========================================================
Market depth is one of the most important yet often overlooked aspects of perpetual futures trading. It offers insights into liquidity, order flow, and potential price movements—making it an essential tool for professional traders, hedge funds, and even serious retail participants. Understanding how to analyze market depth changes in perpetual futures can help traders anticipate market shifts, optimize entries and exits, and manage risk effectively.
In this article, we will cover key concepts, practical methods, case studies, and advanced strategies for analyzing market depth in perpetual futures markets. We will also explore two different approaches to market depth analysis, comparing their strengths and weaknesses before recommending the best practices.
What is Market Depth in Perpetual Futures?
Market depth represents the volume of buy and sell orders across different price levels in the order book of perpetual futures contracts. It provides a snapshot of supply and demand beyond the last traded price.
- Bid side (buy orders): Shows demand at various price levels.
- Ask side (sell orders): Shows supply at different prices.
- Order imbalance: The difference between buy and sell orders, which can indicate potential directional pressure.
This makes it a critical tool for traders asking: How to understand market depth in perpetual futures and apply it effectively to their strategies.
Why Market Depth Changes Matter
Analyzing changes in market depth can help traders identify:
- Liquidity Shifts – A sudden drop in order book liquidity can signal potential volatility.
- Spoofing or Order Book Manipulation – Fake orders placed to mislead traders, often detected through unusual depth changes.
- Support and Resistance Levels – Large buy or sell walls often act as short-term barriers.
- Execution Risk – Thin depth may cause slippage during large trades.
For these reasons, market depth is important in perpetual futures because it provides information beyond simple price action, helping traders anticipate hidden risks and opportunities.
Methods for Analyzing Market Depth Changes
1. Order Book Heatmap Analysis
An order book heatmap visually represents liquidity at different levels over time. By analyzing heatmaps, traders can detect:
- Liquidity zones where large clusters of orders sit.
- Liquidity migration when large orders shift up or down the book.
- Spoofing detection when orders appear and disappear unusually fast.
Advantages:
- Intuitive visual representation.
- Excellent for detecting short-term market moves.
Disadvantages:
- Can overwhelm beginners.
- Requires advanced software to track changes.
2. Order Flow Imbalance Analysis
Order flow imbalance focuses on the ratio of buy vs. sell orders. A significant imbalance often signals short-term directional bias.
For example:
- If buy orders dominate across multiple levels, upward momentum is likely.
- If sell orders outweigh buy orders, downside pressure is building.
Advantages:
- Provides actionable signals for intraday trading.
- Quantifiable and easy to integrate into algorithms.
Disadvantages:
- Can generate false signals in low-volume periods.
- Sensitive to short-lived liquidity spikes.
3. Market Depth Ratio Metrics
Traders often calculate depth ratios, such as:
- Bid-to-Ask Ratio (BAR): Total bid volume divided by total ask volume.
- Top-of-Book Liquidity Ratio: Volume within the nearest 5–10 levels of bid/ask.
These metrics help identify whether liquidity is skewed to one side.
Advantages:
- Easy to calculate.
- Useful for systematic trading strategies.
Disadvantages:
- Oversimplifies complex dynamics.
- Ratios may fluctuate rapidly without clear signals.
4. Event-Driven Market Depth Analysis
Depth changes during key events (e.g., CPI reports, Fed announcements, Bitcoin halving) often provide advance warning of volatility.
For example, a thinning book before a Fed decision usually signals participants are withdrawing liquidity, anticipating sharp moves.
Advantages:
- Contextualizes market depth with macro events.
- Helps anticipate high-risk periods.
Disadvantages:
- Requires experience in both macro trading and microstructure.
- Can lead to false alarms if misinterpreted.
Comparing Two Popular Methods
Let’s compare Order Book Heatmap Analysis and Order Flow Imbalance Analysis:
| Criteria | Heatmap Analysis | Order Flow Imbalance |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Visual, intuitive but complex | Numeric, easy to quantify |
| Best Use Case | Detecting spoofing, liquidity zones | Intraday directional signals |
| Adaptability | Requires advanced software | Easily adapted to algorithms |
| Weakness | Data-heavy, less beginner-friendly | False signals in low liquidity |
Recommendation:
For professional traders and hedge funds, heatmap analysis combined with order flow imbalance offers the strongest edge. For beginners, starting with depth ratio metrics is easier before progressing to advanced tools.
