===============================================
Introduction: Why Halting Matters in Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures are one of the most traded instruments in the cryptocurrency market. Their continuous trading structure and absence of expiry make them attractive for retail, institutional, and high-frequency traders. However, the phenomenon of halting in perpetual futures—a temporary suspension of trading activity due to volatility, technical glitches, or risk control protocols—plays a critical role in shaping market dynamics.
This analysis report on halting in perpetual futures aims to explore the reasons behind halting, its effects on pricing and liquidity, strategies for traders, and industry best practices. By combining theoretical insights with practical trading experiences, we provide a comprehensive guide for both novice and professional participants in the perpetual futures ecosystem.
Market volatility often triggers halting events in perpetual futures.
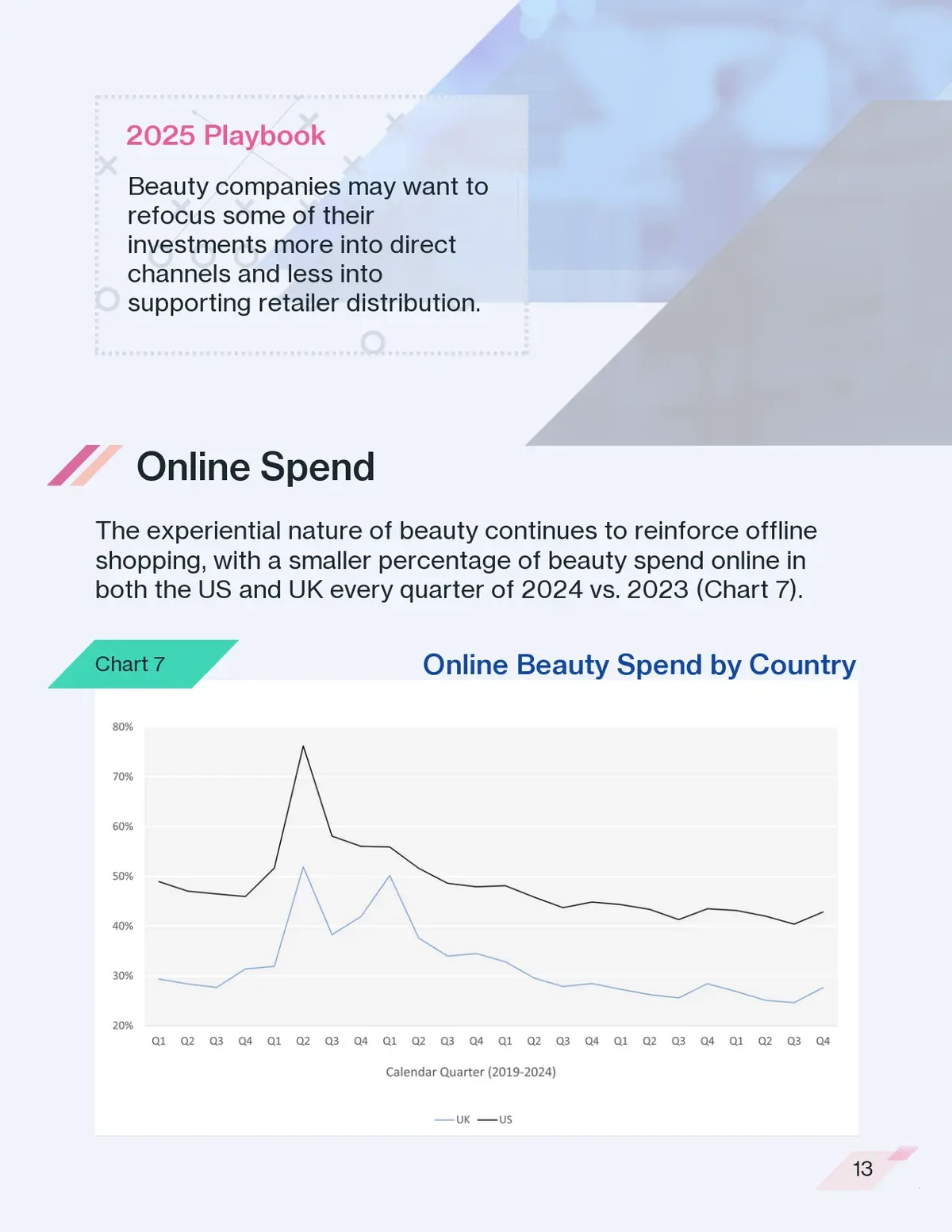
Understanding Halting in Perpetual Futures
What Is Halting?
