
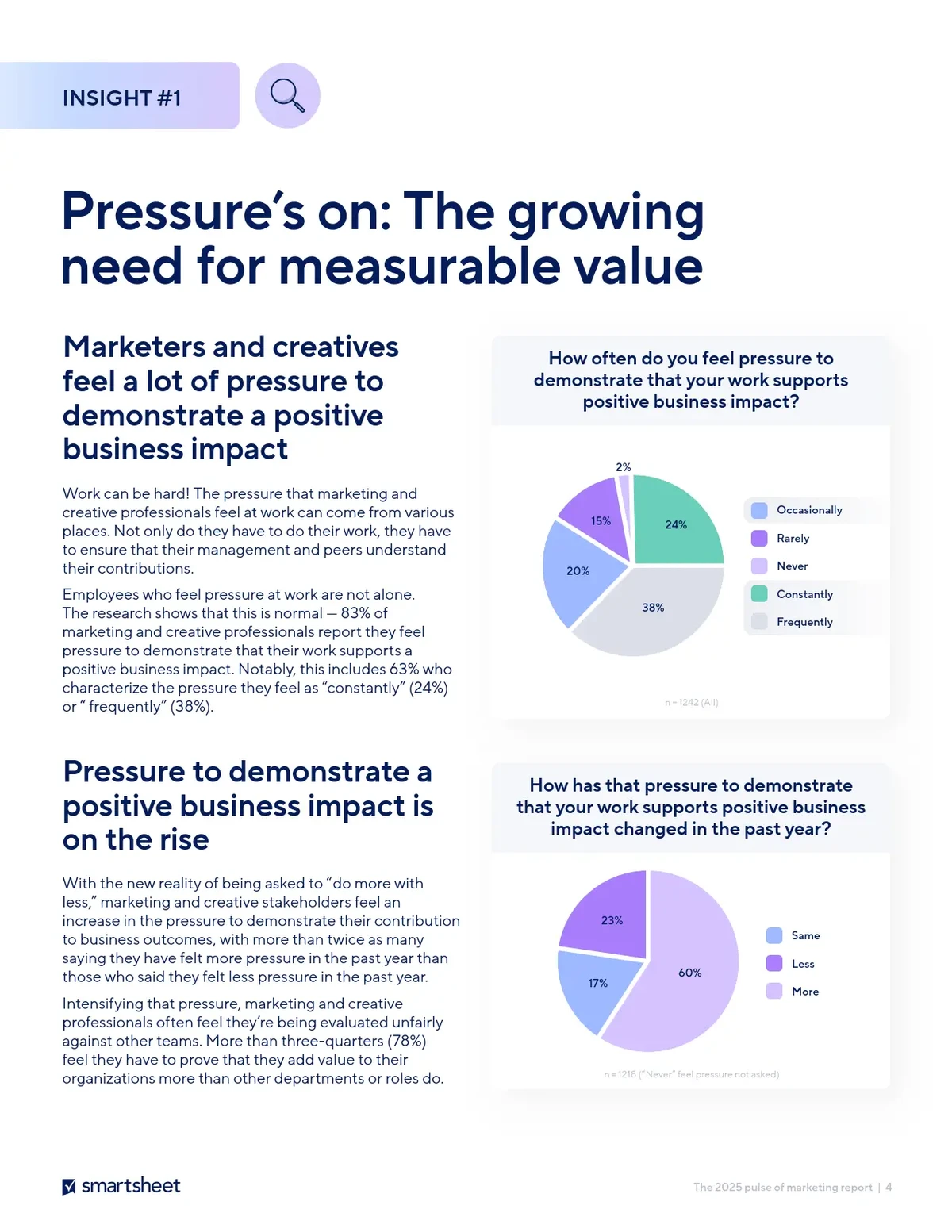
=============================================================
In the dynamic world of perpetual futures trading, where assets are bought and sold without an expiry date, optimizing a quantitative strategy is essential for staying competitive. Whether you’re an institutional investor or an individual trader, a well-crafted strategy can help you capitalize on market opportunities, manage risk, and achieve more consistent returns.
This article explores how to develop, optimize, and implement quantitative strategies for perpetual futures. We’ll cover the core principles, advanced techniques, and provide guidance on making data-driven decisions to enhance your trading performance.
What is Perpetual Futures Trading?
Before diving into strategy optimization, it’s essential to understand perpetual futures. These financial instruments are similar to traditional futures contracts, but they do not have a fixed expiration date. Traders can hold positions indefinitely, as long as they can meet the margin requirements.
Unlike traditional futures, which have a defined settlement date, perpetual futures are marked to market continuously. This creates unique opportunities for long-term exposure without worrying about rollover costs or expiry dates.
Key benefits of perpetual futures:
- No expiry: You can hold positions as long as you wish.
- Leverage: Traders can use leverage, potentially amplifying returns.
- Liquidity: Popular in cryptocurrencies, they offer high liquidity.
However, trading perpetual futures also introduces challenges, such as price volatility and liquidation risks, which is why optimizing a quantitative strategy is crucial for managing these factors.
What is a Quantitative Strategy?