Visual Example of Market Depth Analysis
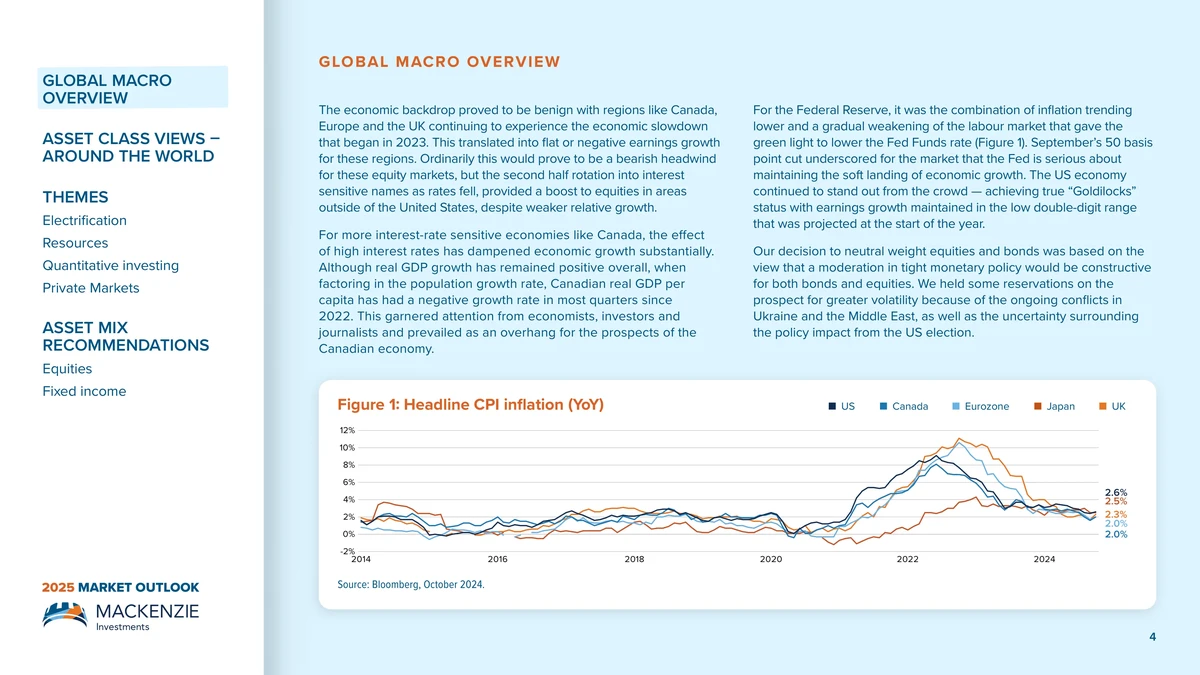
Market depth heatmap example showing liquidity walls and shifts
Integrating Market Depth into Trading Strategies
- Scalping Strategies – Use order flow imbalance to time quick entries and exits.
- Swing Trading with Depth Confirmation – Identify large order walls as support/resistance confirmation.
- Risk Management – Avoid entering large positions when depth is too thin.
Traders often ask: Where to find market depth data for perpetual futures? The answer lies in exchange APIs, institutional-grade platforms like Bookmap, and real-time trading dashboards offered by exchanges such as Binance Futures or Bybit.
Advanced Market Depth Insights
- Algorithmic Integration: Quant models can include bid-ask ratio as part of execution logic.
- Machine Learning Enhancements: ML can detect unusual depth patterns predictive of manipulation.
- Cross-Exchange Depth Analysis: Comparing depth across multiple venues helps detect arbitrage opportunities.
For advanced traders, market depth insights for crypto hedge funds can enhance execution strategies by identifying liquidity fragmentation across exchanges.
FAQ: Market Depth Analysis in Perpetual Futures
1. How reliable is market depth in predicting price moves?
Market depth is not a crystal ball—it provides probabilities. Large walls can disappear instantly (spoofing). However, when combined with order flow and volume analysis, it significantly improves predictive accuracy.
2. What tools are best for market depth analysis?
Professional traders often use platforms like Bookmap, TensorCharts, or exchange-native APIs. Beginners can start with built-in depth charts on Binance, Bybit, or OKX before moving to advanced visualization tools.
3. Can market depth analysis work for both retail and institutional traders?
Yes. Retail traders benefit from depth ratios and simple charts, while institutions use advanced real-time analytics, AI-driven monitoring, and cross-exchange liquidity mapping.
Conclusion
Analyzing market depth changes in perpetual futures is an essential skill for anyone serious about trading these instruments. Whether you are a beginner using simple depth ratios or a professional deploying AI-enhanced heatmaps, market depth analysis provides a competitive edge in anticipating liquidity shifts and directional bias.
The best approach is layered: combine heatmap visualization, order flow imbalance, and ratio metrics with contextual market events. This multi-dimensional strategy reduces noise and enhances decision-making.
If you found this guide useful, share it with fellow traders or drop a comment below with your favorite market depth strategy—your insights might help another trader improve their edge.
Would you like me to also prepare a step-by-step trading workflow infographic that shows how to analyze depth changes before placing a perpetual futures trade?