins per trade.
Challenges of High-Frequency Execution:
- Infrastructure Costs: High-frequency trading requires state-of-the-art hardware, data feeds, and colocation services, making it cost-prohibitive for many traders.
- Regulatory Risks: HFT is often subject to regulatory scrutiny due to concerns over market manipulation and unfair advantages.
2. Algorithmic Trading with Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) algorithms can be employed to analyze large datasets and optimize trading strategies based on evolving market conditions. These algorithms can learn from past market behaviors and adapt to new data, improving execution strategies over time.
How Machine Learning Optimizes Execution
ML algorithms analyze historical market data and use predictive models to forecast future price movements, liquidity conditions, and volatility levels. By integrating this information into the execution process, machine learning-based strategies can make smarter decisions on when and where to place trades, reducing execution costs and improving profitability.
Benefits of Machine Learning in Execution:
- Adaptability: Machine learning models can learn from new data and adjust strategies in real-time.
- Enhanced Precision: These algorithms can predict optimal entry and exit points, reducing the risk of poor execution.
Drawbacks of Machine Learning in Execution:
- Data Dependency: ML algorithms require vast amounts of historical data to function effectively, and poor-quality data can lead to suboptimal execution.
- Complexity: Machine learning algorithms can be complex to design and implement, requiring specialized knowledge and resources.
FAQ: Execution in Perpetual Futures for Algorithmic Traders
1. What is the importance of execution in perpetual futures?
Execution is critical in perpetual futures because it directly affects the profitability of trades. In volatile markets, slippage, poor liquidity, and delayed execution can turn profitable trades into losses. Efficient execution ensures that trades are filled at the best prices with minimal slippage, thus maximizing profit potential.
2. How can I reduce slippage in perpetual futures trading?
To reduce slippage in perpetual futures, consider using limit orders, partial fills, and time-weighted average price (TWAP) strategies. These techniques help control the price at which your order is filled, ensuring better execution outcomes.
3. What tools can help improve execution in perpetual futures?
There are several tools available to algorithmic traders to improve execution:
- Smart Order Routing (SOR) systems to find the best execution venues.
- Slippage control algorithms like TWAP and VWAP.
- High-frequency trading platforms for fast execution.
- Machine learning algorithms to optimize execution strategies based on historical data.
Conclusion
Execution is a key factor that can make or break a trader’s success in perpetual futures markets. By employing strategies like Smart Order Routing, slippage control, and high-frequency trading, algorithmic traders can improve their execution and maximize profits. Advanced techniques, such as machine learning, further enhance execution, enabling traders to adapt to dynamic market conditions. By understanding the nuances of execution and adopting best practices, traders can achieve better performance in the competitive world of perpetual futures trading.