Halting in perpetual futures refers to the temporary suspension of trading on an exchange. It can last from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the reason. Unlike traditional equity markets, halting in crypto futures is not standardized across exchanges, making it important for traders to understand each platform’s rules.
Common Causes of Halting
- Extreme Volatility: Sudden price swings can trigger automatic risk controls.
- System Overload: Exchange servers may pause to manage surges in trading volume.
- Regulatory or Compliance Interventions: Rare in crypto, but possible in regulated jurisdictions.
- Margin Imbalances: When too many traders face liquidation simultaneously, platforms may halt to prevent cascading failures.
Why Halting Occurs
For traders asking why does halting occur in perpetual futures, the answer lies in risk mitigation. Exchanges halt markets to stabilize prices, protect liquidity, and prevent systemic crashes.
[
{
"Aspect": "What is Halting?",
"Description": "Temporary suspension of trading on exchanges, lasting from seconds to minutes, based on specific triggers."
},
{
"Aspect": "Common Causes of Halting",
"Description": "Extreme volatility, system overload, regulatory interventions, and margin imbalances trigger halts."
},
{
"Aspect": "Why Halting Occurs",
"Description": "Halting is used for risk mitigation, to stabilize prices, protect liquidity, and prevent crashes."
},
{
"Aspect": "Impact on Price Behavior",
"Description": "Halting often creates price gaps when trading resumes, based on market sentiment during the pause."
},
{
"Aspect": "Liquidity Concerns",
"Description": "Liquidity dries up before a halt, spikes after resumption as traders re-enter positions."
},
{
"Aspect": "Emotional & Psychological Effects",
"Description": "Halting creates uncertainty, leading to panic orders and large unexpected losses for unhedged traders."
},
{
"Aspect": "Strategy 1: Historical Volatility Analysis",
"Description": "Analyze past halting events to predict potential future triggers, based on volatility thresholds."
},
{
"Aspect": "Strategy 2: Order Book & Liquidity Monitoring",
"Description": "Monitor real-time depth charts to identify stress points, spikes in liquidation orders as red flags."
},
{
"Aspect": "Recommendation",
"Description": "Combine historical volatility analysis with order book tracking for the best risk preparation."
},
{
"Aspect": "Risk Management Strategies: Pre-Halt",
"Description": "Set stop-loss orders, keep leverage conservative, and diversify assets to reduce exposure."
},
{
"Aspect": "Risk Management Strategies: During Halt",
"Description": "Avoid emotional decisions, monitor news, and prepare for action as soon as trading resumes."
},
{
"Aspect": "Risk Management Strategies: Post-Halt",
"Description": "Expect price gaps, place staggered orders, reassess leverage, and log events for future analysis."
},
{
"Aspect": "Case Study 1: March 2020 Crypto Crash",
"Description": "Exchange halting during COVID-19 collapse led to significant price drop from $7,000 to $4,000."
},
{
"Aspect": "Case Study 2: Exchange Outages in 2021",
"Description": "Halting during meme coin frenzy caused slippage as traders couldn't close positions on platforms like Binance."
},
{
"Aspect": "Best Practices for Traders",
"Description": "Stay educated, use alerts, limit leverage, plan exits, and backtest strategies for halting conditions."
},
{
"Aspect": "How Often Does Halting Occur?",
"Description": "Halting is rare but happens during extreme volatility, especially during macroeconomic events or liquidations."
},
{
"Aspect": "How Can Traders Protect Themselves?",
"Description": "Use stop-loss orders, avoid overleveraging, diversify, and stay updated with exchange announcements."
},
{
"Aspect": "Does Halting Always Lead to Losses?",
"Description": "Not always. Prepared traders can profit by anticipating market resumption and adjusting positions."
},
{
"Aspect": "Conclusion: Halting as a Strategic Factor",
"Description": "Halting is a safeguard to prevent systemic risks; understanding it is crucial for survival in volatile markets."
}
]
Price Behavior
Halting often creates gaps when trading resumes. These gaps can be upward or downward depending on market sentiment during the pause.