A quantitative strategy uses mathematical models, algorithms, and statistical analysis to make trading decisions. These strategies rely heavily on historical data, market indicators, and technical patterns to forecast price movements and execute trades at optimal times.
In the context of perpetual futures, a quantitative strategy can help traders identify high-probability trades, manage risk, and avoid common mistakes like overleveraging. The primary goal is to systematize the trading process and remove emotional biases.
Key Components of a Quantitative Strategy:
- Data-driven analysis: Use historical data to predict future price movements.
- Risk management: Set clear rules for stop-losses and position sizing.
- Automation: Algorithmically executing trades based on predefined rules.
Key Considerations for Optimizing a Quantitative Strategy
1. Backtesting the Strategy
One of the most critical aspects of optimizing a quantitative strategy is backtesting. Backtesting allows you to simulate your strategy using historical data to see how it would have performed in different market conditions.
How to Backtest a Quantitative Strategy for Perpetual Futures:
- Collect historical data: Gather data for the asset you are trading, such as price, volume, and open interest.
- Set up your trading rules: Define your entry, exit, and risk management rules clearly.
- Run simulations: Use backtesting platforms like QuantConnect or TradingView to test your strategy over various time frames.
- Analyze performance: Review the Sharpe ratio, drawdown, and profit factor to evaluate the strategy’s robustness.
2. Incorporating Market Indicators
While price history is important, market indicators like moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and Bollinger Bands can help identify trade signals. By adding technical indicators to your quantitative model, you can improve decision-making and reduce the risk of false signals.
Optimizing Technical Indicators:
- Moving averages: Use short-term and long-term moving averages to identify trends and reversals.
- RSI: Helps in identifying overbought or oversold conditions, signaling potential price corrections.
- Bollinger Bands: Useful for determining price volatility and breakout points.
3. Position Sizing and Risk Management
A crucial aspect of optimizing any trading strategy, particularly with leveraged products like perpetual futures, is effective risk management. Using appropriate position sizing and stop-loss orders can help protect your capital and maximize profitability.
Key Risk Management Strategies:
- Kelly Criterion: A formula used to determine the optimal size of a trade based on expected returns and variance.
- Fixed percentage: Limit risk to a small percentage of your total capital on each trade.
- Stop-losses and take-profits: Set predefined exit points to lock in profits and cut losses.
4. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
To further optimize your strategy, consider integrating machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns that traditional methods might overlook.
How AI Improves Quantitative Strategies:
- Pattern recognition: AI can identify subtle market patterns and trends based on historical data.
- Predictive modeling: Machine learning algorithms can forecast future price movements more accurately than rule-based models.
- Adaptability: ML models can adjust in real-time to new data, improving strategy effectiveness.
Comparing Different Optimization Strategies
1. Algorithmic Strategies
Algorithmic trading uses advanced mathematical models to automate trading decisions. It’s based on predefined rules, such as momentum, mean reversion, or arbitrage strategies.
Advantages of Algorithmic Trading:
- Speed: Algorithms can execute trades in milliseconds, capturing optimal market conditions.
- Precision: Algorithms follow predefined rules, removing human error and emotional bias.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Requires deep knowledge of programming and statistics.
- Overfitting risk: Models may perform well in backtesting but fail in live markets due to overfitting.
2. Manual Optimization with Backtesting
Manual optimization involves setting up a strategy based on intuition and manual adjustments, which are then tested with backtesting. This method provides flexibility but requires substantial knowledge of the markets and thorough testing.
Advantages of Manual Optimization:
- Customization: Offers more flexibility to adapt strategies based on personal experience.
- No coding: Traders don’t need coding skills to implement strategies.
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming: Requires significant time for research and testing.
- Human bias: Traders may introduce personal biases or emotions into the strategy.
Best Practices for Optimizing Quantitative Strategies
- Regularly update your models: Markets evolve, and so should your strategies. Ensure regular updates to models based on recent data and market conditions.
- Diversify strategies: Use a combination of strategies to avoid relying on a single method, spreading out risk.
- Test across different market conditions: Ensure your strategy performs well across bull, bear, and sideways markets.
FAQ: How to Optimize a Quantitative Strategy for Perpetual Futures
1. How do I know if my strategy is optimized?
An optimized strategy should show a positive Sharpe ratio, minimal drawdowns, and high consistency in returns across different time frames. Regular backtesting and forward testing can also provide insights into its robustness.
2. What are the risks of using a quantitative strategy for perpetual futures?
The main risks include overfitting, model decay, and slippage. These can be mitigated by using robust backtesting, ensuring a well-diversified strategy, and continuously monitoring the strategy’s performance in real market conditions.
3. How can machine learning improve my strategy?
Machine learning can help identify hidden patterns and trends in market data, improving prediction accuracy. It can also adapt in real-time to new data, making it more resilient to changing market conditions compared to traditional models.
Conclusion
Optimizing a quantitative strategy for perpetual futures trading involves combining sound statistical methods with market insight and advanced technologies like machine learning. By backtesting, refining risk management practices, and constantly adapting to market changes, traders can increase their chances of long-term success.