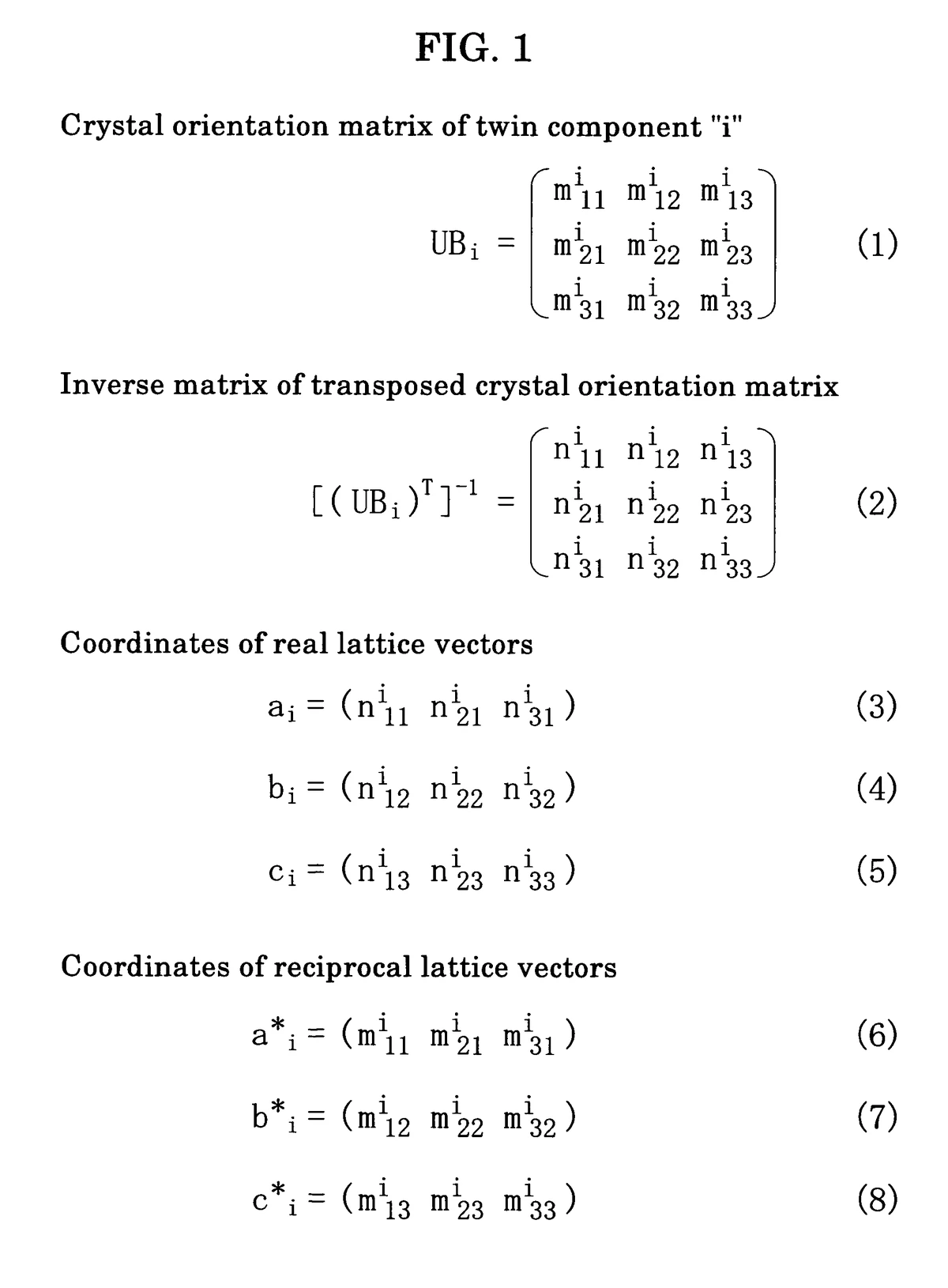
========================================================================
Understanding turnover calculation methods in perpetual futures is crucial for traders, analysts, and institutional investors aiming to optimize performance, manage risk, and enhance profitability. Turnover, a key liquidity and activity metric, provides insights into market dynamics, trading strategies, and operational efficiency in perpetual futures markets. This article explores detailed turnover calculation methods, compares strategies, and provides actionable insights for both beginners and experienced professionals.
Understanding Turnover in Perpetual Futures
Definition of Turnover
Turnover in perpetual futures refers to the total trading volume or value of contracts exchanged over a specific period, often expressed in USD or the underlying asset quantity. It serves as a proxy for market liquidity and trading activity, indicating how actively participants are entering and exiting positions.
Key Aspects:
- Higher turnover generally signals better liquidity and narrower bid-ask spreads
- Turnover helps assess market depth and investor participation
- It is essential for risk management, hedging efficiency, and algorithmic trading strategies
Importance of Turnover Analysis
Turnover is more than a statistic; it is a strategic metric. Traders and fund managers rely on turnover insights to make decisions regarding position sizing, leverage use, and strategy optimization.