Liquidity Concerns
- Before a halt: Liquidity dries up as traders rush to exit positions.
- After a halt: Liquidity spikes as both buyers and sellers re-enter.
Emotional & Psychological Effects
Halting creates uncertainty, often leading to panic orders post-resumption. Traders with unhedged positions may face large, unexpected losses.
Understanding how does halting affect perpetual futures helps traders prepare better by adjusting risk exposure and order placement.
Methods of Analyzing Halting Events
Strategy 1: Historical Volatility Analysis
By analyzing past halting events, traders can predict potential future triggers. Exchanges often release data on volatility thresholds, making it possible to backtest.
- Pros: Data-driven, provides clear risk signals.
- Cons: Past volatility doesn’t guarantee future outcomes.
Strategy 2: Order Book & Liquidity Monitoring
Tracking real-time depth charts helps identify stress points before halts occur. Spikes in liquidation orders are a red flag.
- Pros: Immediate warning signals, useful for day traders.
- Cons: Requires advanced tools and constant monitoring.
Recommendation
For most traders, combining historical volatility analysis with real-time order book tracking provides the best balance between preparation and execution.
Order book analysis is a practical method to anticipate halting in perpetual futures.

Risk Management Strategies During Halting
1. Pre-Halt Precautions
- Always set stop-loss orders.
- Keep leverage levels conservative.
- Diversify across assets to reduce exposure.
2. During a Halt
- Avoid emotional decisions.
- Monitor news and announcements from the exchange.
- Prepare to act immediately once trading resumes.
3. Post-Halt Adjustments
- Expect price gaps—place staggered orders.
- Reassess leverage based on new volatility.
- Log the event in a trading journal for future analysis.
For traders seeking solutions to mitigate halting in perpetual futures, risk discipline is the most effective tool.
Case Studies: Halting in Practice
Case Study 1: March 2020 Crypto Crash
During the COVID-19 market collapse, exchanges like BitMEX experienced halting as liquidity dried up and mass liquidations occurred. This accelerated Bitcoin’s drop from \(7,000 to \)4,000 within hours.
Case Study 2: Exchange Outages in 2021
Platforms such as Binance and Coinbase reported halts during the meme coin frenzy. Traders unable to close positions faced huge slippage upon resumption.
Lesson: Halts magnify both risks and opportunities. Prepared traders who hedge effectively often benefit, while unprepared traders face amplified losses.
Best Practices for Traders
- Stay Educated: Continuously update yourself on exchange halting protocols.
- Use Alerts: Automated halting alerts for day perpetual futures traders can help mitigate risk.
- Limit Leverage: Excessive leverage increases vulnerability during halts.
- Plan Exits: Predetermine exit points before halts occur.
- Backtest Strategies: Simulate halting conditions with trading bots to improve readiness.
By following these practices, traders can align with best practices for handling halting in perpetual futures and avoid costly mistakes.
FAQ: Halting in Perpetual Futures
1. How often does halting occur in perpetual futures?
Halting is not frequent but can occur during extreme volatility, especially around macroeconomic events, Bitcoin halvings, or sudden liquidations. On average, large exchanges report a handful of halting events per year.
2. How can traders protect themselves during halting?
- Use stop-loss orders.
- Avoid overleveraging.
- Diversify across multiple exchanges.
- Stay updated with exchange announcements.
3. Does halting always lead to losses?
Not necessarily. While many traders lose due to gaps and slippage, prepared traders can profit by anticipating resumption momentum and positioning accordingly.
Conclusion: Halting as a Strategic Factor
Halting in perpetual futures is not just a technical glitch—it’s a strategic safeguard that exchanges employ to prevent systemic risks. For traders, understanding halting is crucial for survival and success in volatile crypto markets.
This analysis report on halting in perpetual futures shows that:
- Halting occurs due to volatility, liquidity stress, and systemic protection.
- It impacts pricing, liquidity, and trader psychology.
- Strategies like historical analysis and order book monitoring help anticipate halts.
- Risk management, diversification, and discipline are key to navigating halting successfully.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your trading community, comment with your halting experiences, and help build a more resilient trading ecosystem.
Would you like me to create a visual halting timeline infographic that highlights major halting events in perpetual futures history?