Internal Link Integration: Understanding why turnover is important in perpetual futures trading helps traders and investors appreciate its impact on strategy effectiveness and profitability.
Key Turnover Calculation Methods
Method 1: Volume-Based Turnover
Description:
Volume-based turnover measures the number of contracts traded over a defined period. It is the simplest and most widely used method.
Formula:
Turnover=Total Contracts Traded×Contract Size\text{Turnover} = \text{Total Contracts Traded} \times \text{Contract Size}Turnover=Total Contracts Traded×Contract Size
Advantages:
- Easy to compute and interpret
- Provides immediate insight into trading activity
Limitations:
- Does not account for price changes or market value
- Can overestimate activity in low-volatility periods
Use Case: Ideal for day traders and high-frequency traders tracking activity spikes.
Illustration of daily turnover based on contract volume in perpetual futures
Method 2: Value-Based Turnover
Description:
Value-based turnover considers the monetary value of all contracts traded within a period, providing a more comprehensive view of market activity.
Formula:
Turnover=∑(Contract Price×Contracts Traded)\text{Turnover} = \sum (\text{Contract Price} \times \text{Contracts Traded})Turnover=∑(Contract Price×Contracts Traded)
Advantages:
- Reflects both trading volume and price changes
- Useful for assessing liquidity and capital allocation
Limitations:
- More complex to calculate in highly volatile markets
- Sensitive to extreme price swings
Use Case: Preferred by institutional traders and hedge funds assessing market participation and exposure.
Internal Link Integration: Learning how to calculate turnover in perpetual futures allows traders to apply these methods accurately in real-world markets.
Comparative Analysis of Turnover Calculation Methods
| Method | Advantages | Limitations | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume-Based Turnover | Simple, quick insight | Ignores price | High-frequency monitoring |
| Value-Based Turnover | Reflects market value, liquidity | Sensitive to volatility, complex | Institutional risk assessment |
Insight: Traders often combine both methods for a balanced perspective, using volume to track activity and value to assess market significance.
Advanced Turnover Strategies
Strategy 1: Turnover Optimization for Day Traders
- Focuses on maximizing trading efficiency by selecting contracts with optimal liquidity
- Uses volume trends to identify entry and exit points
- Helps reduce slippage and trading costs
Strategy 2: Turnover Metrics for Algorithmic Trading
- Integrates turnover data into algorithmic models for predictive analytics
- Identifies liquidity pockets and potential arbitrage opportunities
- Enhances backtesting accuracy and model robustness
Visualization of turnover trends informing algorithmic trading strategies
Comparison:
| Strategy | Focus | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day Trader Turnover Optimization | Liquidity and cost efficiency | Improved execution | Requires continuous monitoring |
| Algorithmic Trading Metrics | Predictive modeling | Accurate signals and arbitrage | Data-intensive, complex |
Turnover Tracking and Analysis Tools
Real-Time Market Data Platforms
- Binance, FTX, and Bybit offer turnover tracking tools for perpetual futures
- Features include tick-level volume, contract value, and liquidity depth
Analytical Software
- Python, R, and MATLAB can compute advanced turnover metrics
- Integration with APIs allows automated updates and visualization
Best Practices:
- Combine real-time data with historical turnover analysis
- Use visual dashboards to track trends and anomalies
Challenges in Turnover Calculation
Market Volatility
- High volatility can distort value-based turnover, leading to misleading conclusions
- Mitigation: Use moving averages or volatility-adjusted turnover metrics
Data Accuracy
- Inconsistent reporting across exchanges can affect results
- Mitigation: Cross-verify with multiple sources and maintain robust data pipelines
Dynamic Contract Specifications
- Different perpetual contracts may have varying contract sizes and leverage
- Mitigation: Normalize turnover by contract value to enable comparison
FAQ: Turnover Calculation in Perpetual Futures
Q1: How often should turnover be calculated?
A1: For high-frequency trading, turnover should be updated in real-time or intraday. For portfolio analysis and risk assessment, daily or weekly turnover calculations are sufficient.
Q2: Which turnover method is better for assessing liquidity?
A2: Value-based turnover provides a more accurate picture of liquidity since it accounts for both contract volume and price. However, volume-based turnover is effective for quick activity insights.
Q3: How can turnover improve trading strategy performance?
A3: Turnover analysis identifies high-liquidity periods, reduces slippage, informs position sizing, and integrates into algorithmic trading models for predictive analytics.
Conclusion
Understanding turnover calculation methods in perpetual futures is essential for traders, investors, and algorithmic systems. By combining volume-based and value-based methods, leveraging advanced analytics, and integrating real-time data, market participants can:
- Enhance liquidity assessment
- Optimize trading strategies
- Minimize risks and slippage
- Improve decision-making for both retail and institutional trading
Call to Action: Start applying these turnover calculation methods today. Track trends, integrate data into trading models, and share insights with your team to maximize performance in perpetual futures markets.